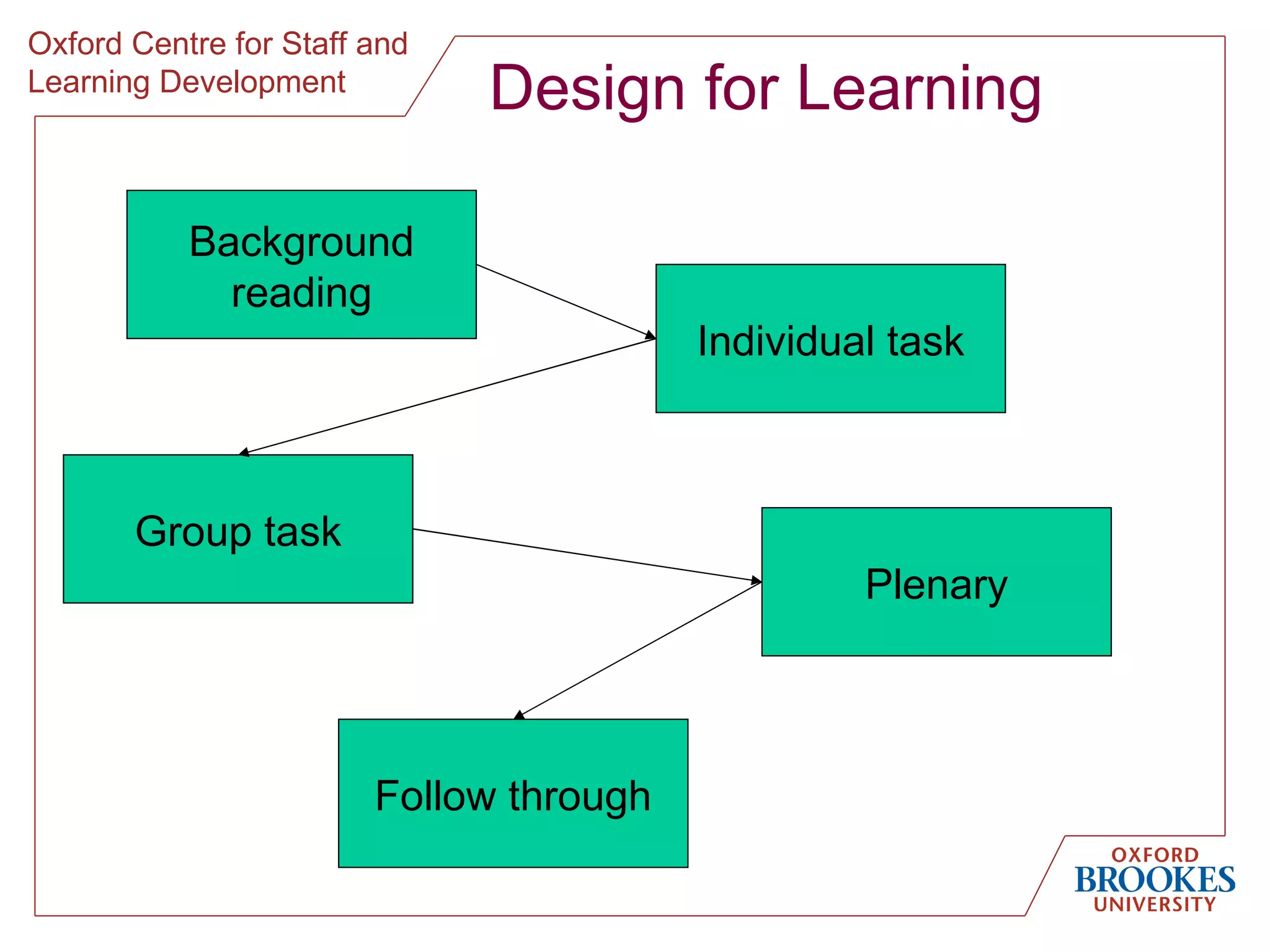
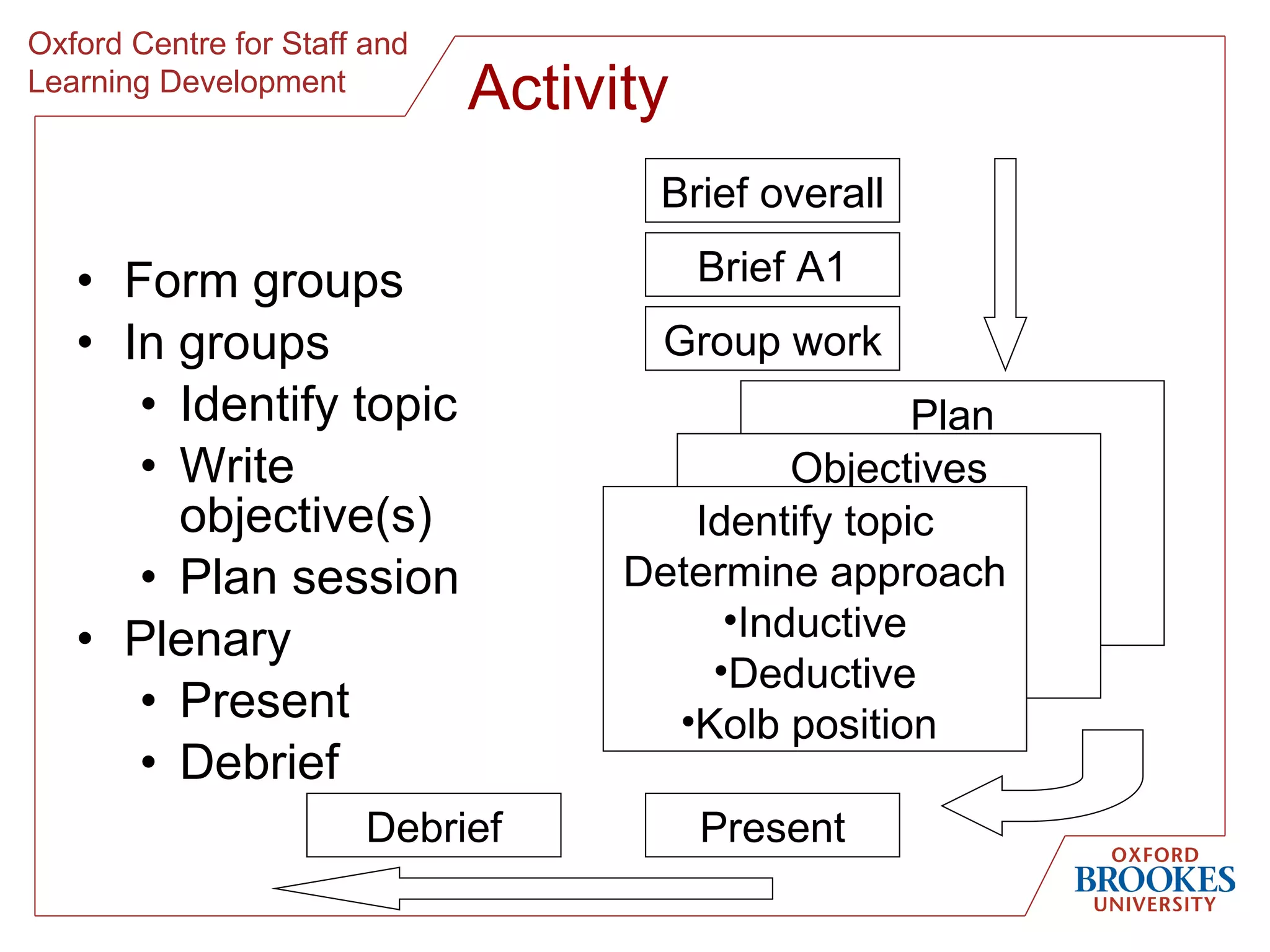
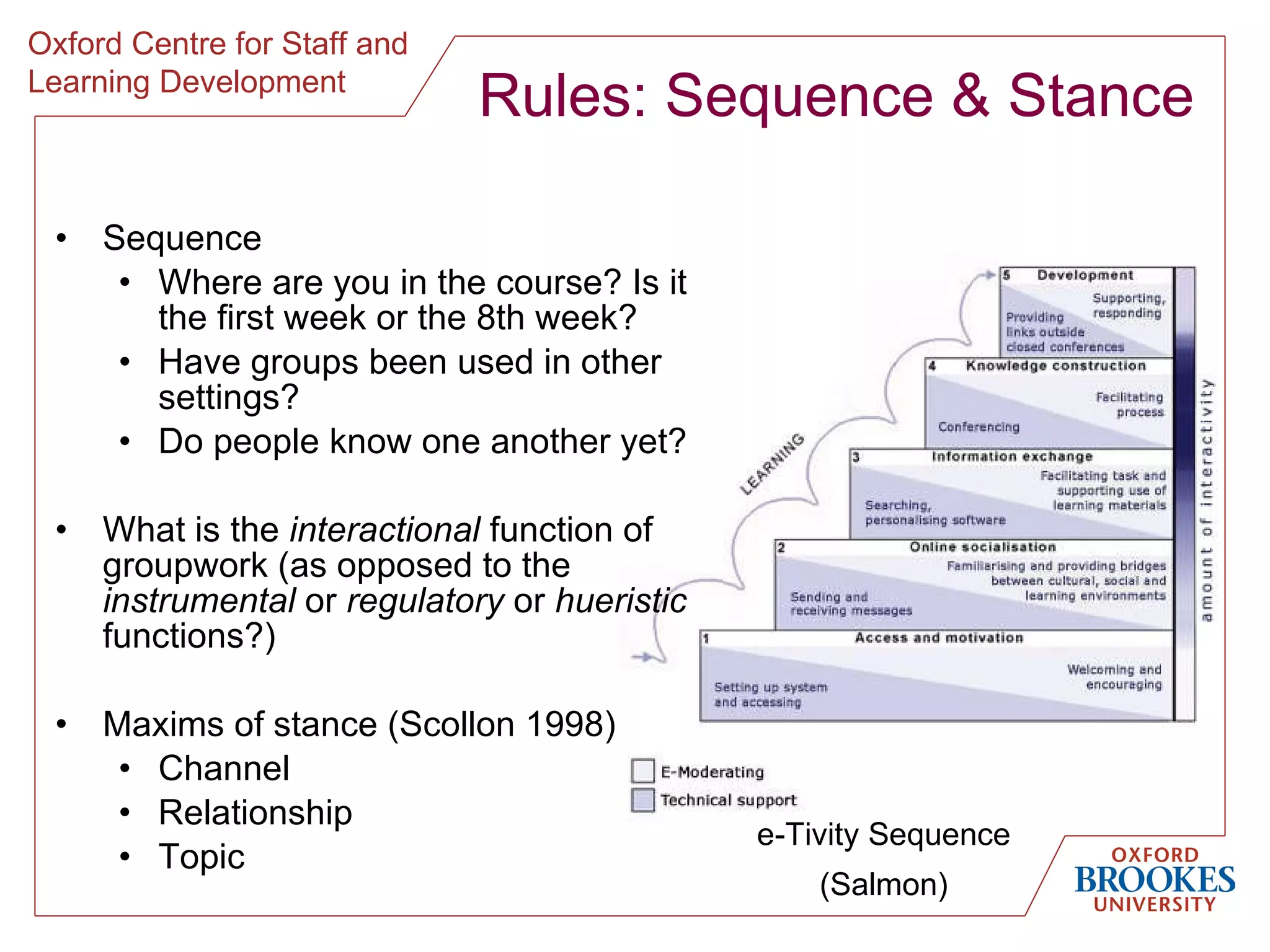
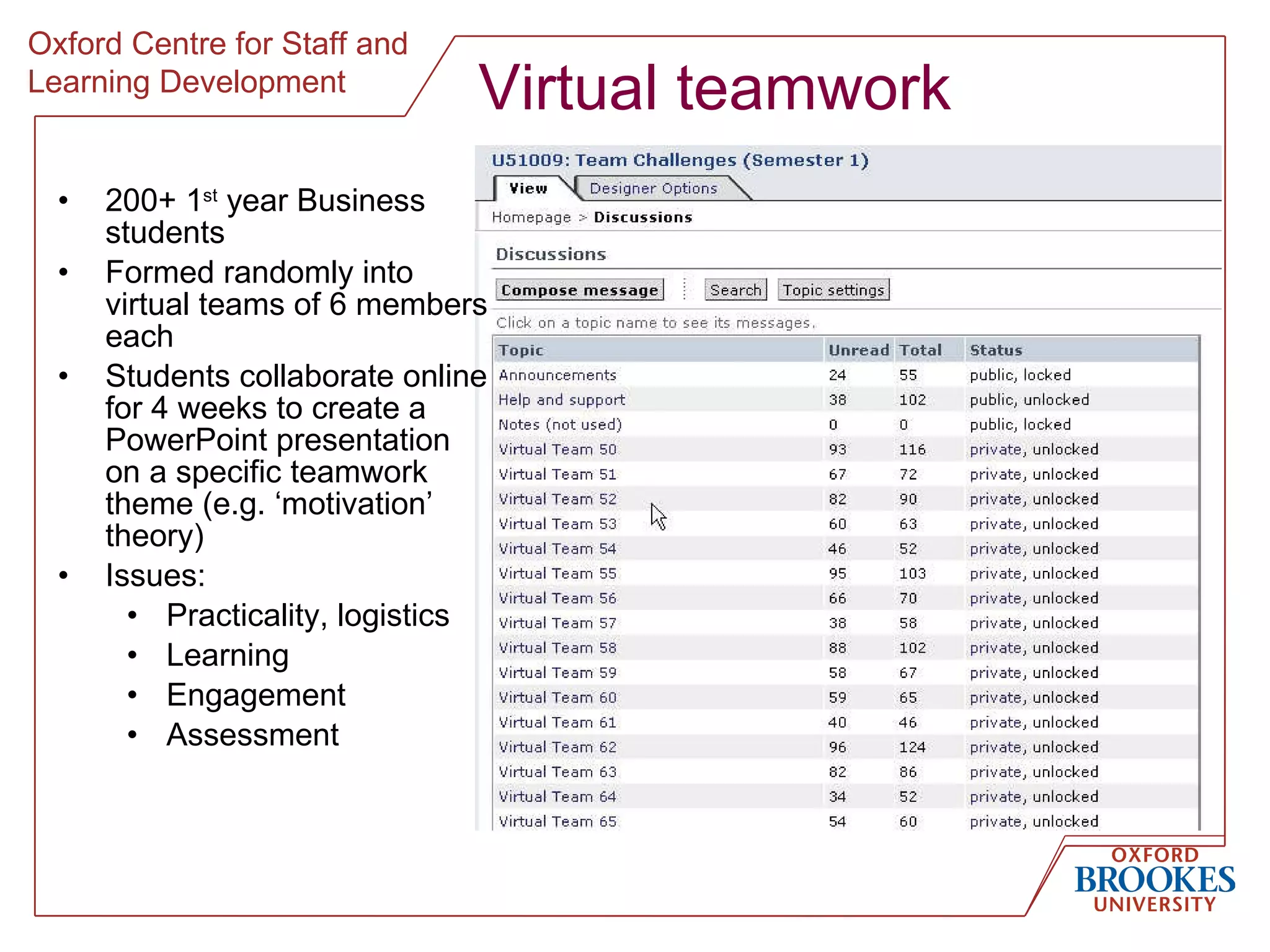
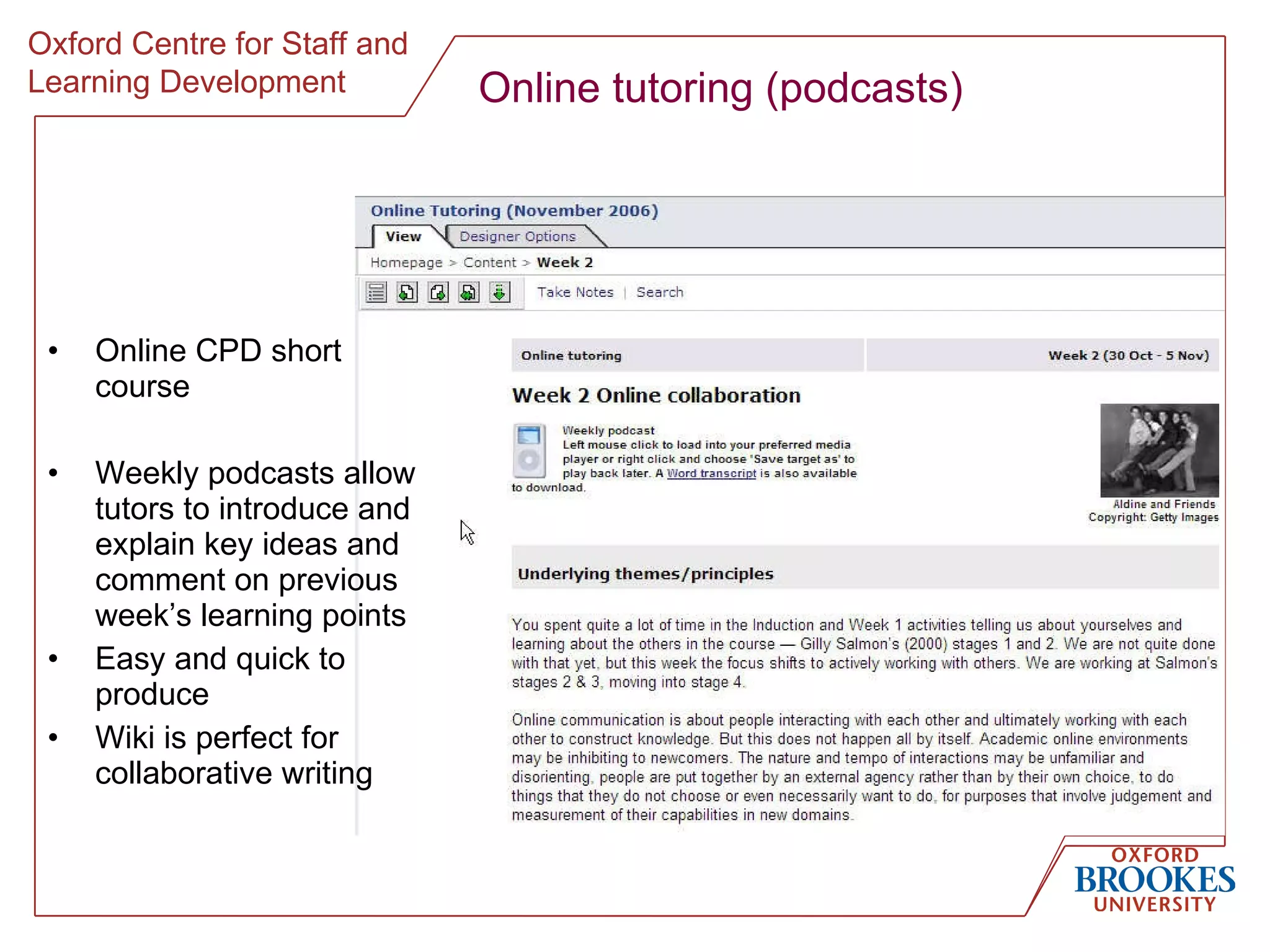
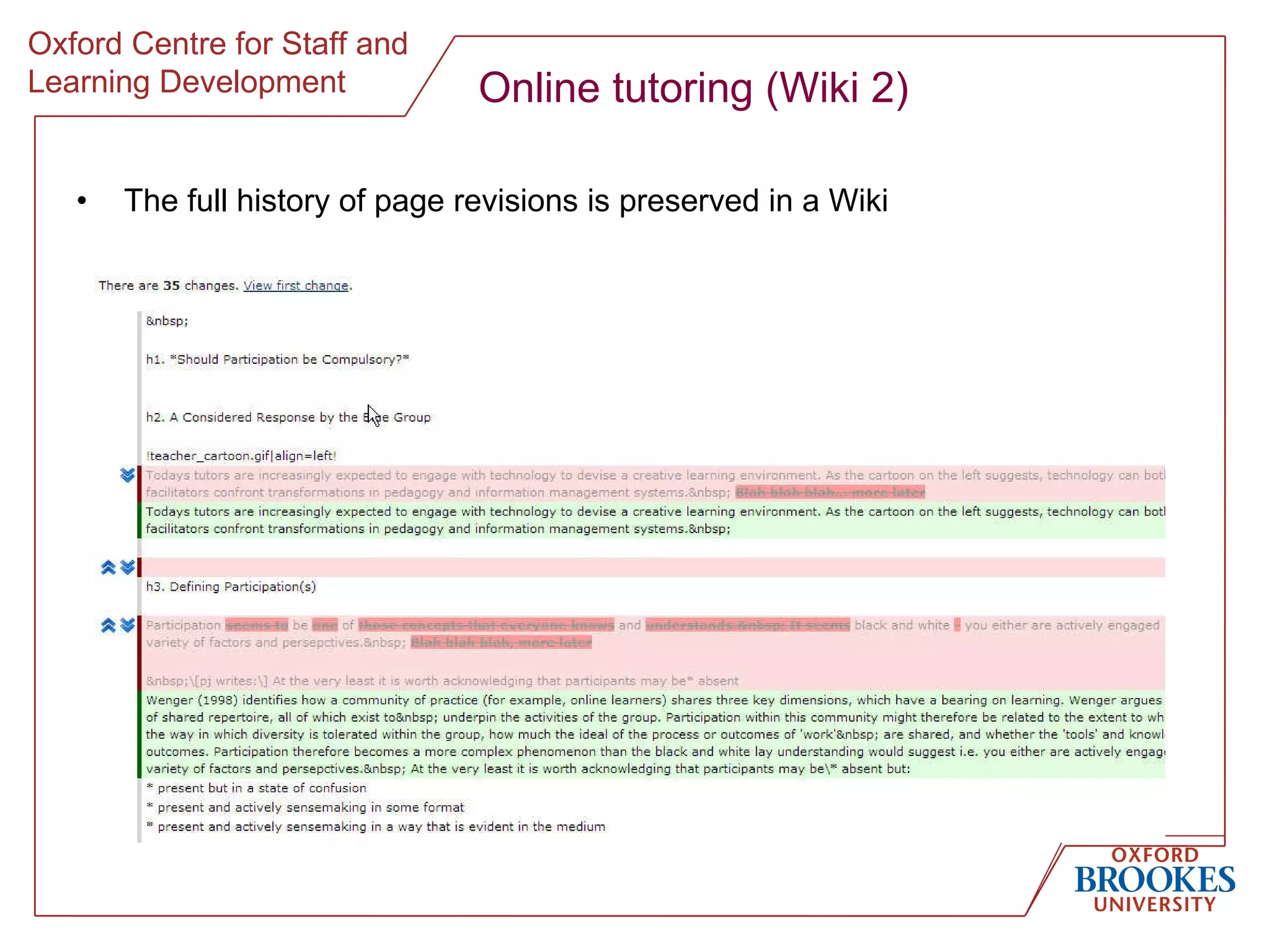
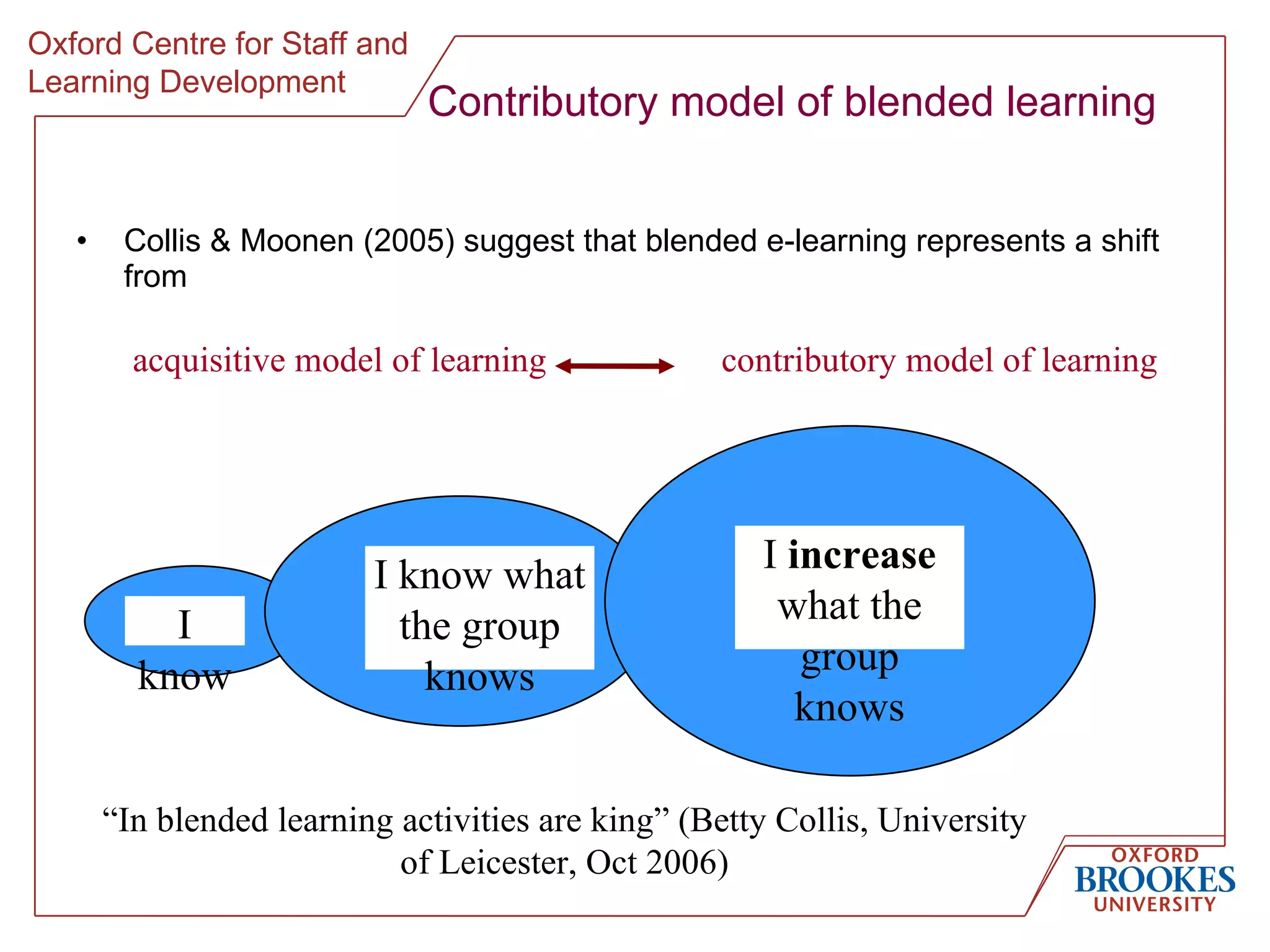
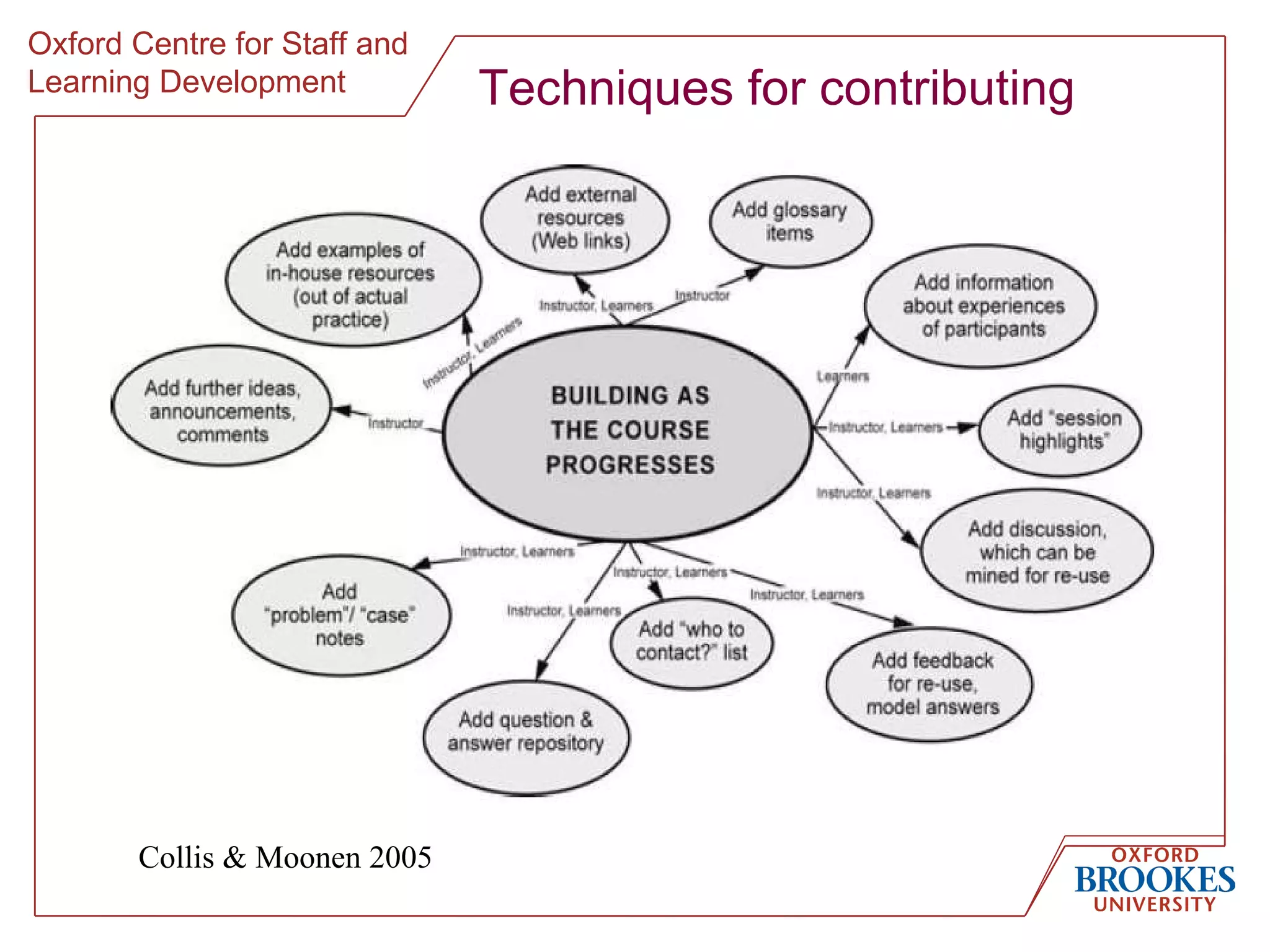
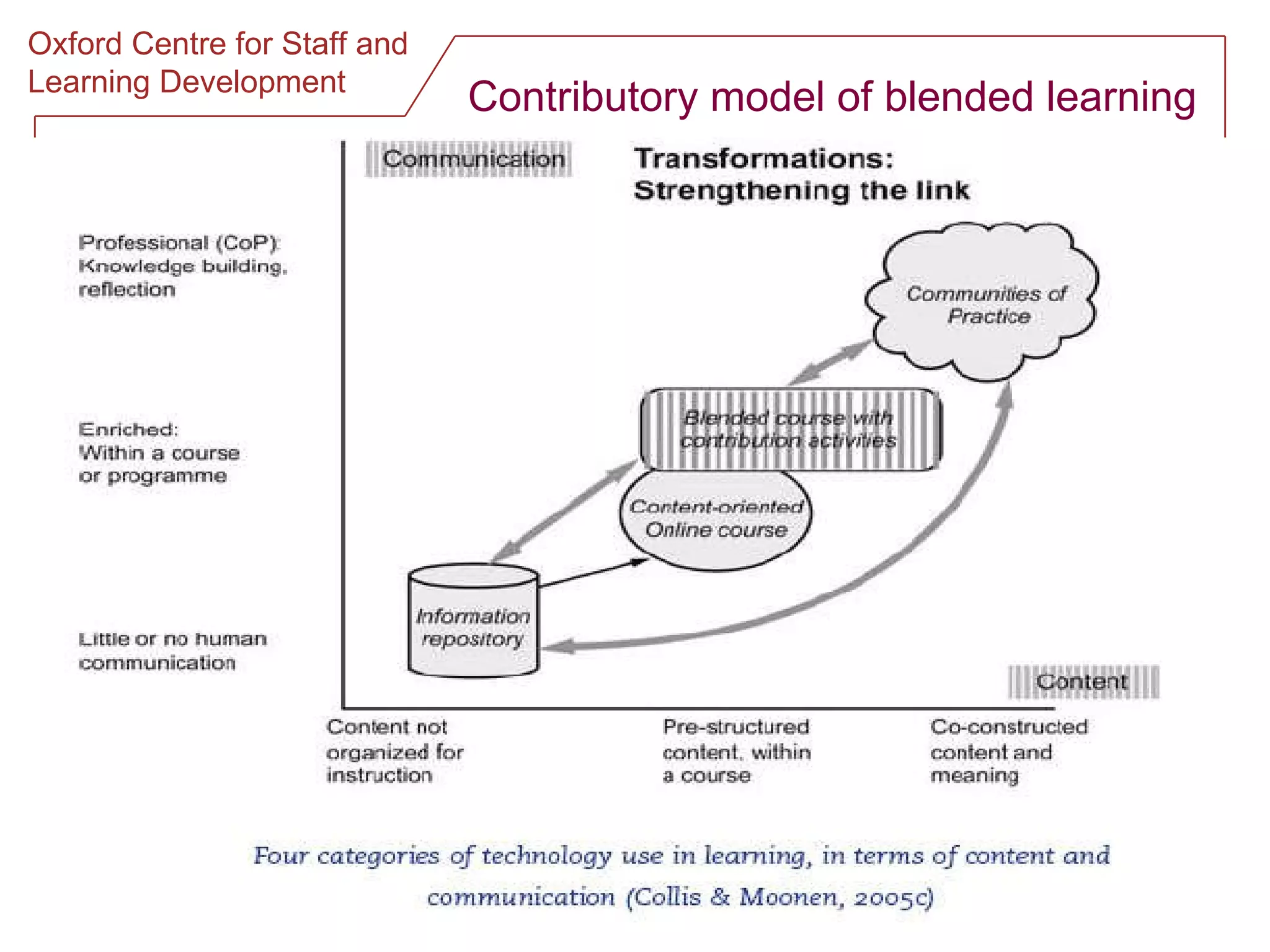
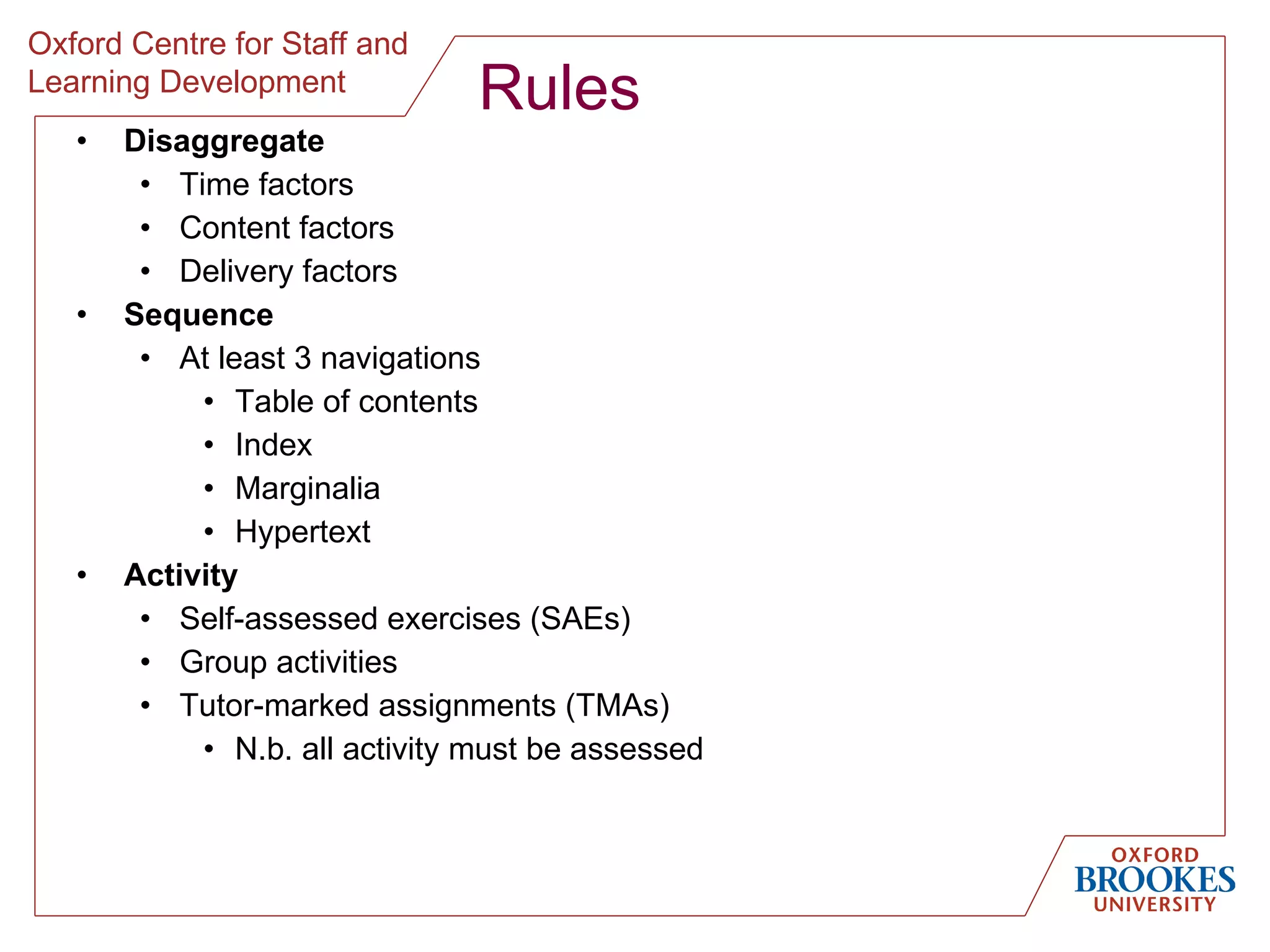
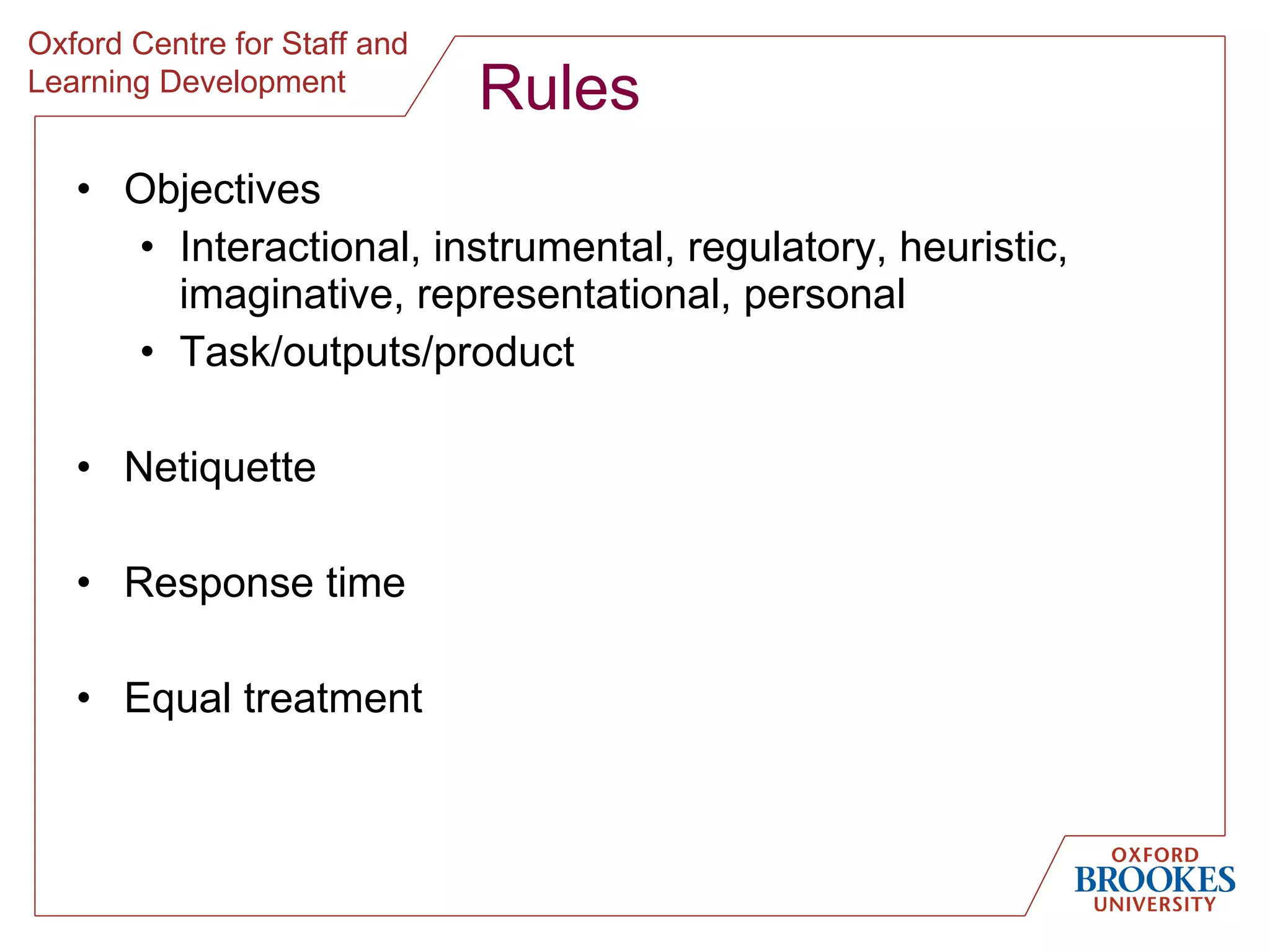
The document discusses designing online group activities and provides guidance on several aspects of distributed collaboration and online group work. It outlines objectives for small group activities, describes roles and issues for moderation. Examples of tools for online collaboration are given along with principles for sequencing activities and establishing an appropriate stance. Guidelines are provided around content, delivery, and assessment of online group work. Participants' experiences with online collaboration and the permanence of online discussions are also summarized.