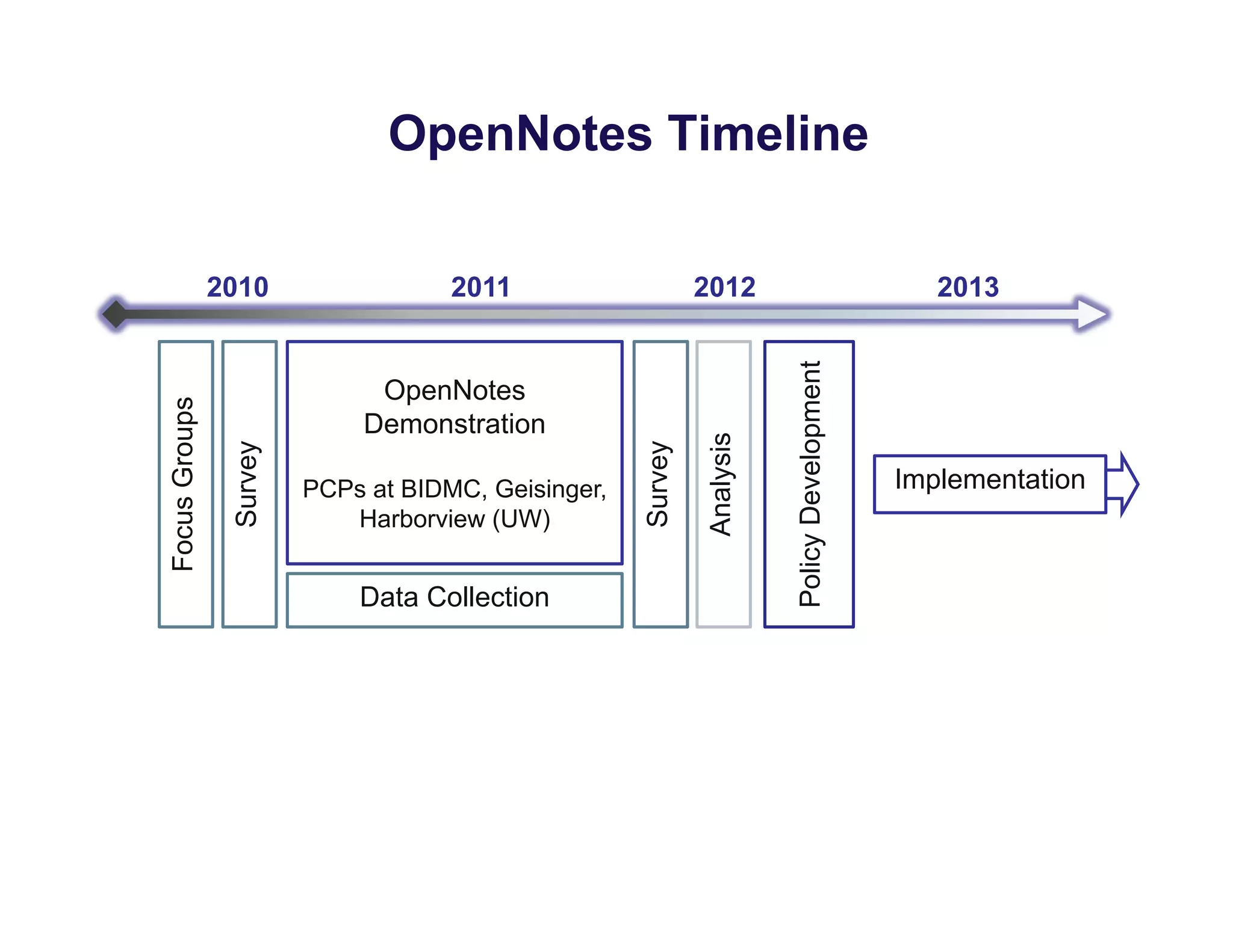
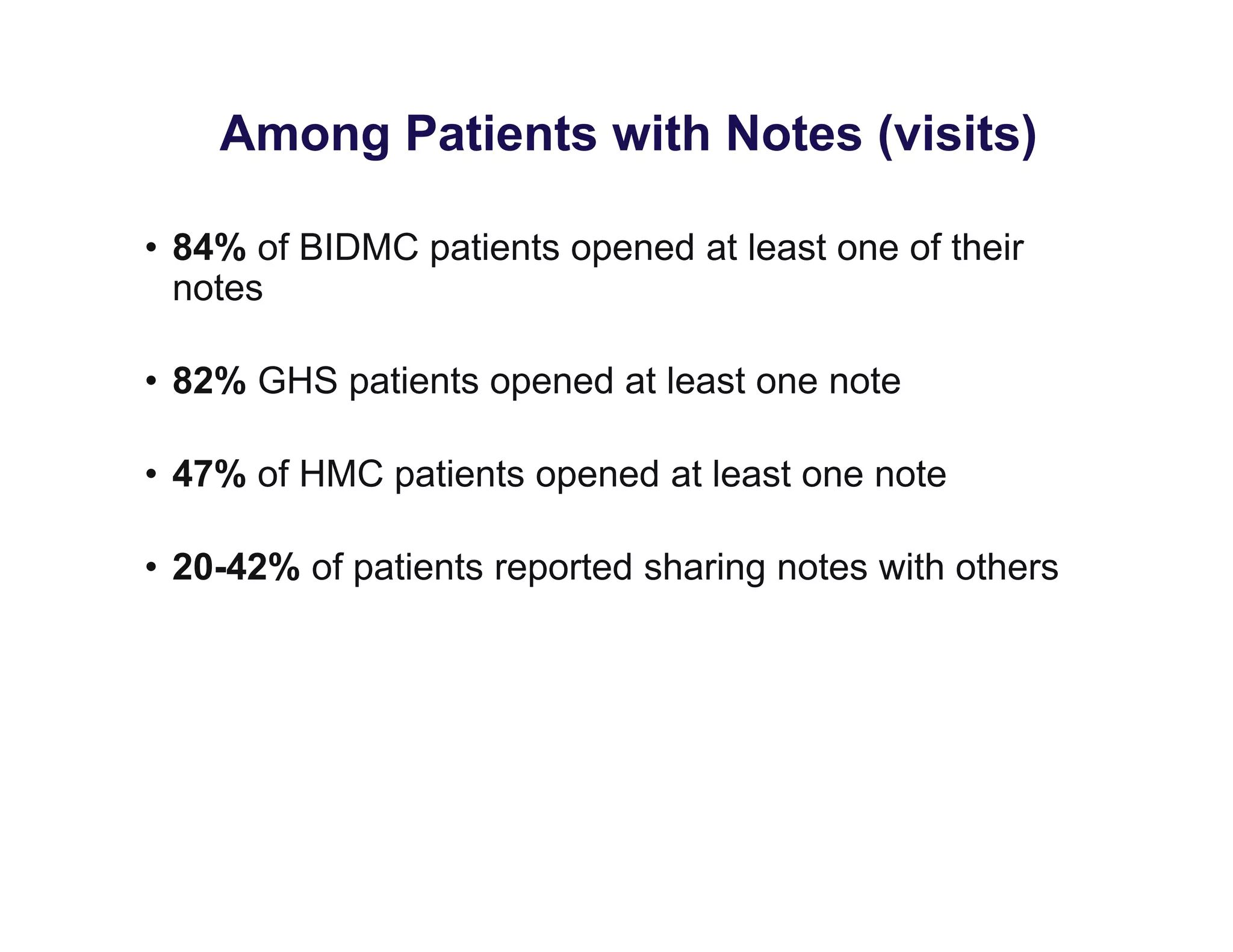
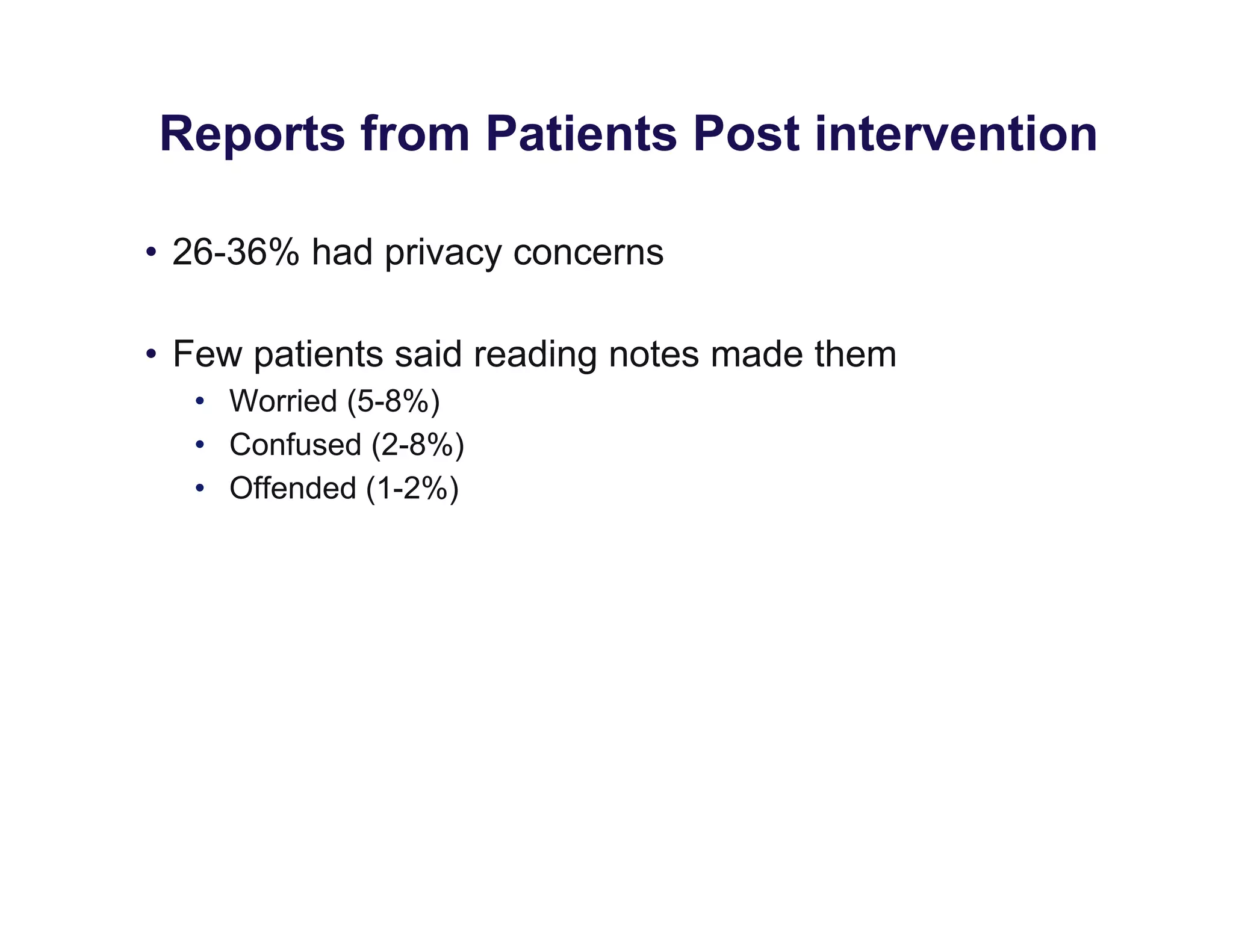
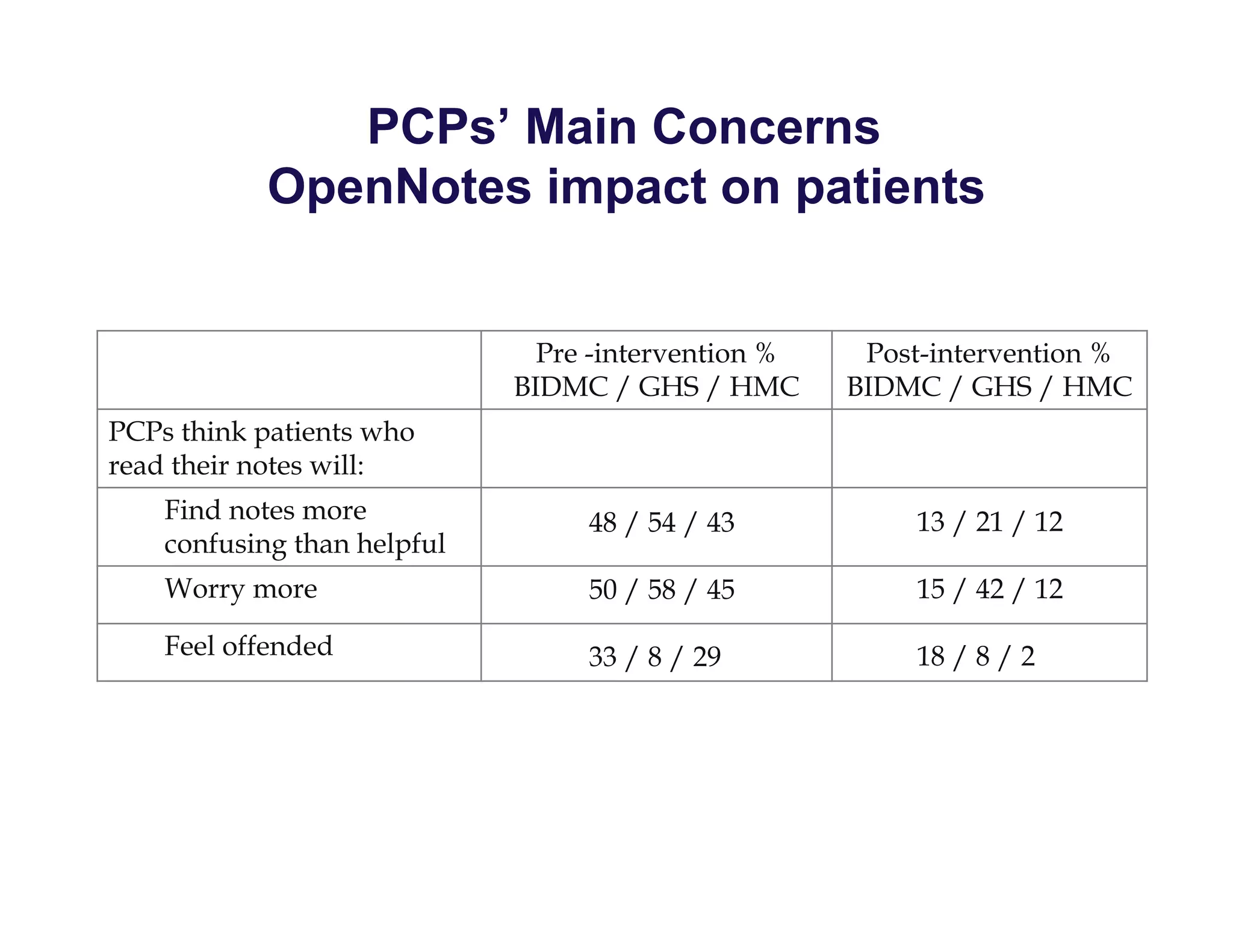
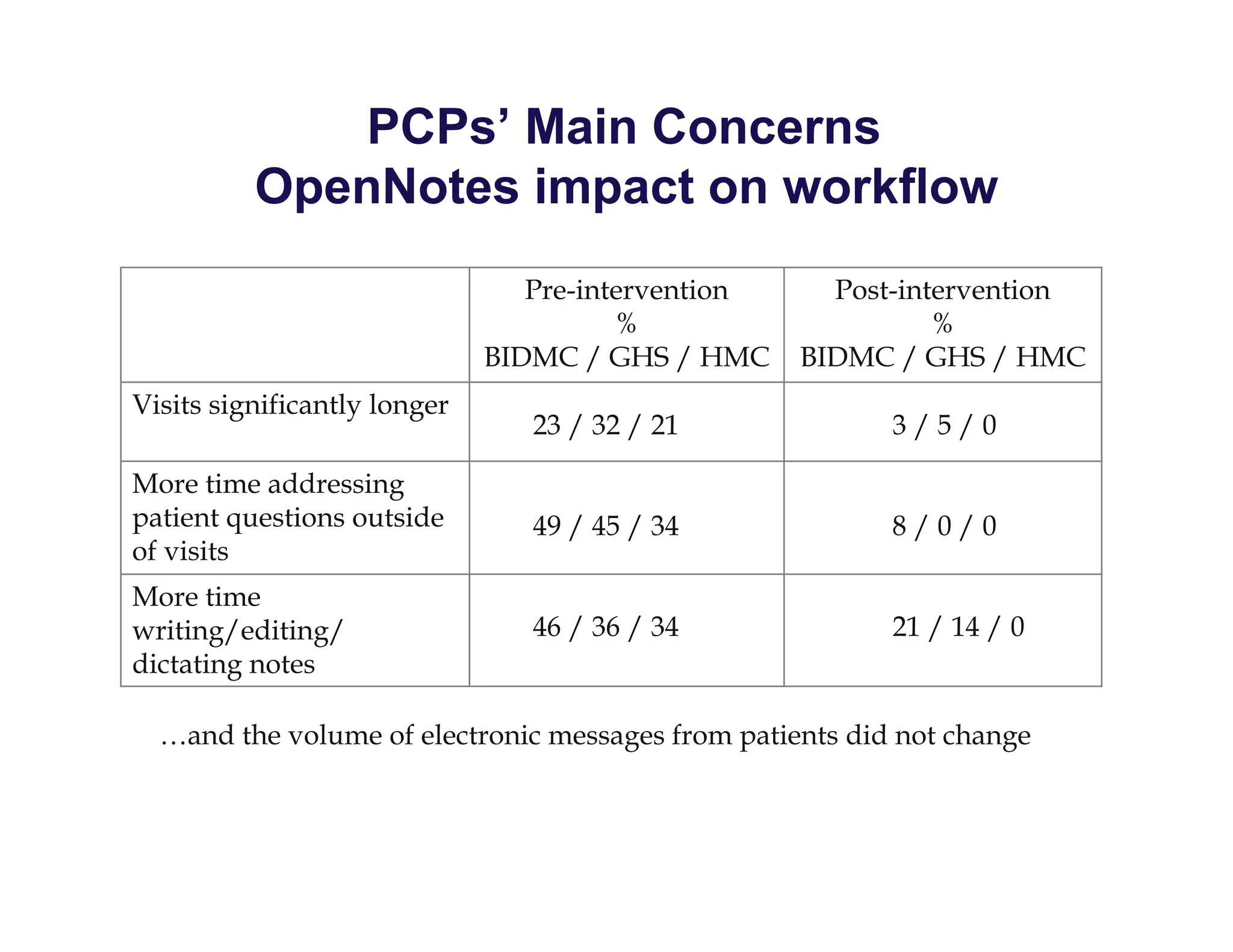
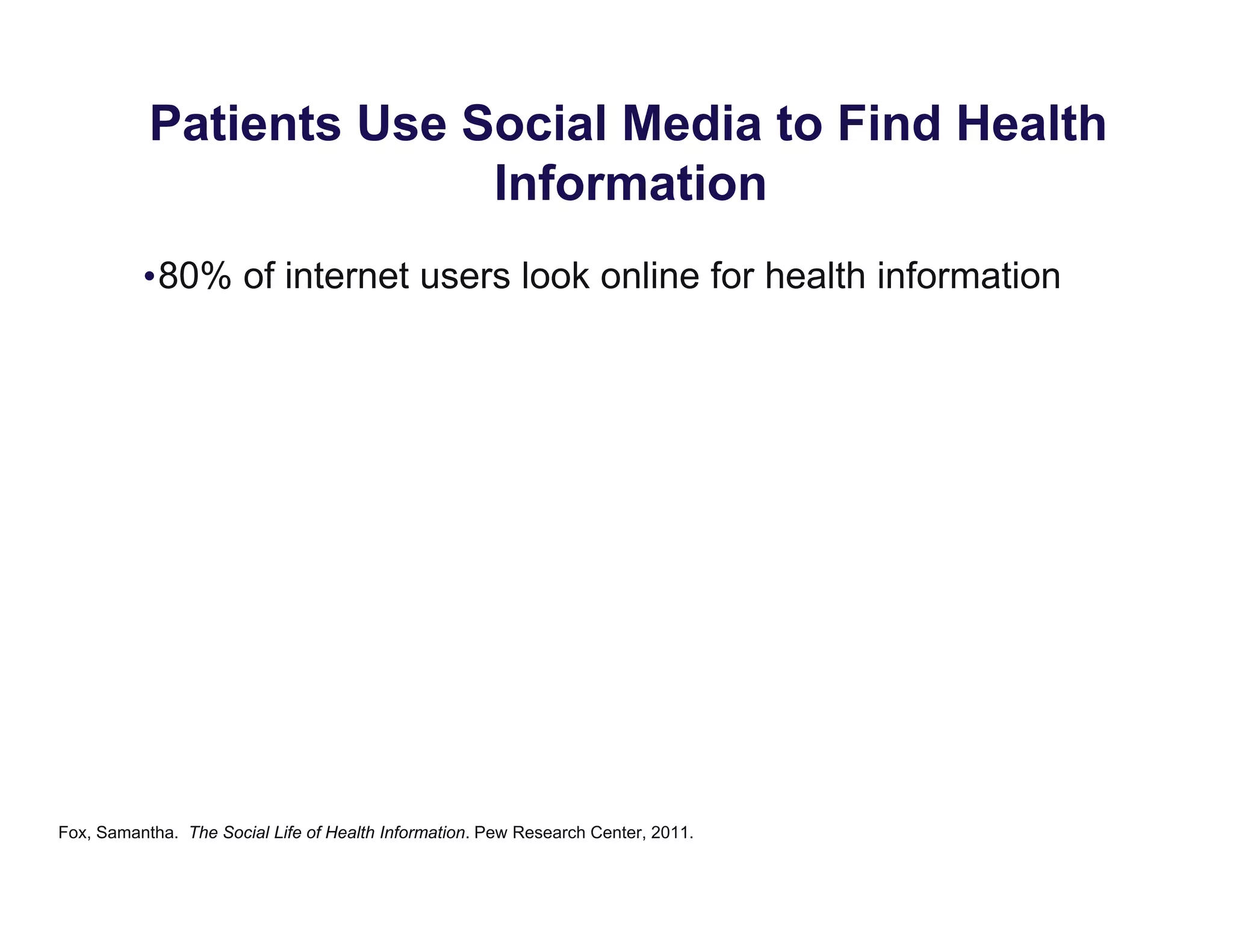
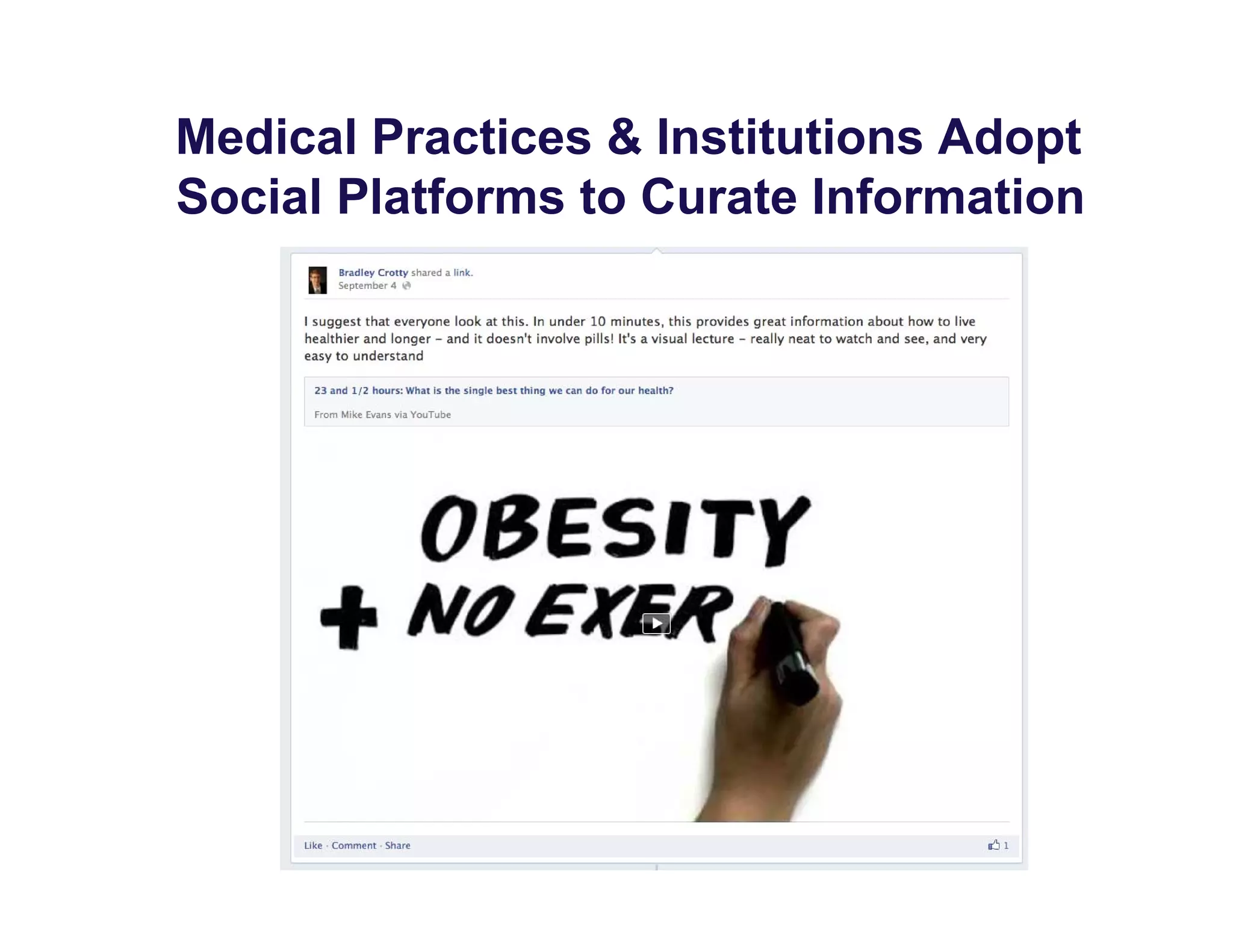
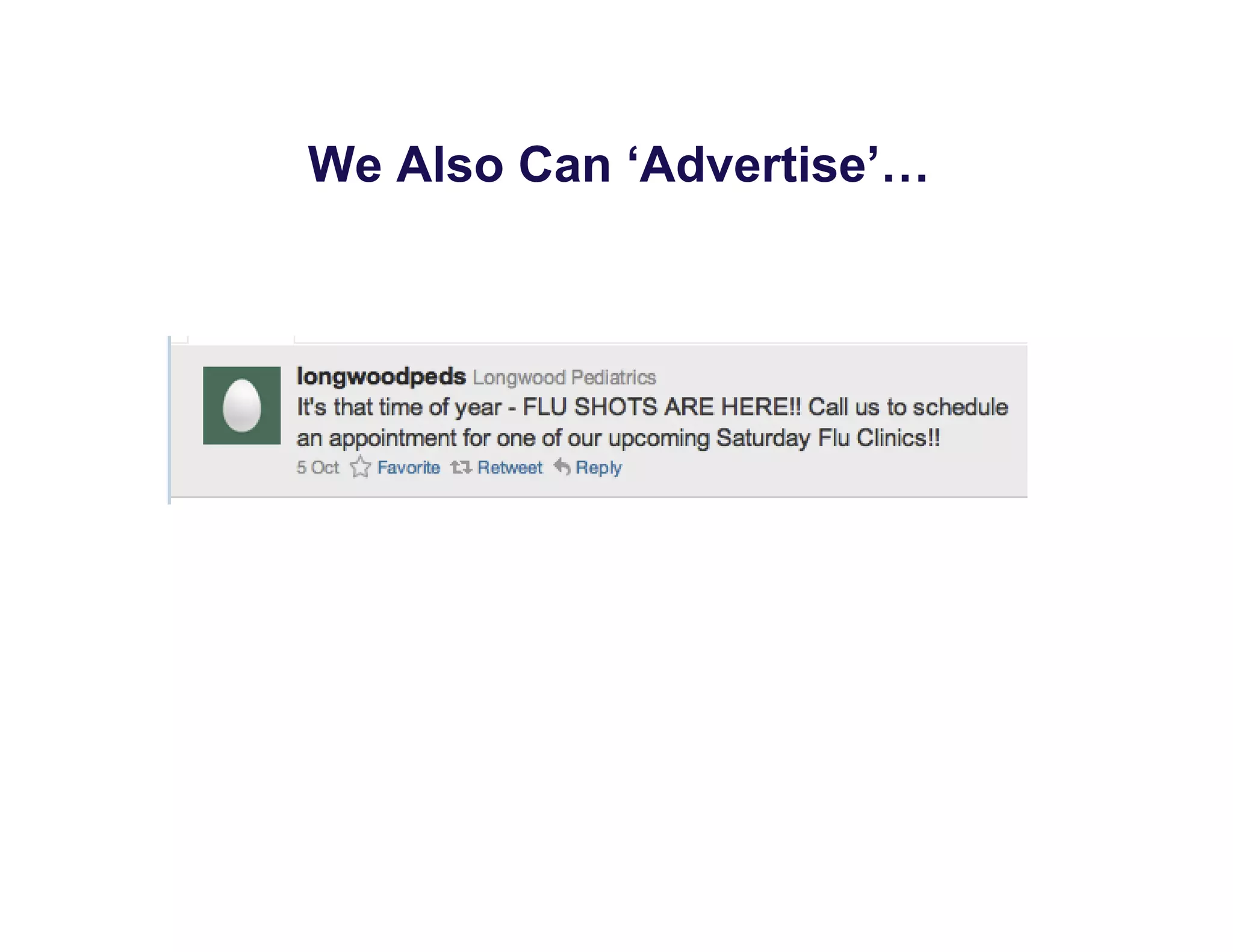
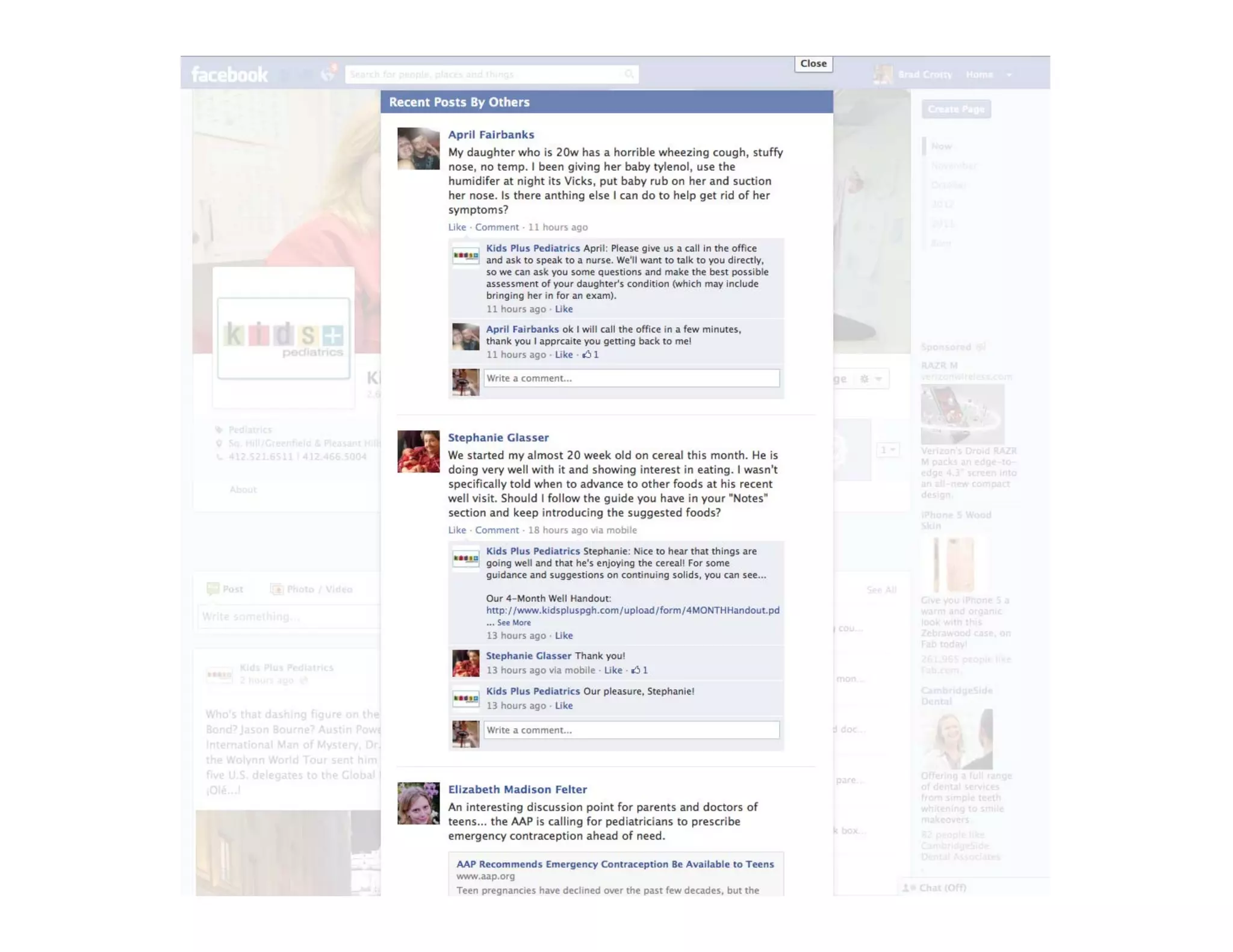
The document discusses new ways to engage patients through open notes and social media. It describes initial findings from the OpenNotes project that showed patients found value in reading clinical notes. It also outlines how patients use social media to find health information and connect with others. The document argues that healthcare providers can leverage these technologies and concepts to reduce information asymmetry, educate patients, and learn from them to provide more engaging and effective care.