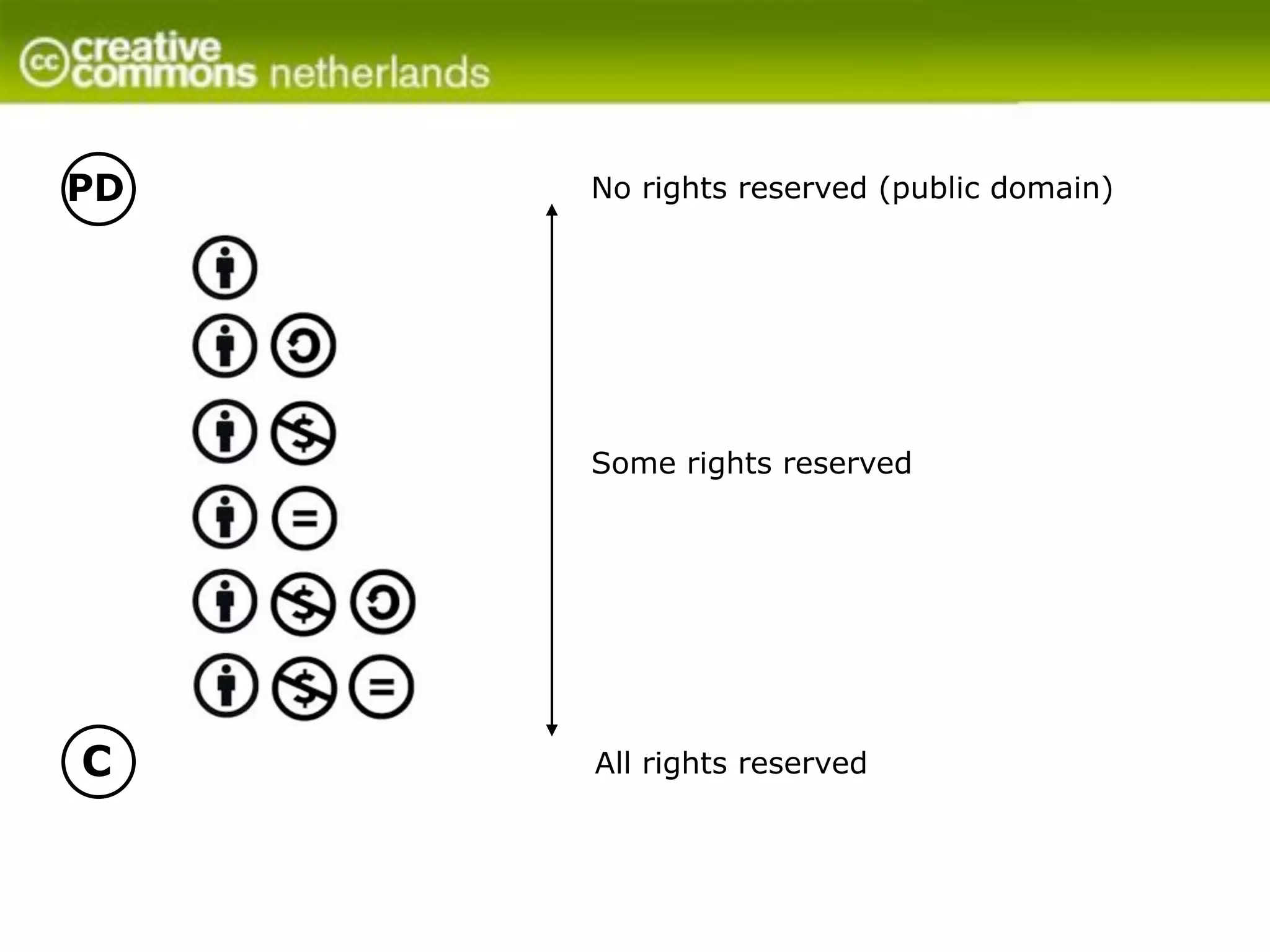
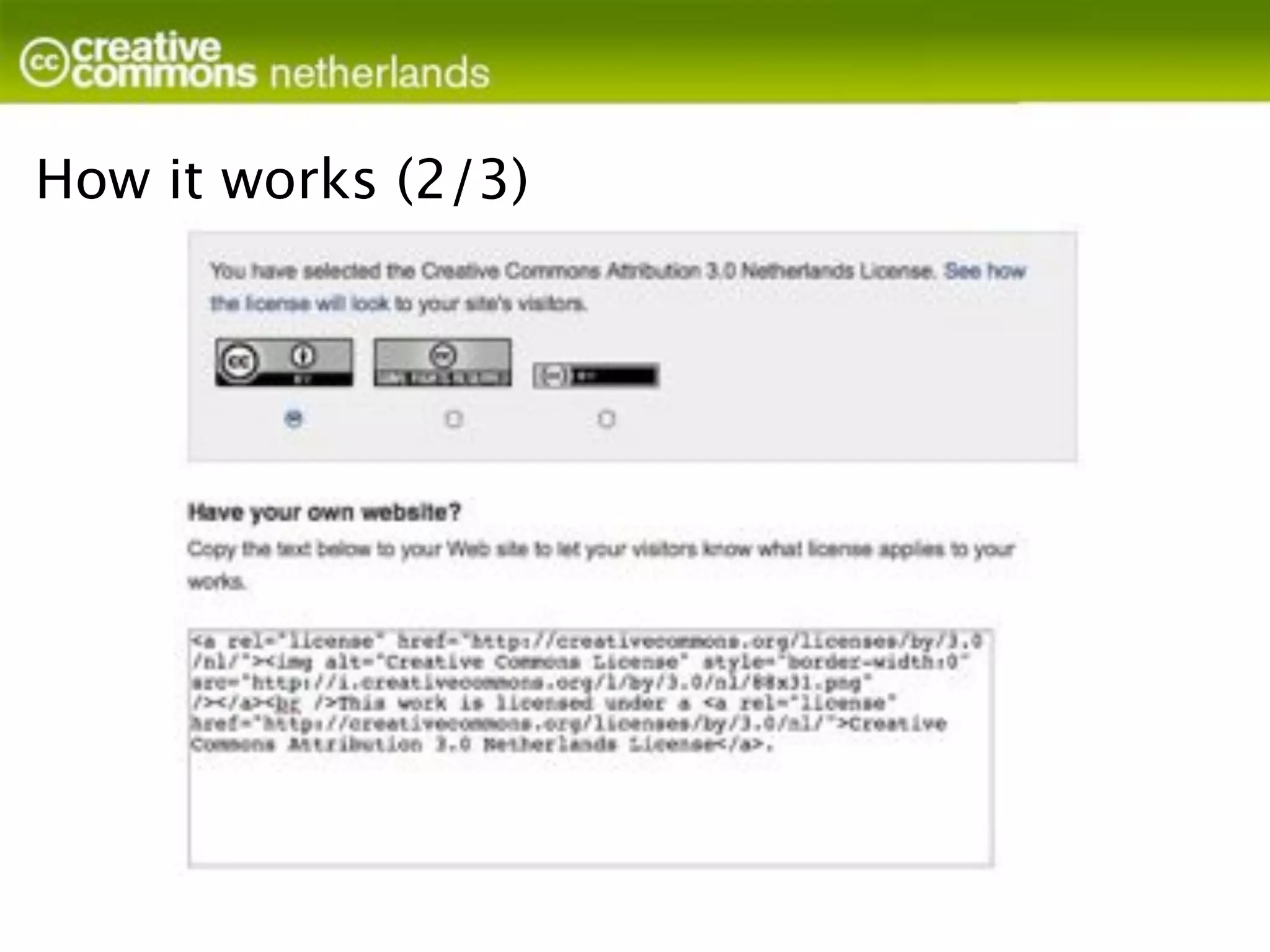
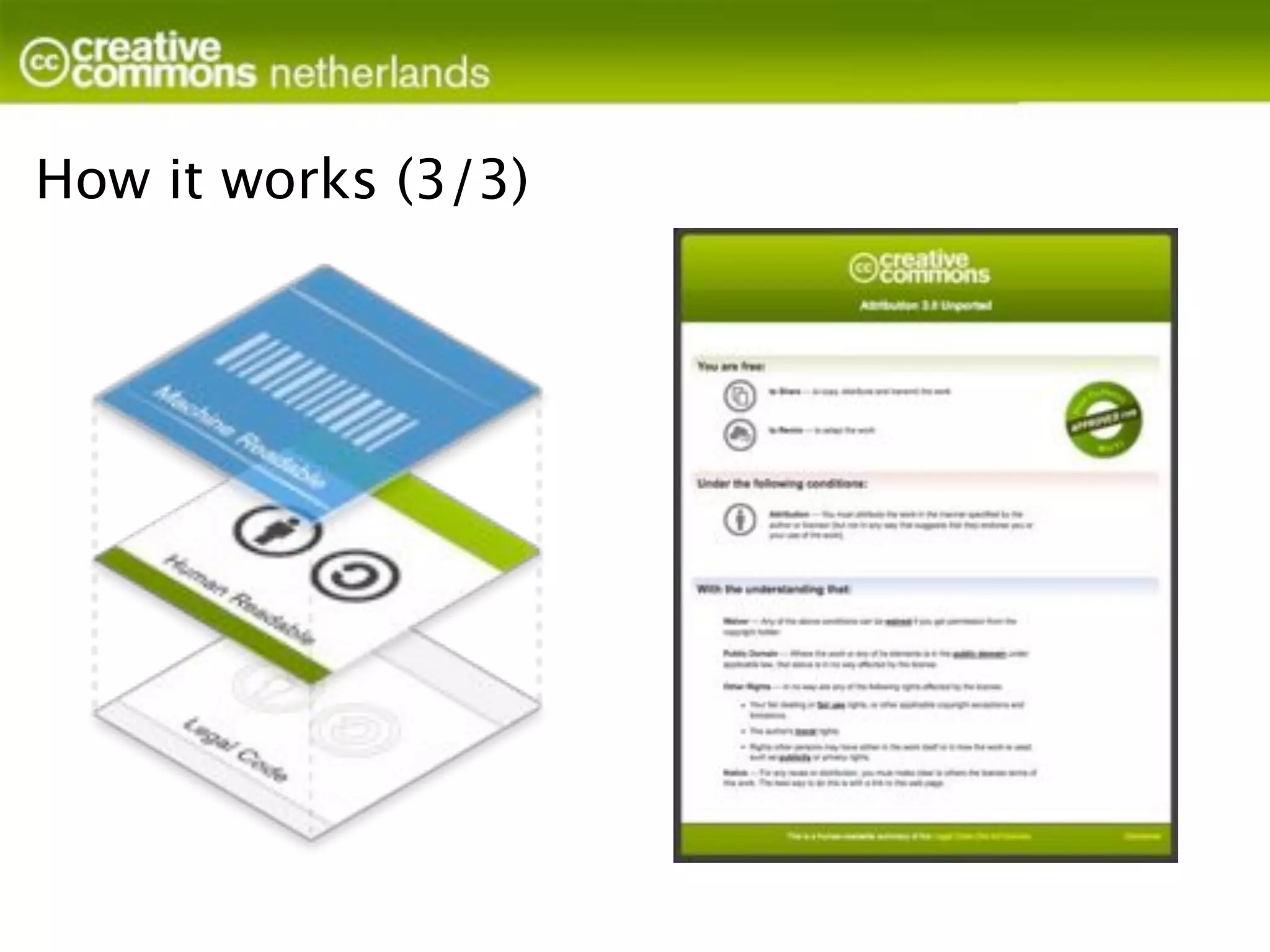
Creative Commons licenses provide alternatives to traditional copyright for authors and creators to grant permissions for others to use their work. The licenses offer options for allowing commercial use, modifications, and sharing derivatives under the same license (Attribution, NonCommercial, NoDerivatives, ShareAlike). Licenses are granted to the public and last as long as copyright, though authors retain moral rights. Works can be licensed by adding attribution and license information. Creative Commons does not enforce licenses but provides tools and education to help authors share their work while maintaining control over how it is used.