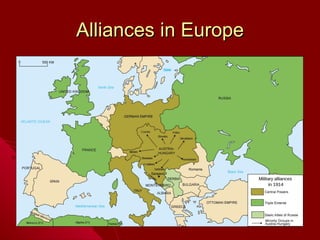
1. The document discusses the alliances and leanings of the United States during World War I, with Americans divided between sympathizing with Britain and Germany due to cultural and ethnic ties.
2. It also outlines the naval blockade imposed by Britain on Germany, Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare campaign, and the sinking of civilian ships like the Lusitania that increased pro-Allied sentiment in the US.
3. Trade relationships shifted greatly during this period, with US trade with the Allies like Britain skyrocketing as the US became an important supplier of munitions and raw materials, while trade with Germany declined sharply.