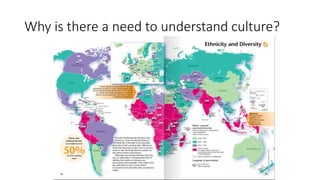
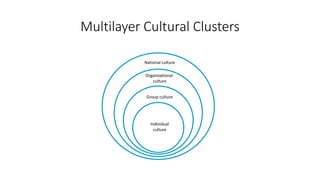
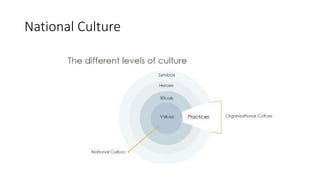
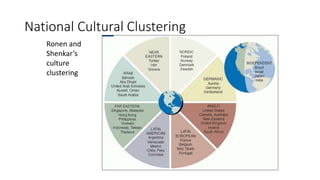
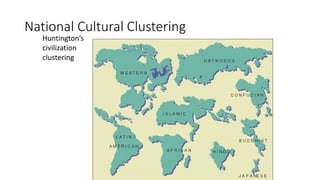
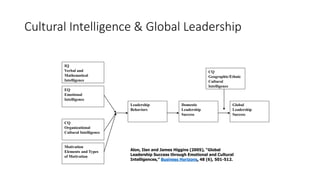
This document discusses cultural intelligence and its importance. It defines culture and cultural awareness, and explains that culture exists at multiple levels, including individual, group, organizational, national, corporate, ethnic, industry, and demographic levels. It also discusses national cultural dimensions and clustering. Cultural intelligence is defined as the ability to adapt to and work effectively in different cultural contexts. A cultural intelligence instrument called the BCIQ is presented, which measures cultural intelligence across six dimensions: motivation, adaptive communication, cognitive preparation, active learning, cognitive awareness, and global/national knowledge. Developing cultural intelligence is important for leadership, work performance, and functioning in multicultural environments.