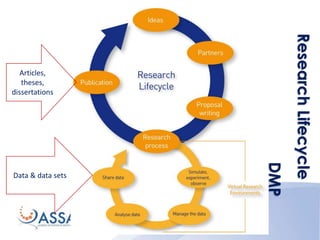
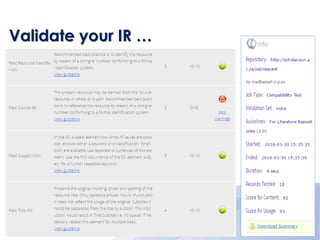
This document discusses the criteria for a trusted institutional repository. It begins by defining a trusted digital repository as one that provides reliable long-term access to managed digital resources for its designated community. It then outlines several key criteria for a trusted institutional repository, including accepting responsibility for long-term maintenance, applying common standards, and regularly evaluating systems. The document also summarizes several methodologies for assessing trusted repositories, such as the ISO 16363 standard. Finally, it discusses principles of trusted repositories like commitment to preservation, adequate technical infrastructure, and fulfillment of dissemination requirements.