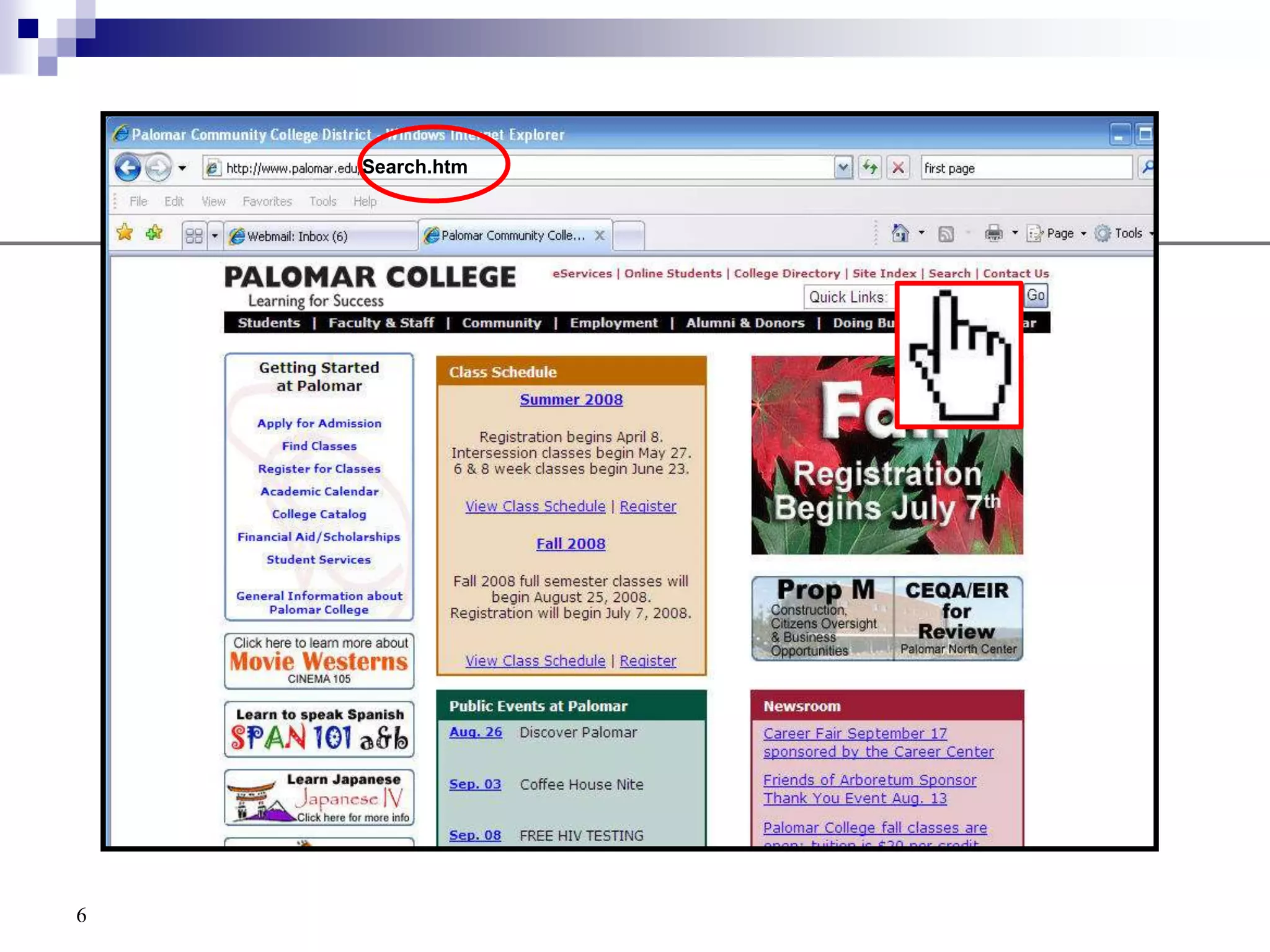
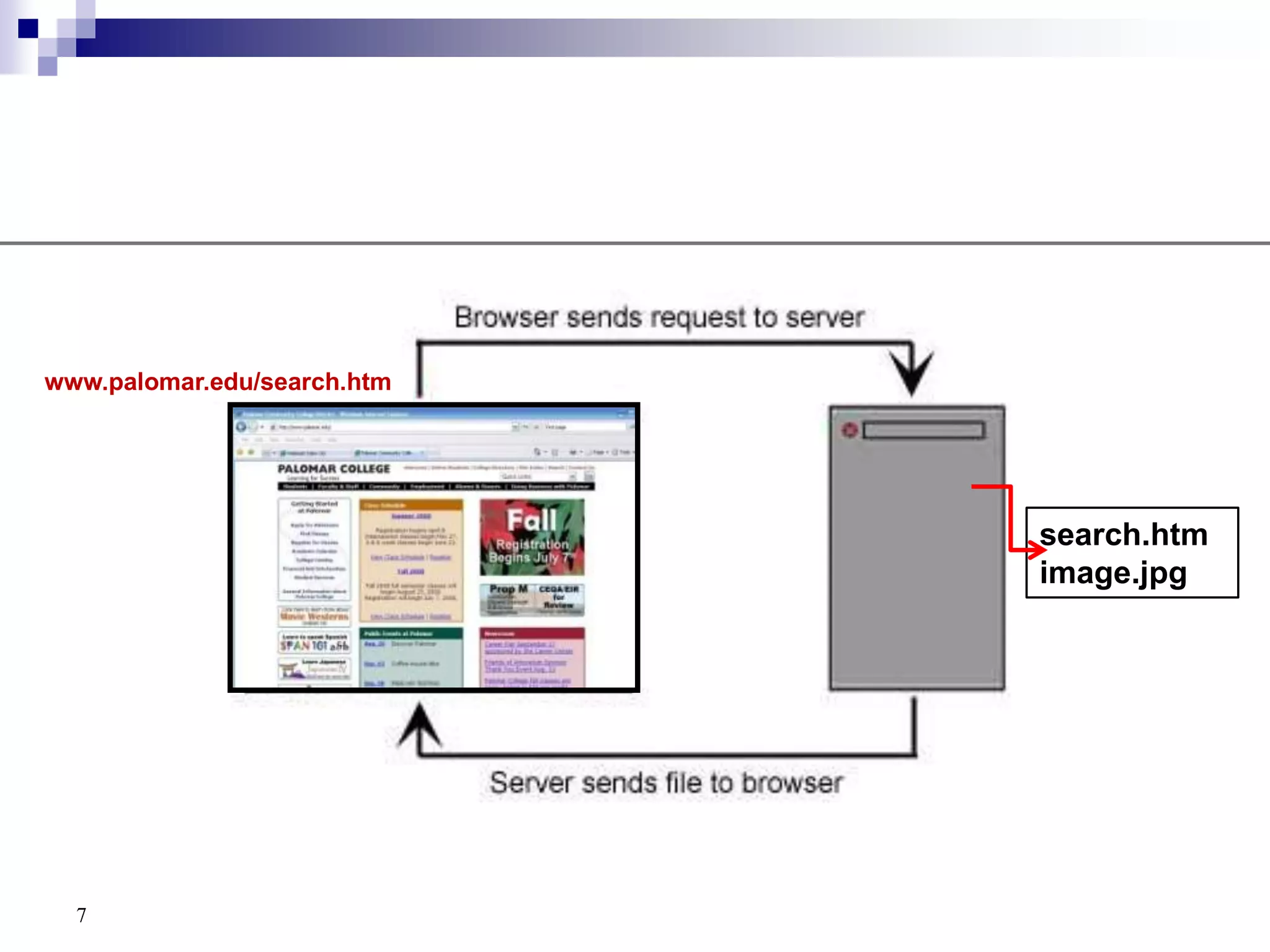
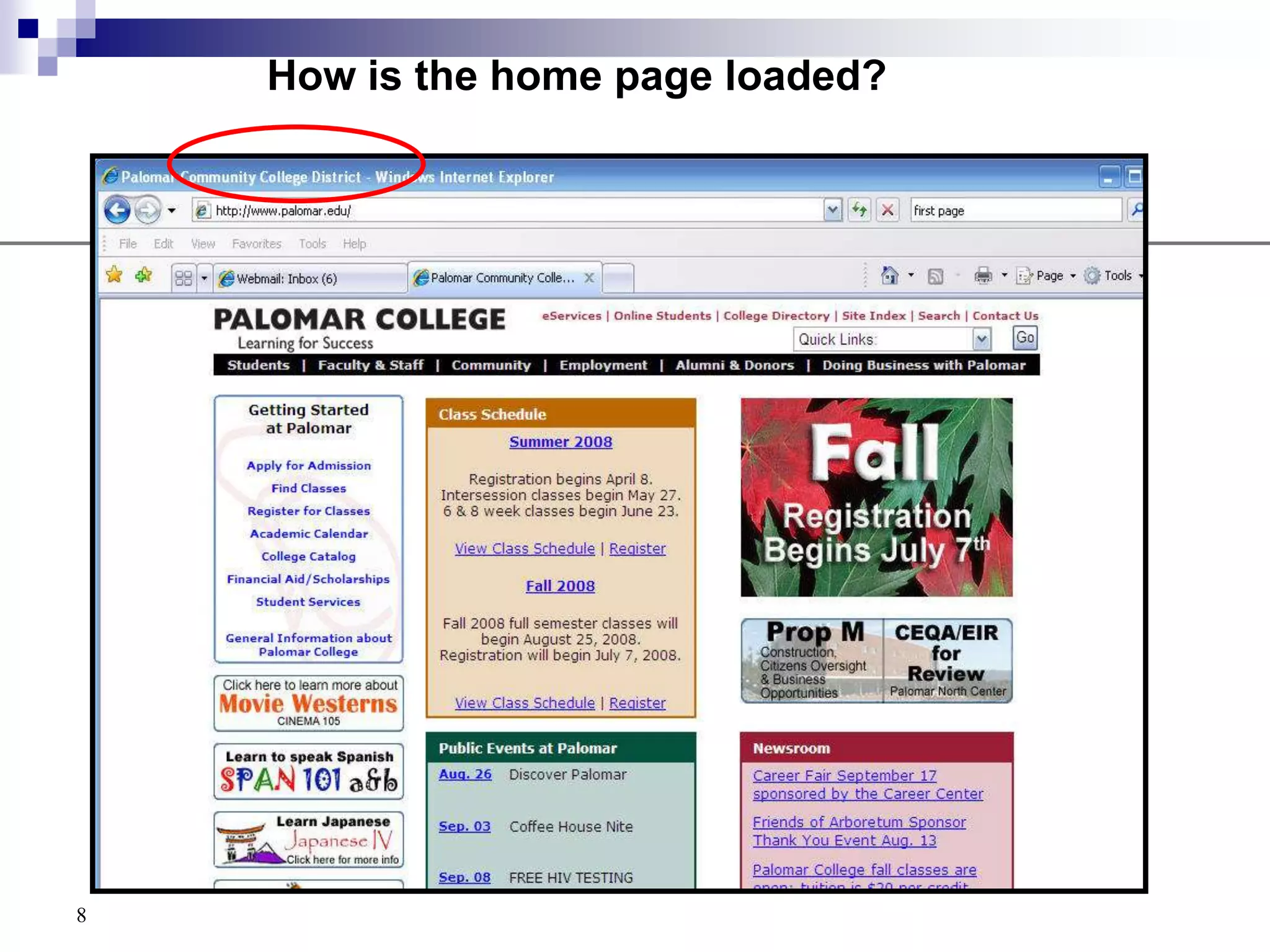
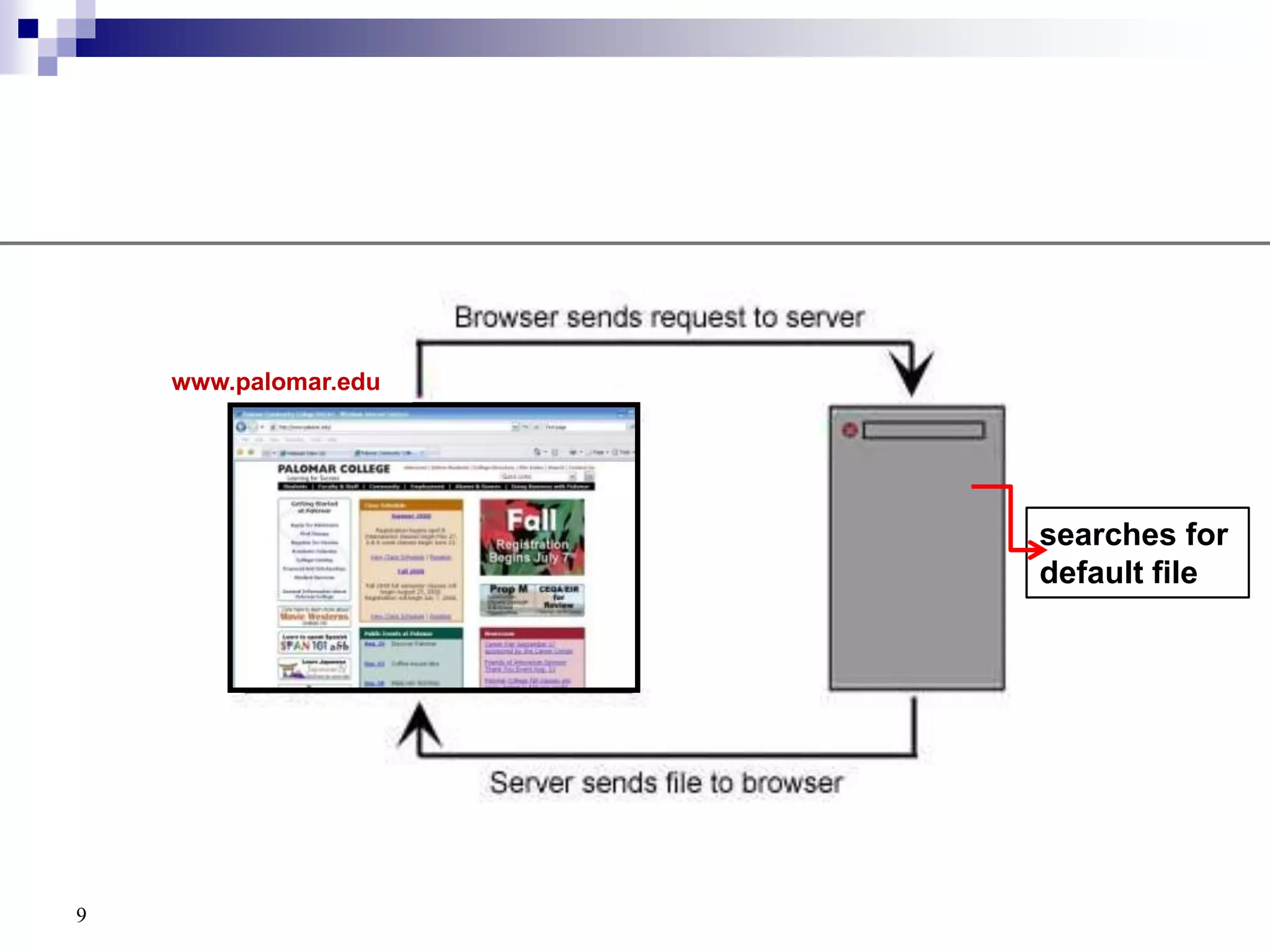
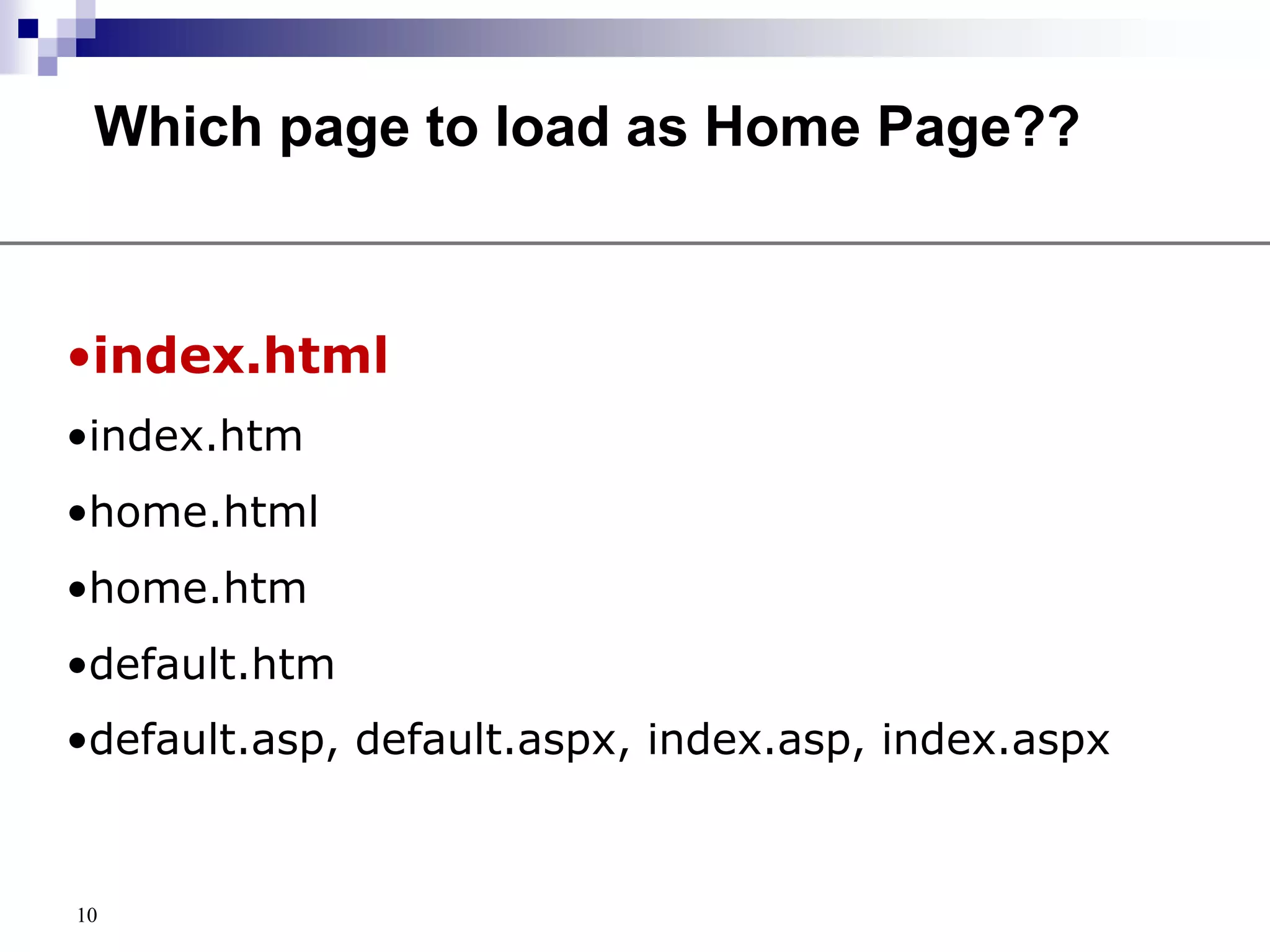
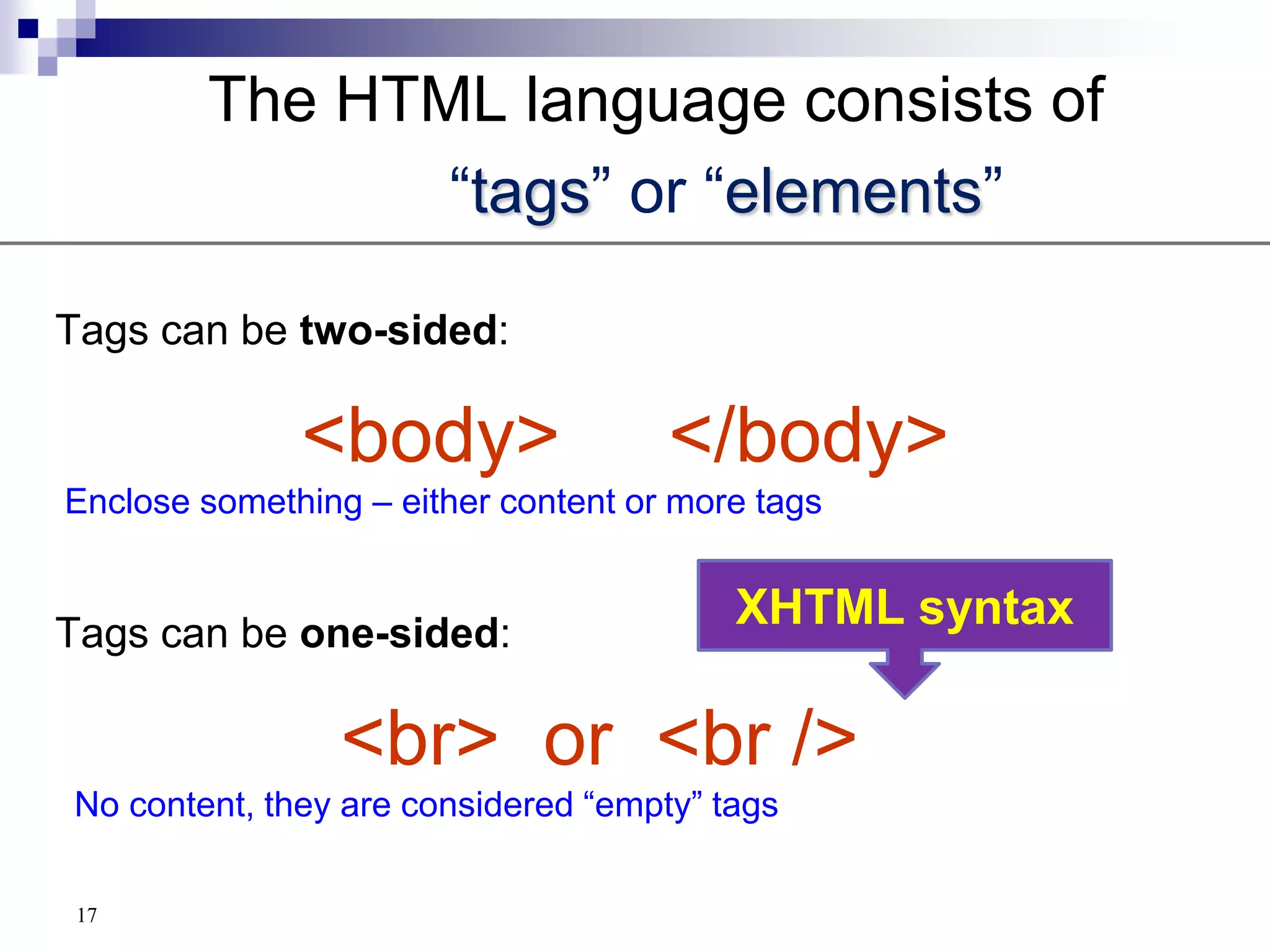
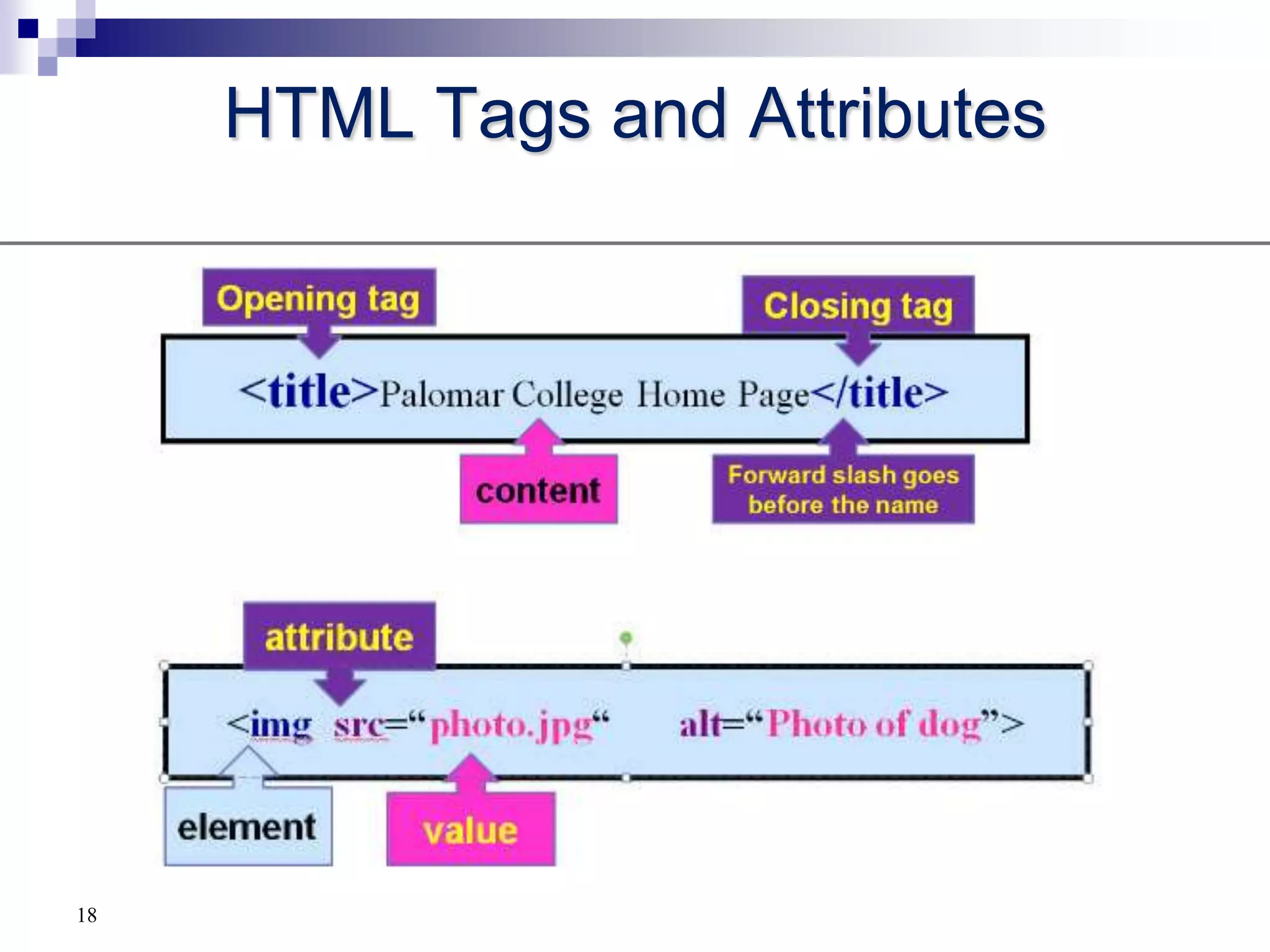
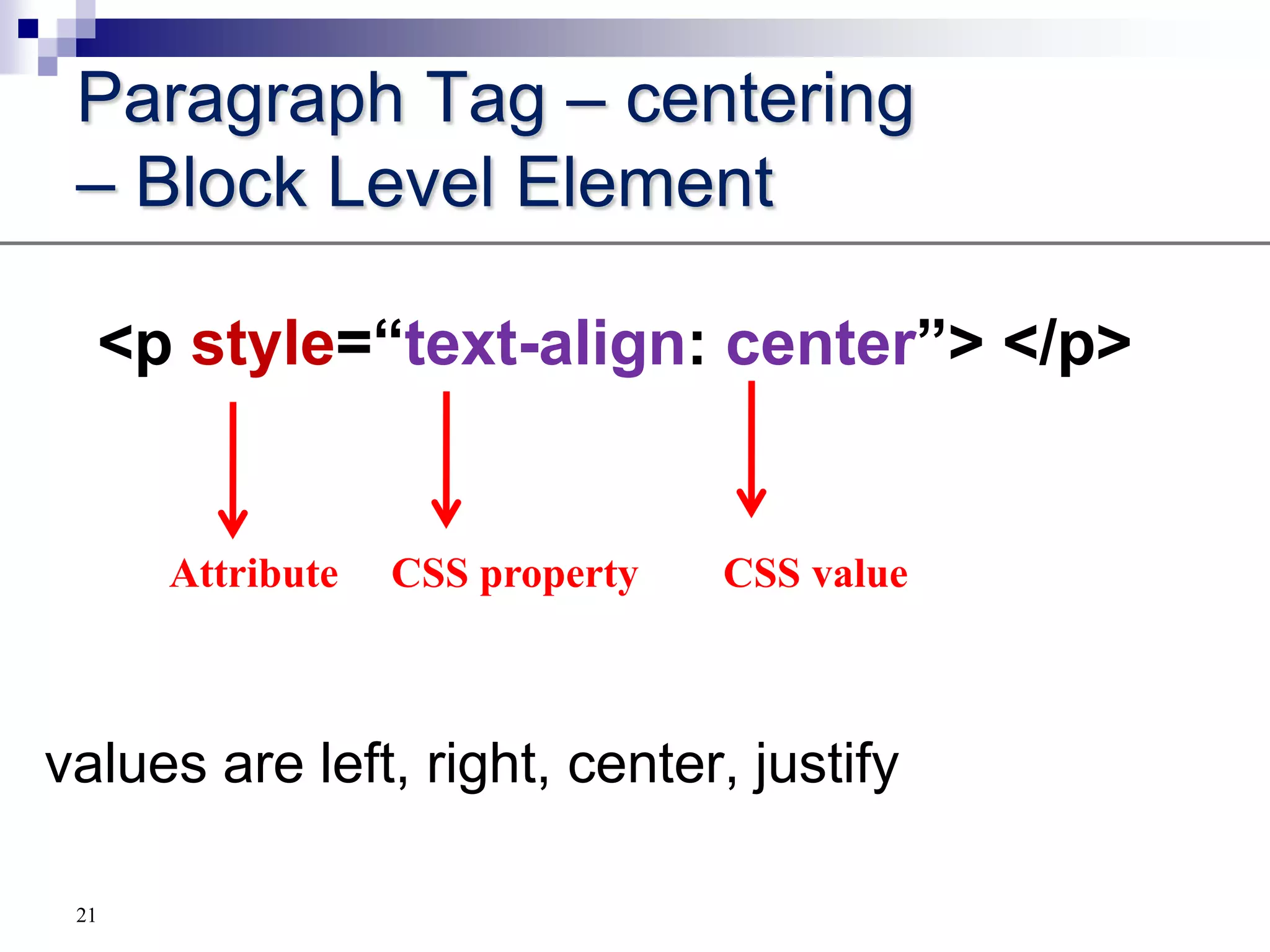
The document provides a history of the development of the internet and world wide web from 1969 to 1995. It then discusses key concepts related to the world wide web including hypertext documents, web servers, web browsers, and the HTML language. The document proceeds to explain HTML elements, attributes, and basic page structure to begin teaching HTML. It covers common tags like headings, paragraphs, breaks, bold, and italic. It also notes the replacement of deprecated HTML attributes with CSS properties.