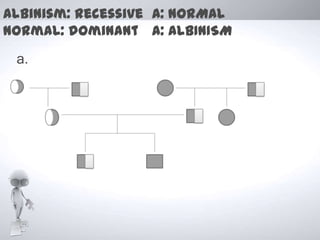
Gregor Mendel performed experiments with pea plants to study inheritance patterns of traits. He developed three hypotheses: hereditary determinants do not mix with each other, alleles segregate independently during gamete formation, and gametes combine randomly during fertilization. Mendel also discovered the laws of segregation and independent assortment. His work helped establish the foundations of classical genetics and laid the basis for understanding patterns of inheritance.