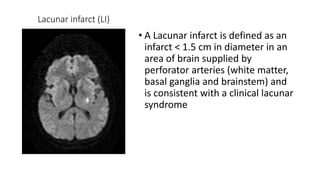
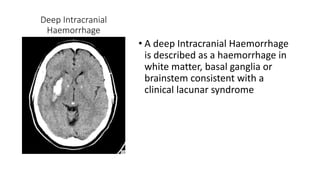
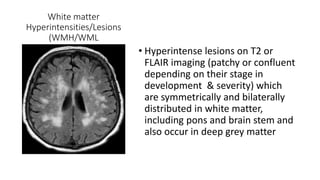
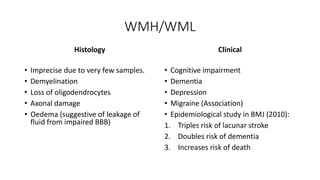
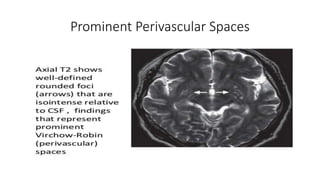
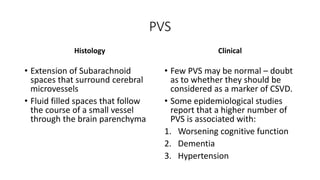
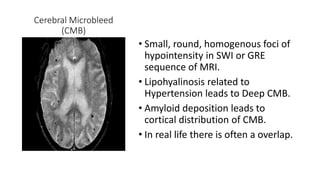
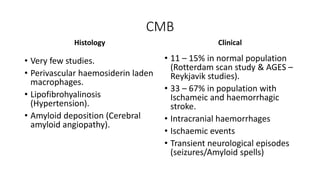
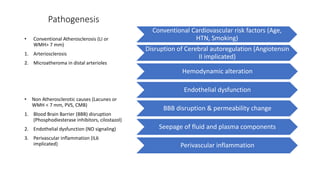
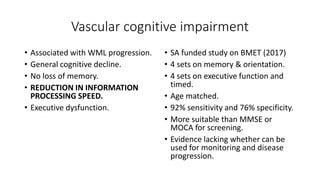
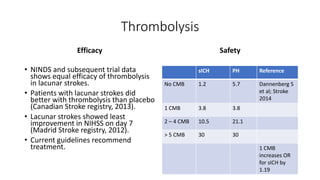
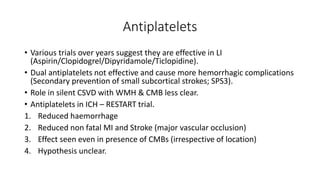
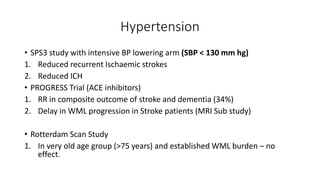
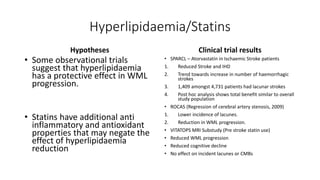
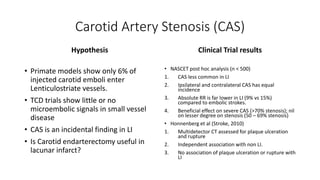
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a condition characterized by clinical and radiological findings associated with pathologies in cerebral arterioles, capillaries, and venules, commonly leading to syndromes like vascular dementia and parkinsonism. The diagnosis relies heavily on radiological markers such as lacunar infarcts, white matter hyperintensities, and cerebral microbleeds, while management options include thrombolysis and the use of antiplatelets. Future directions in treatment may involve candidate drugs focusing on improving blood-brain barrier integrity and managing traditional cardiovascular risk factors.