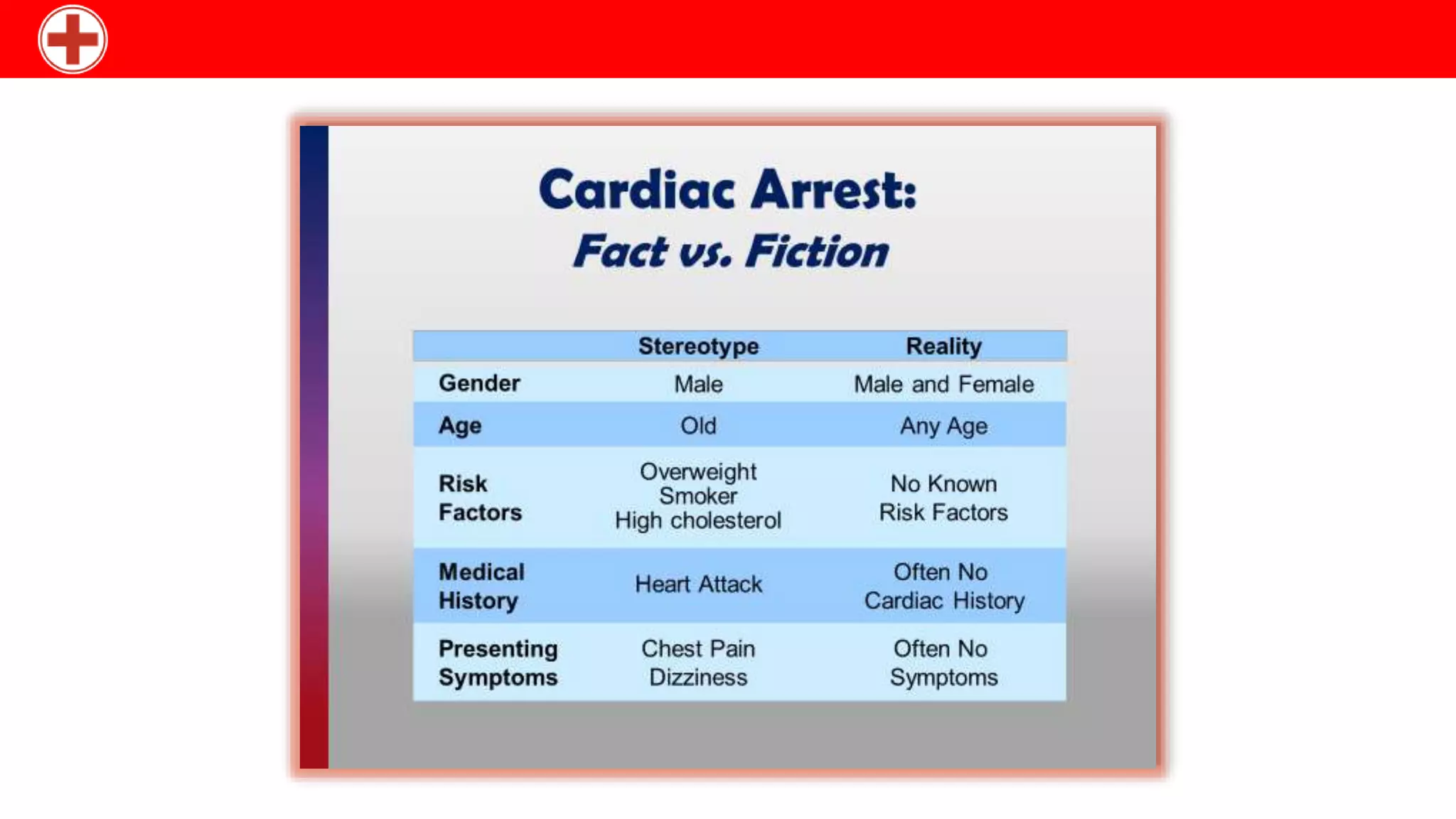
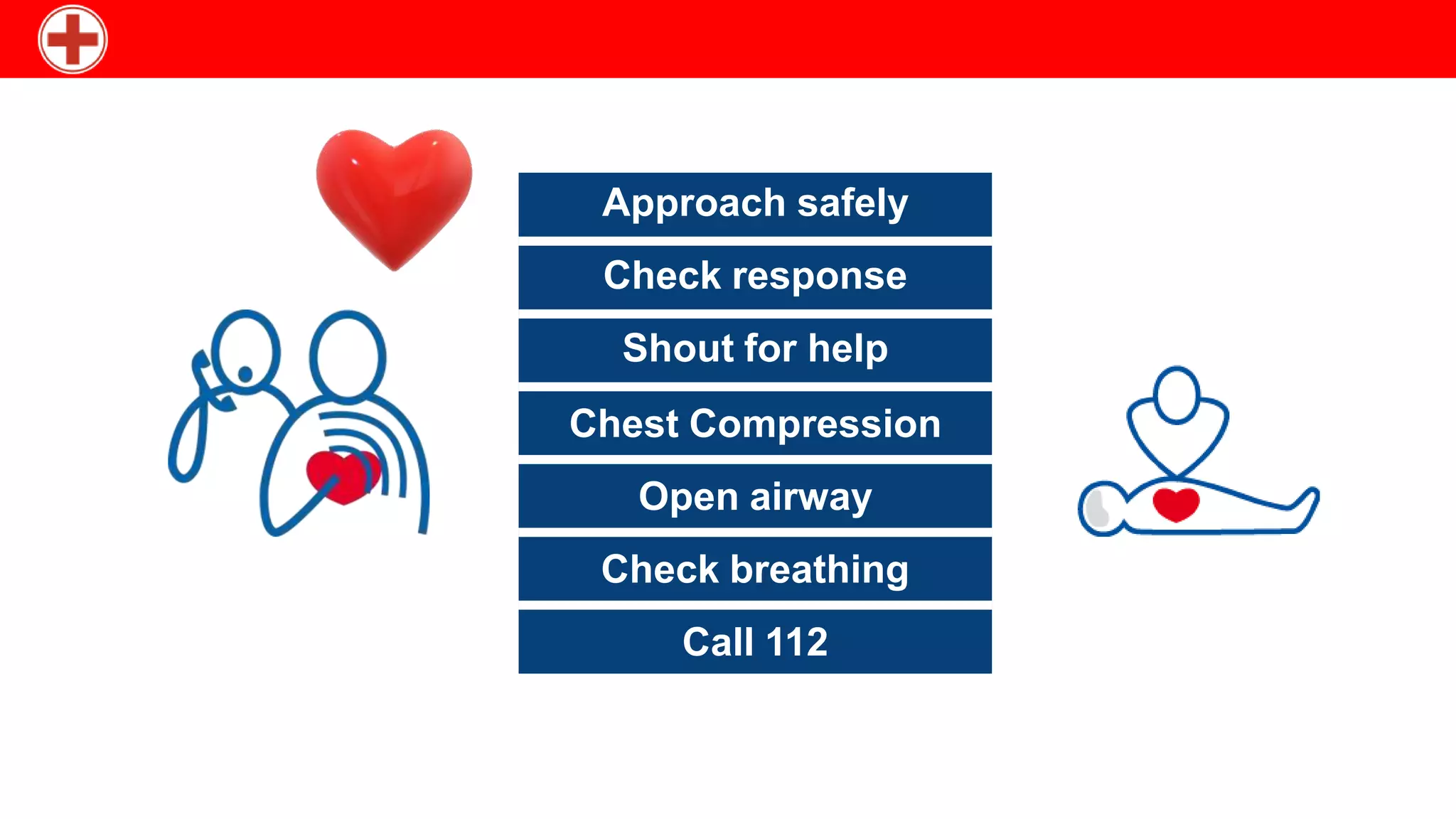
CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to manually pump the heart and provide oxygen to the brain until medical treatment can restore normal heart function. When the heart stops, CPR can buy crucial time by mimicking the heart's pumping action to circulate blood to vital organs. The key steps of CPR are checking for response, calling for help, opening the airway, checking breathing, performing chest compressions at 100 per minute with a depth of 4-5cm, and providing two rescue breaths before resuming compressions. Drugs like adrenaline, atropine, and amiodarone may also be used during resuscitation attempts to treat cardiac arrest.