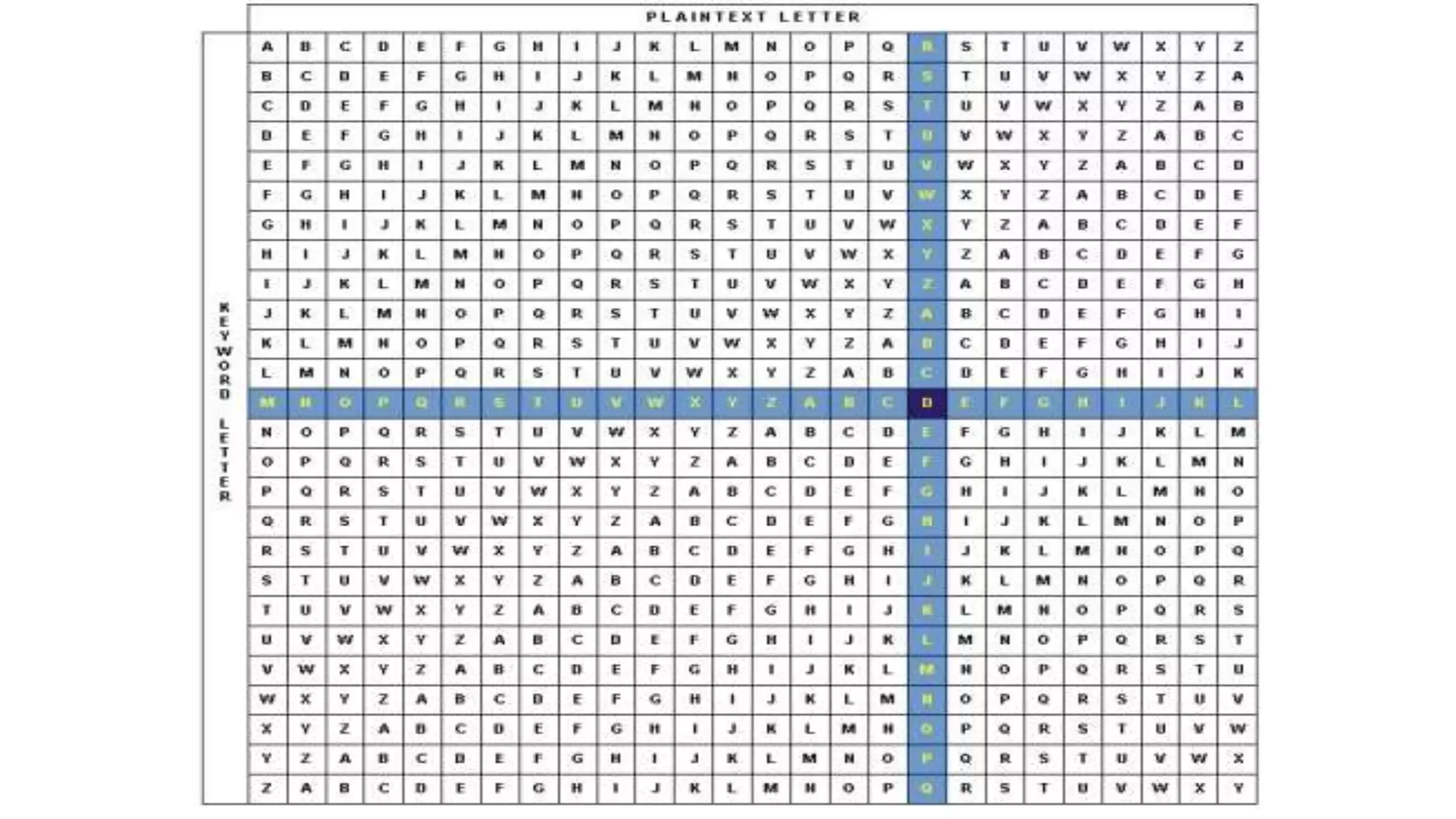
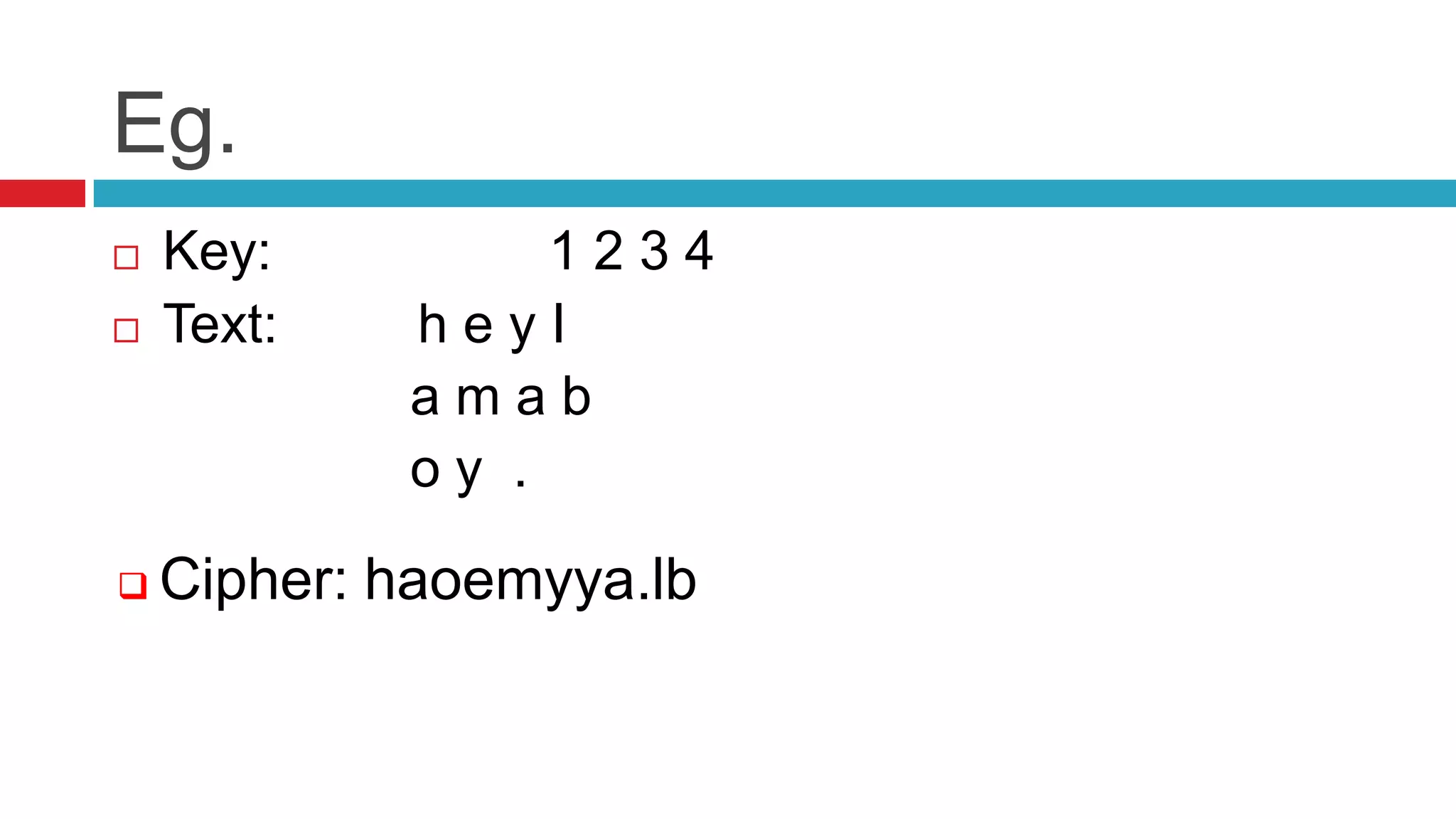
This document discusses several symmetric and asymmetric ciphers. It describes Caesar cipher, Vigenere cipher, transposition cipher, one-time pad, and RSA cipher. For each cipher it provides a brief overview of the encryption process and includes examples to demonstrate how the cipher works. It aims to educate the reader about common cryptographic tools and techniques.