Embed presentation
Download to read offline


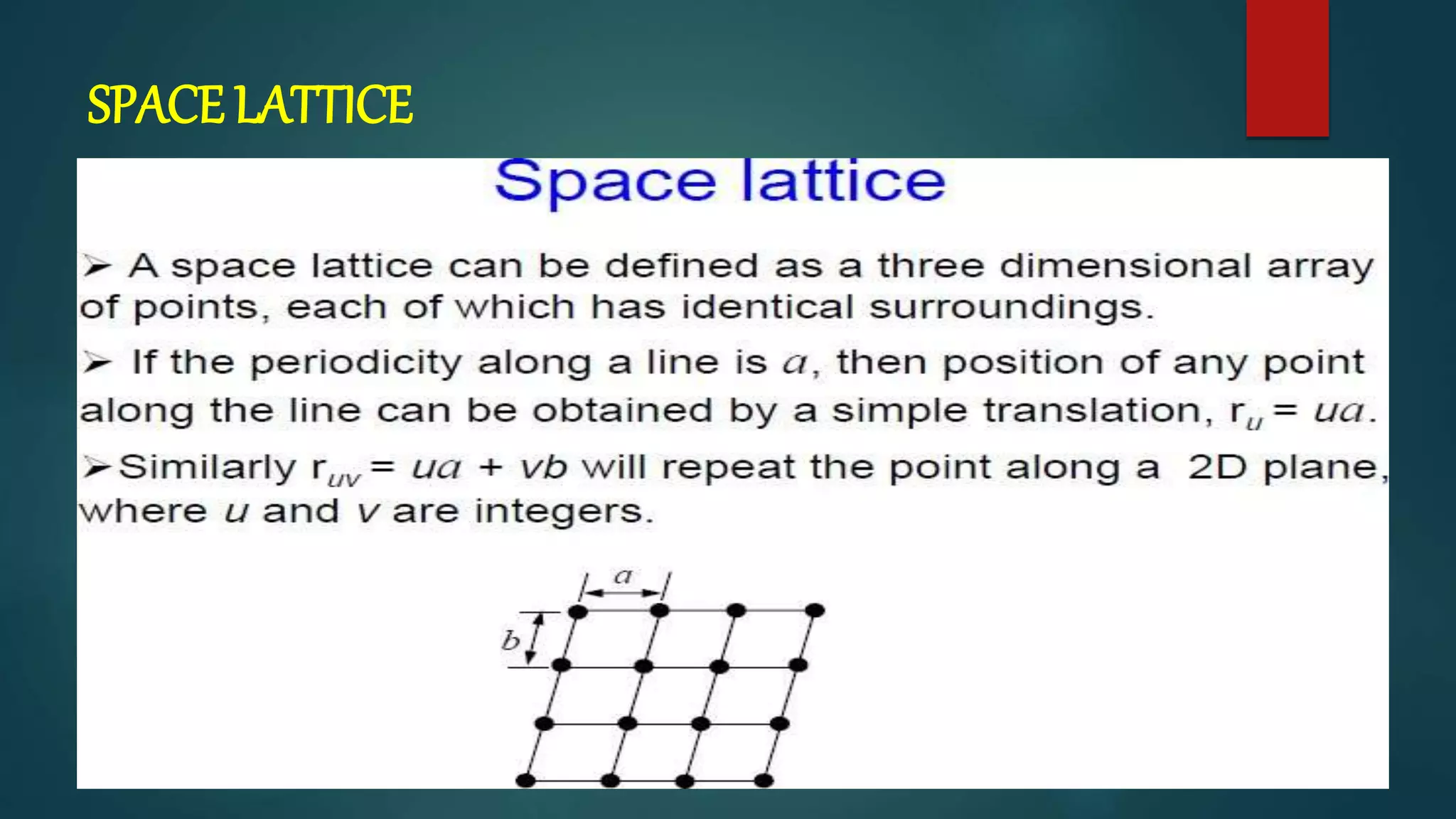
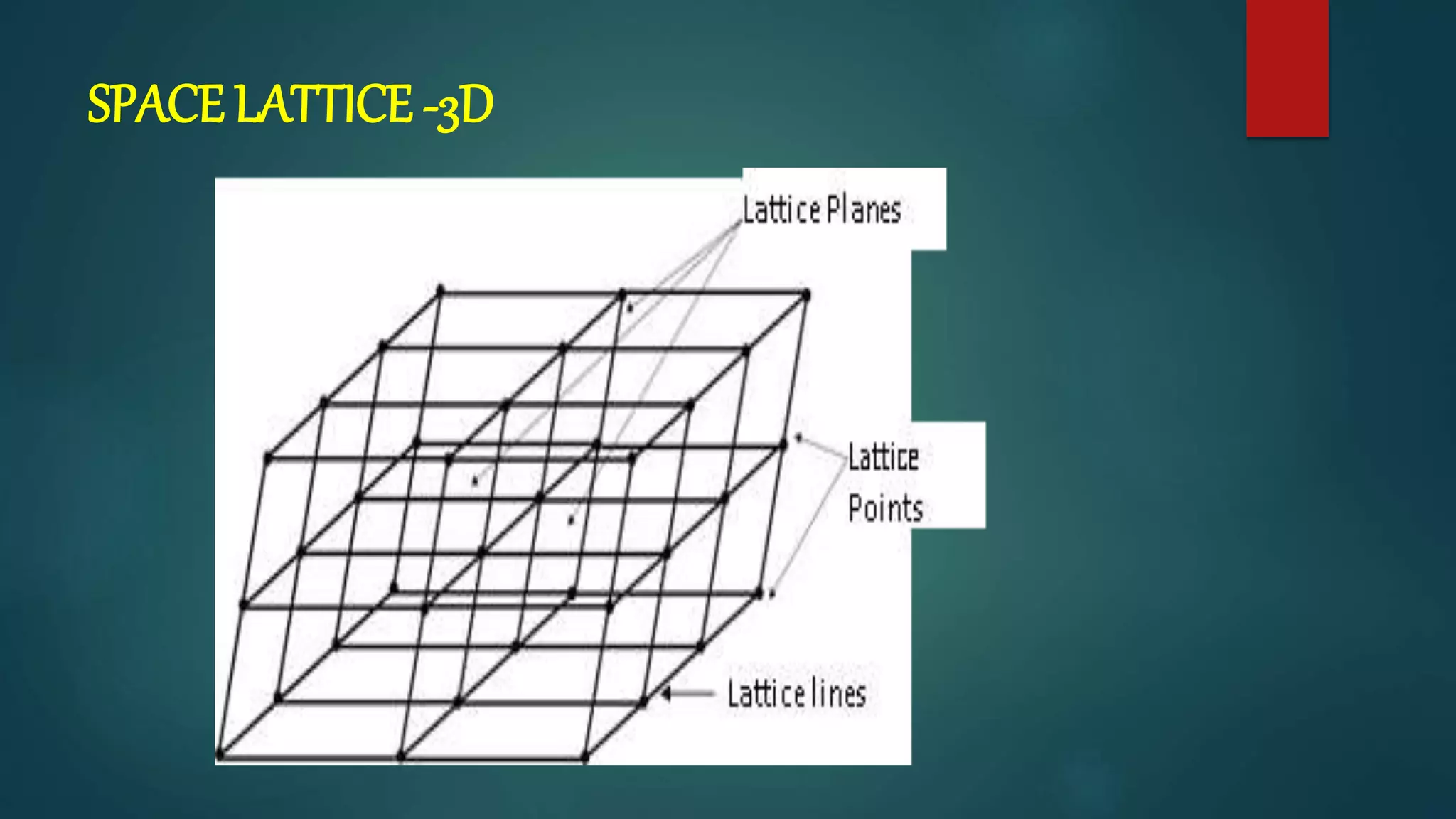

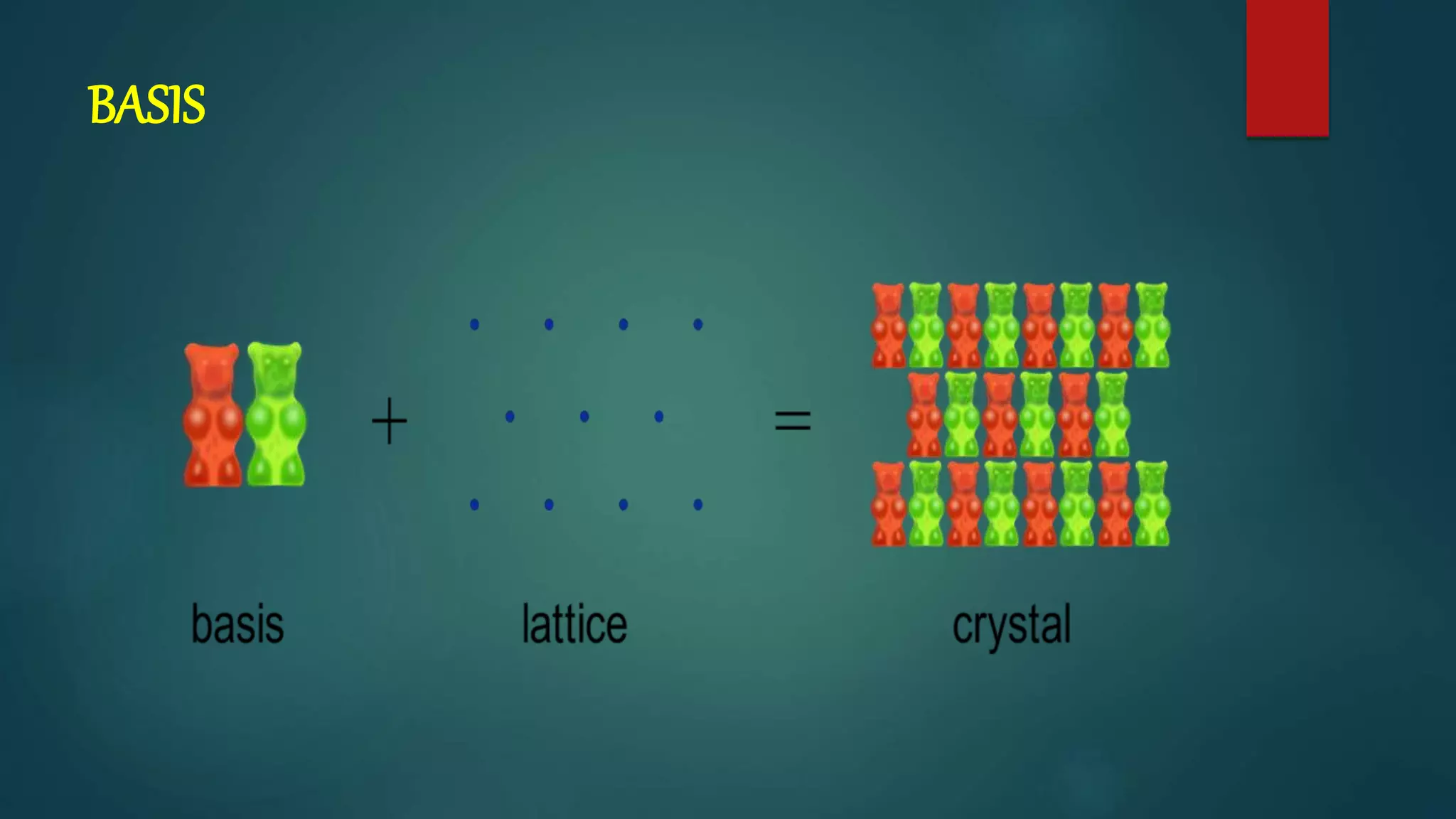
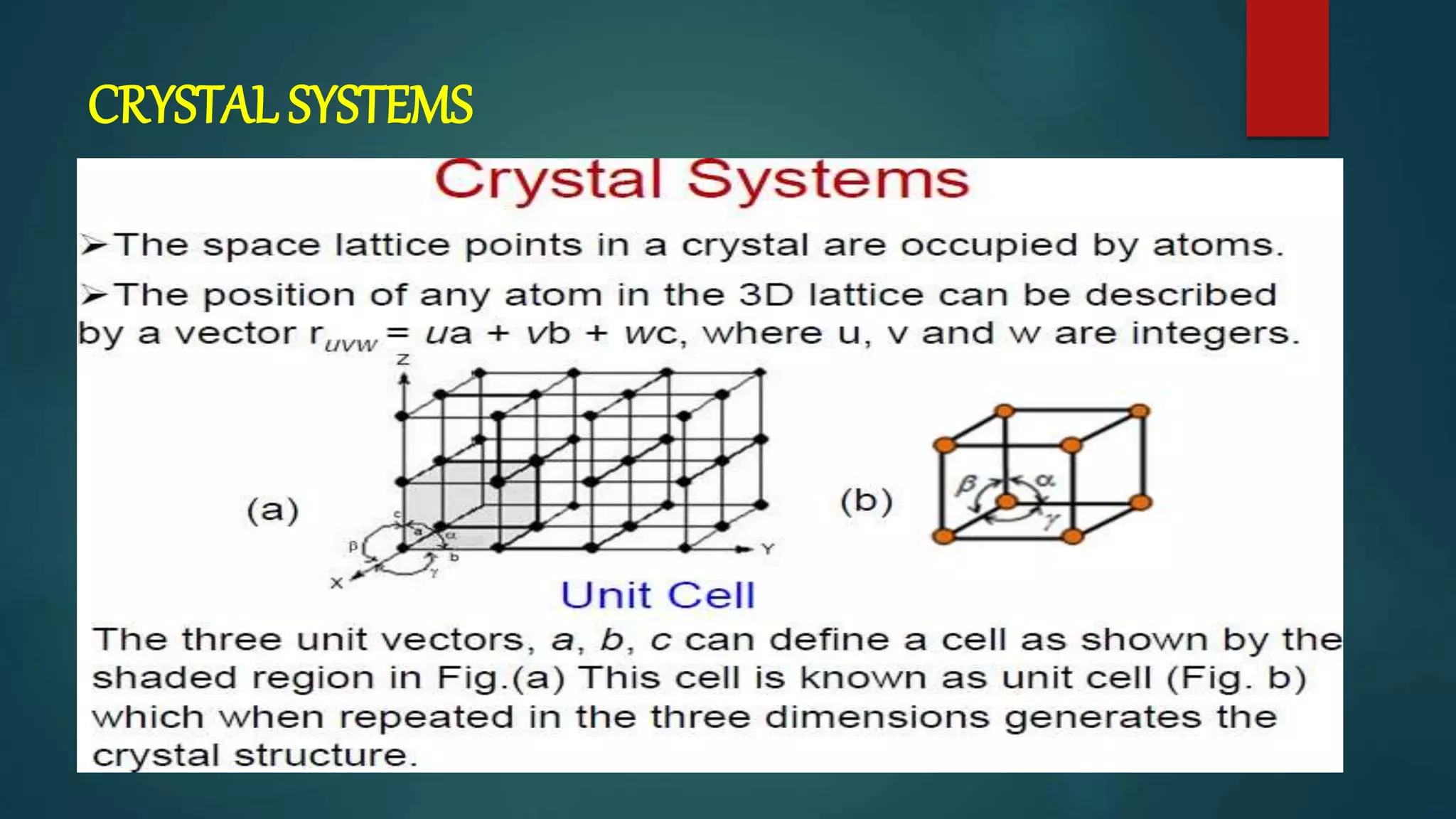

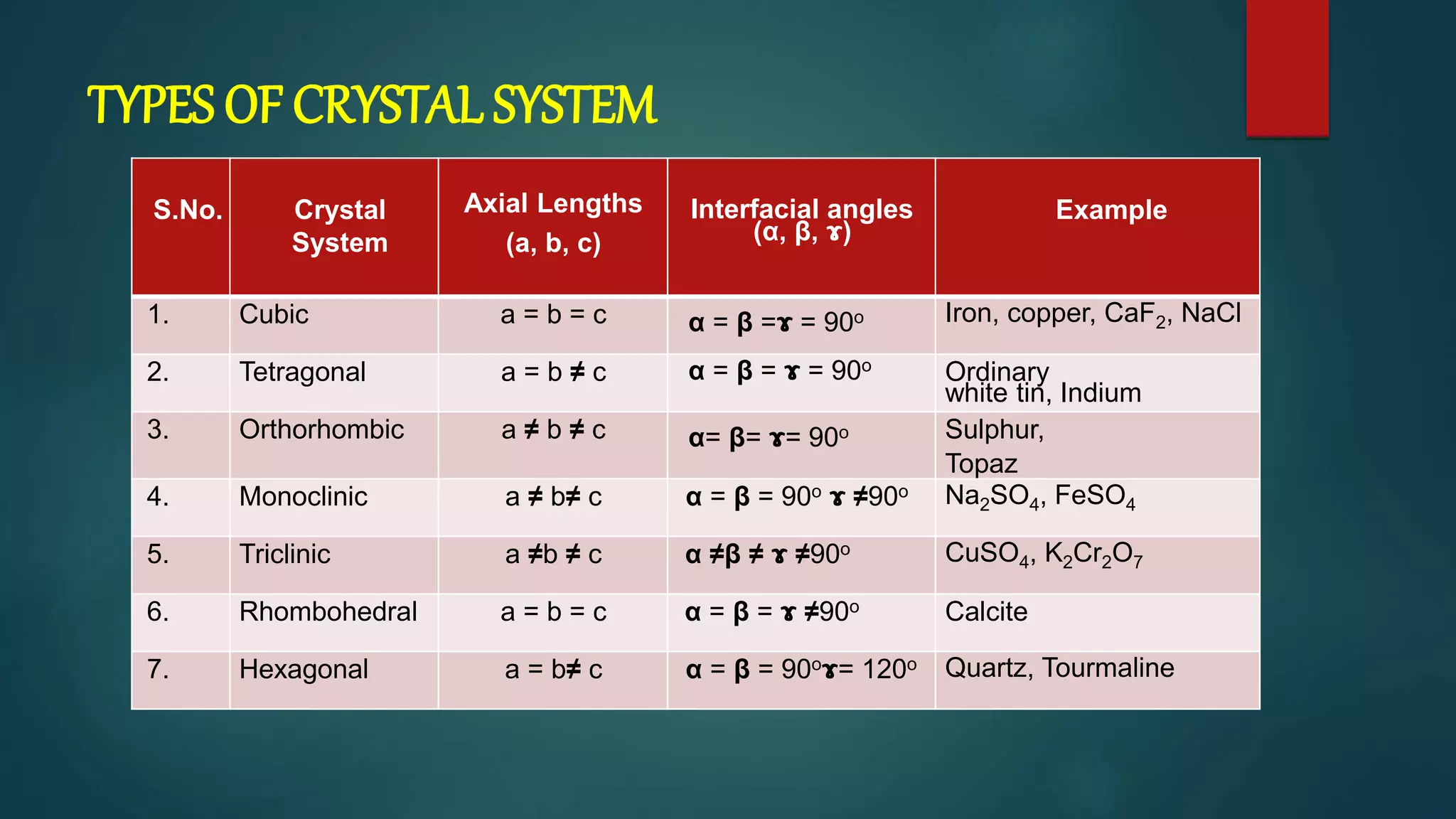
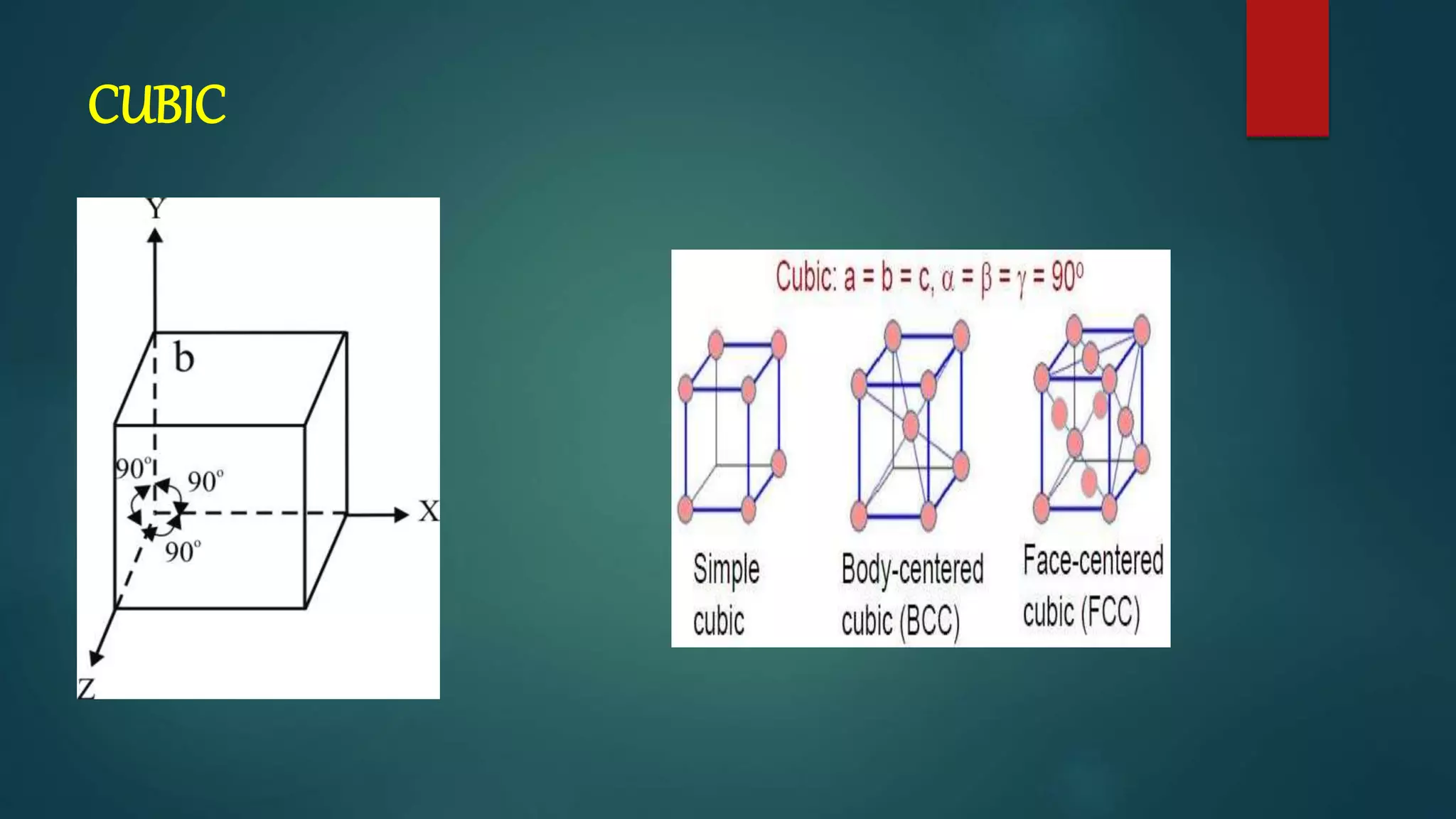


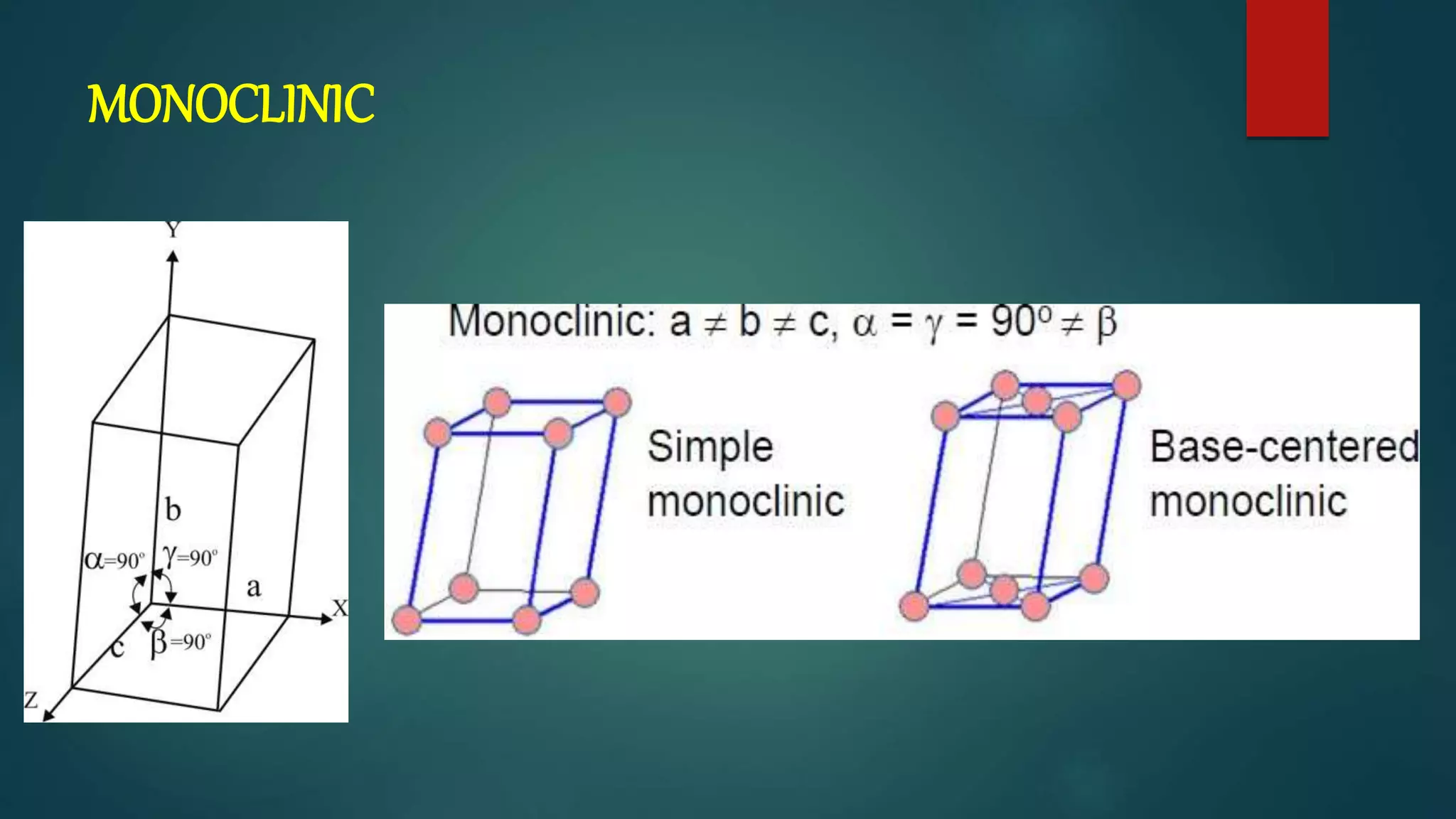


The crystal structure is formed by repeating arrangements of atoms or molecules in a lattice structure. There are 7 crystal systems defined by the length of the lattice axes (a, b, c) and interfacial angles (α, β, γ). The cubic system has equal lattice lengths (a = b = c) and 90 degree angles, while the triclinic system has unequal lengths and non-90 degree angles. The basis refers to the identical assembly of atoms that repeats in the lattice.














