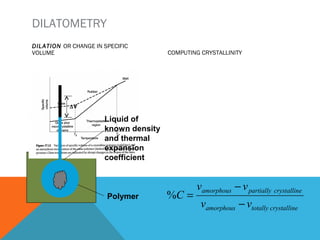
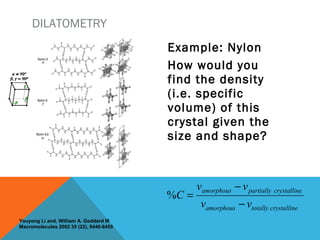
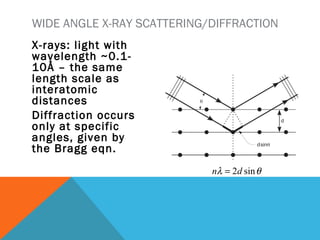
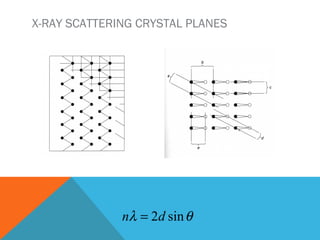
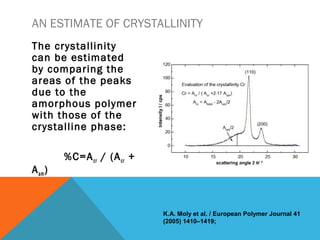
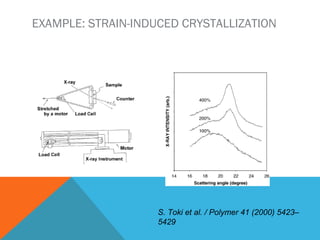
The document discusses crystallinity in polymers. Crystallinity affects the optical, mechanical, thermal and chemical properties of polymers and can range from 10-80% depending on the polymer, making them semi-crystalline. A polymer's structure and intermolecular forces influence its ability to form crystals. Crystallinity can be estimated using different analytical methods like x-ray scattering, dilatometry, and comparing crystalline and amorphous peak areas. Crystallinity contributes to the strength of many polymeric materials.