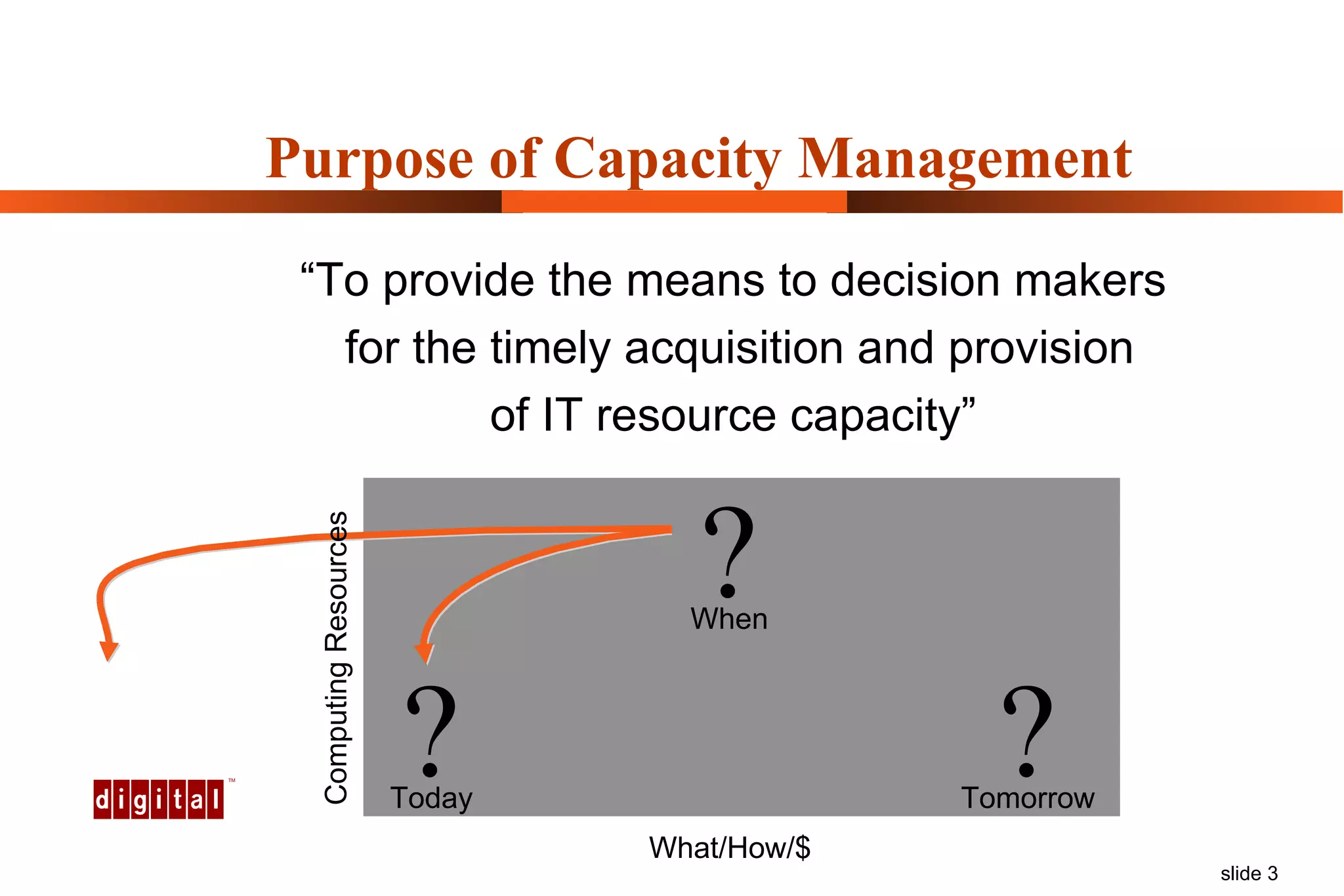
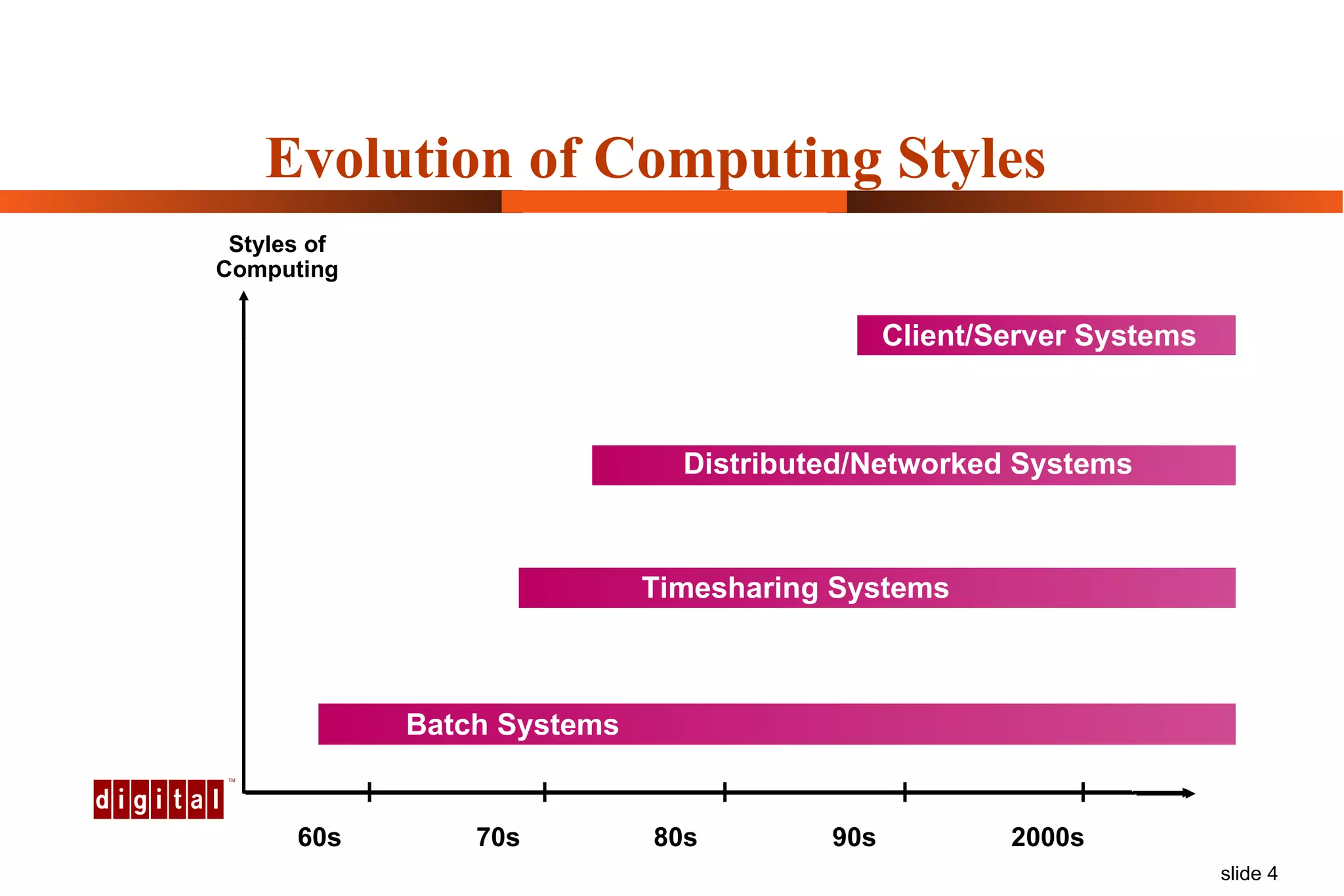
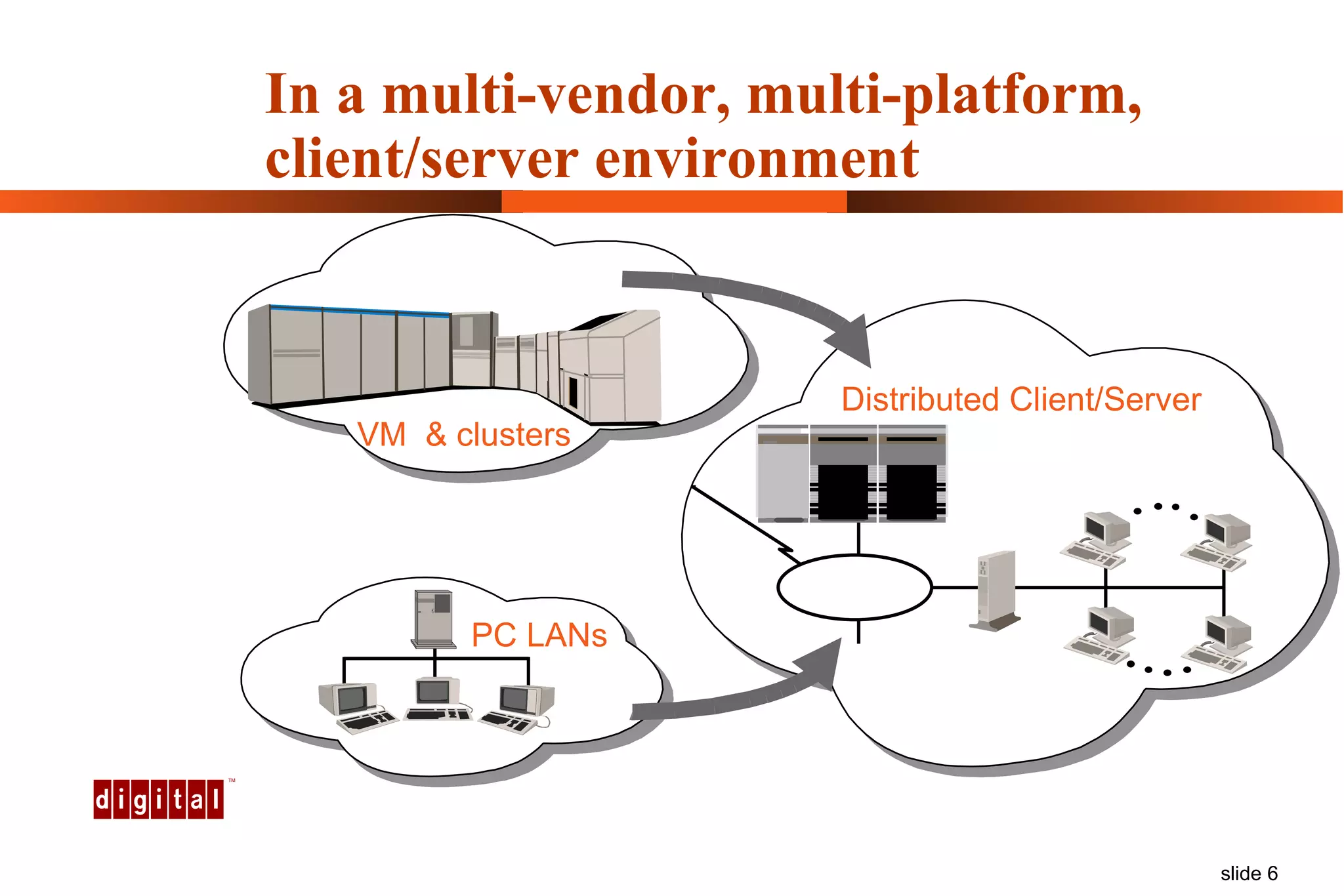
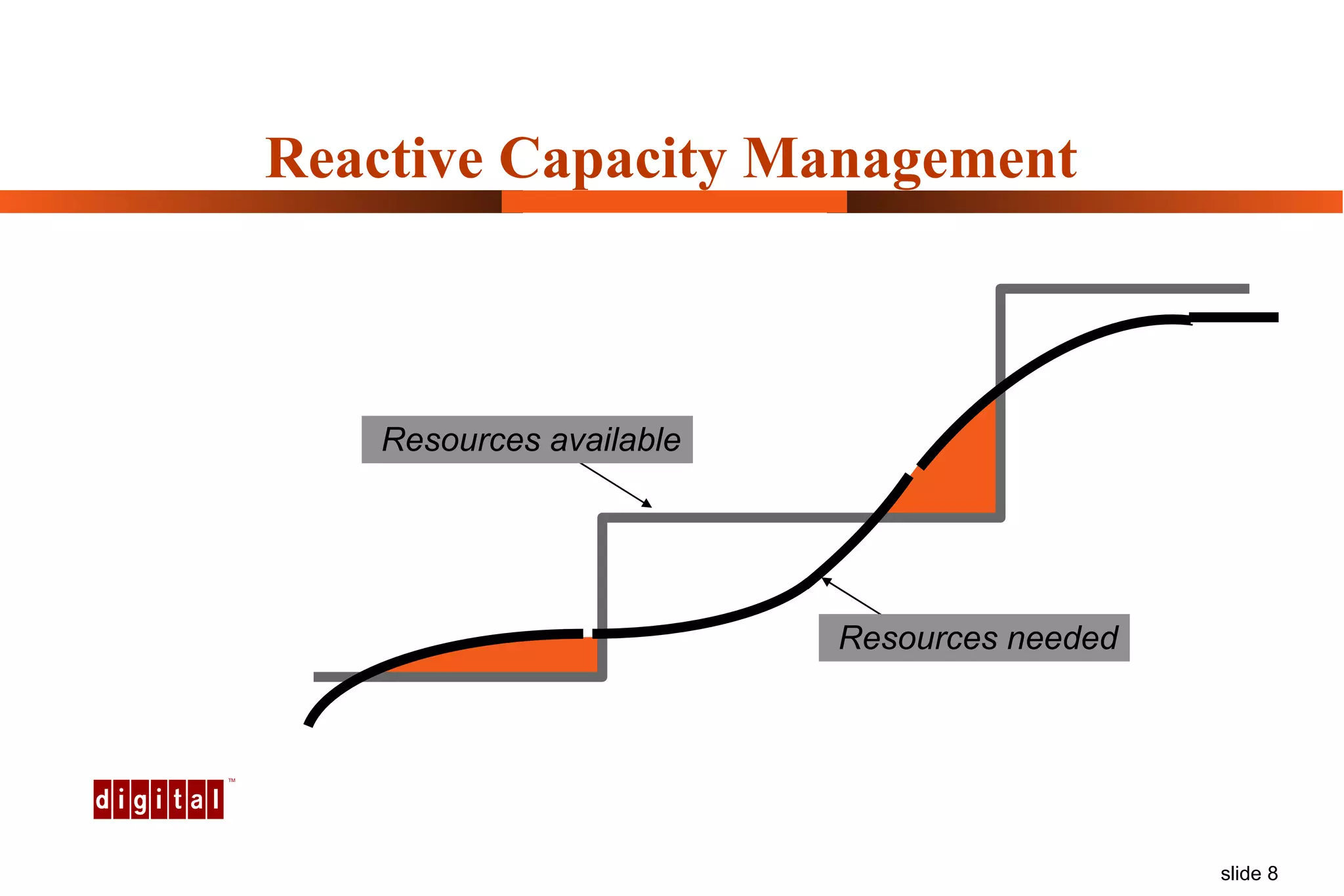
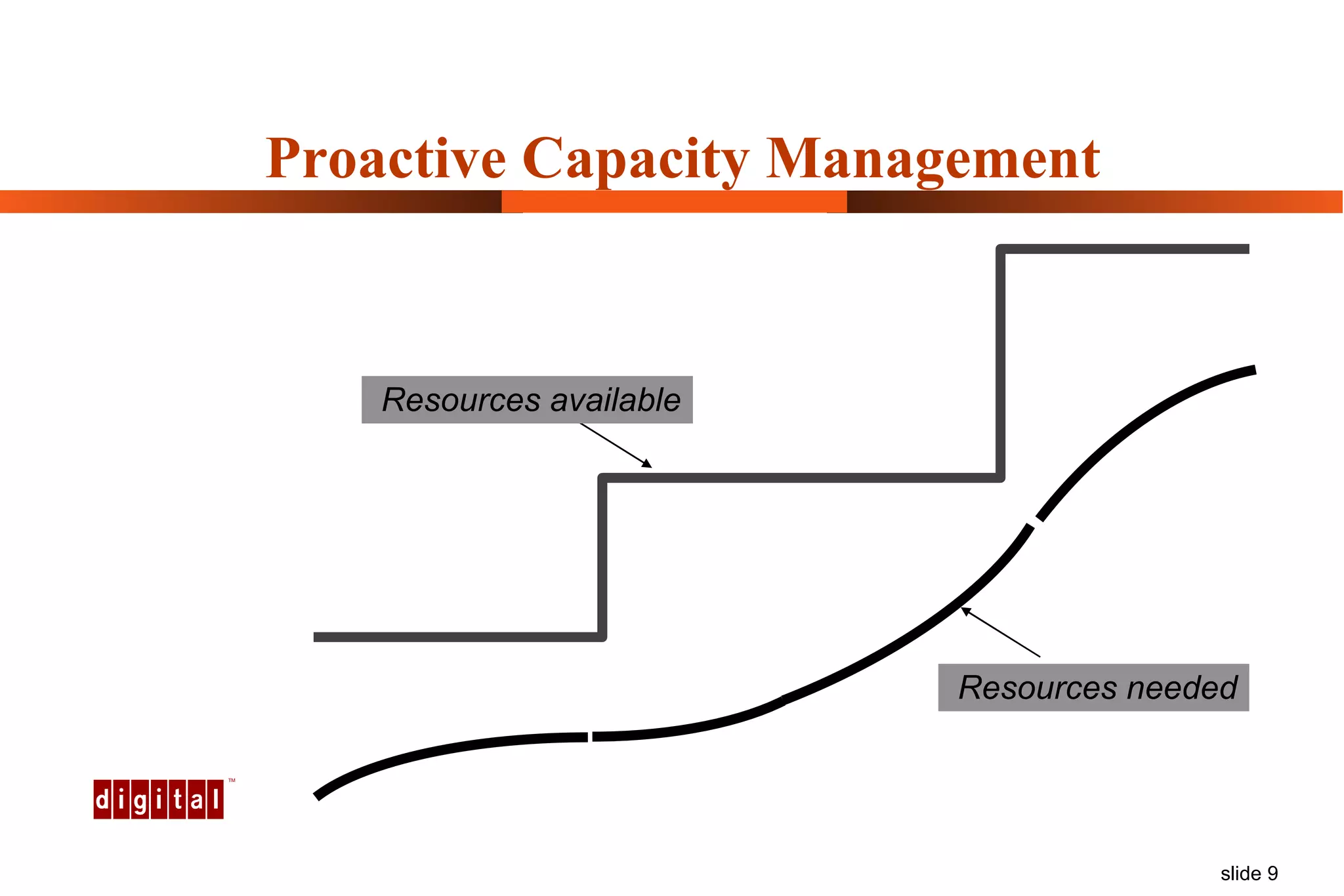
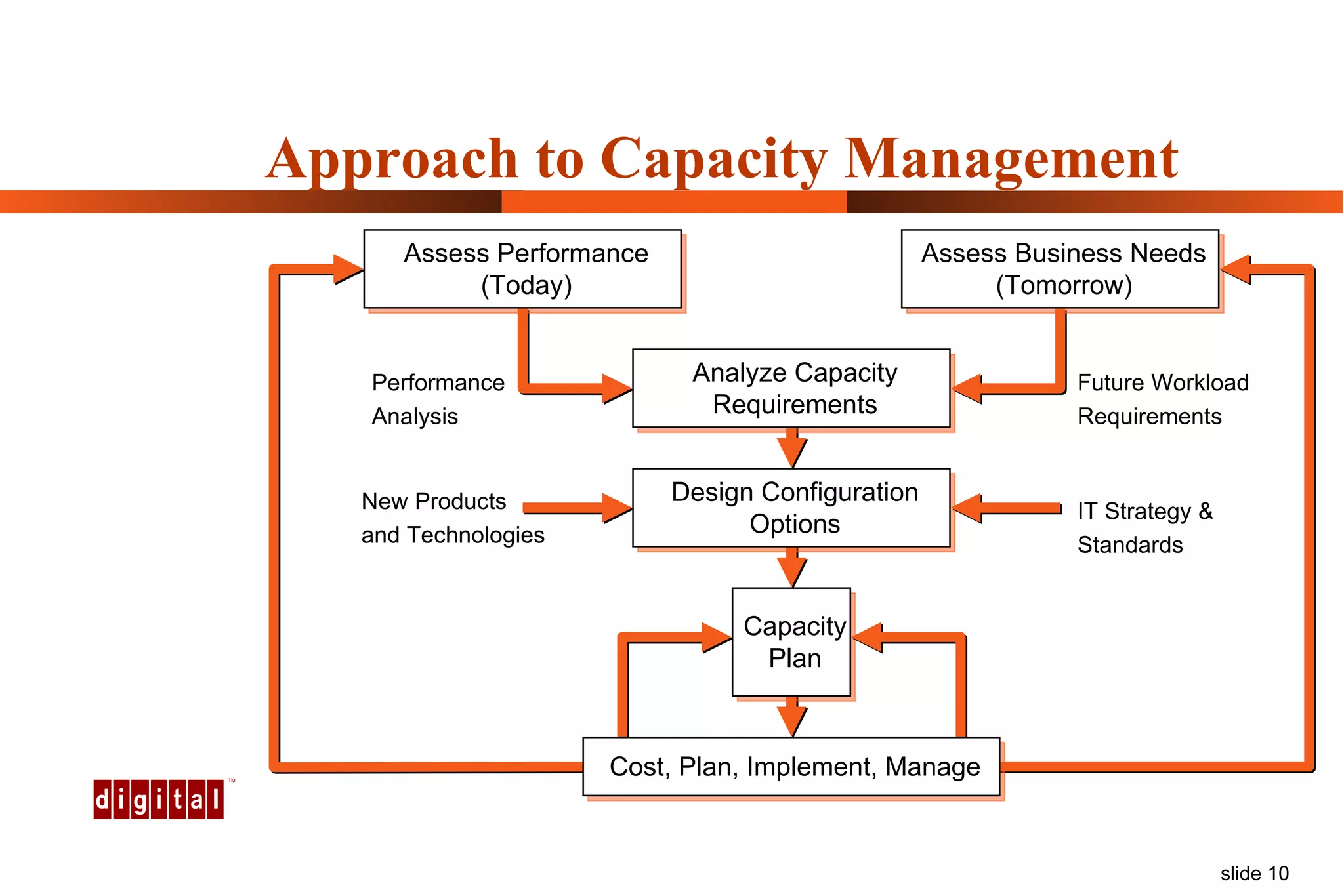
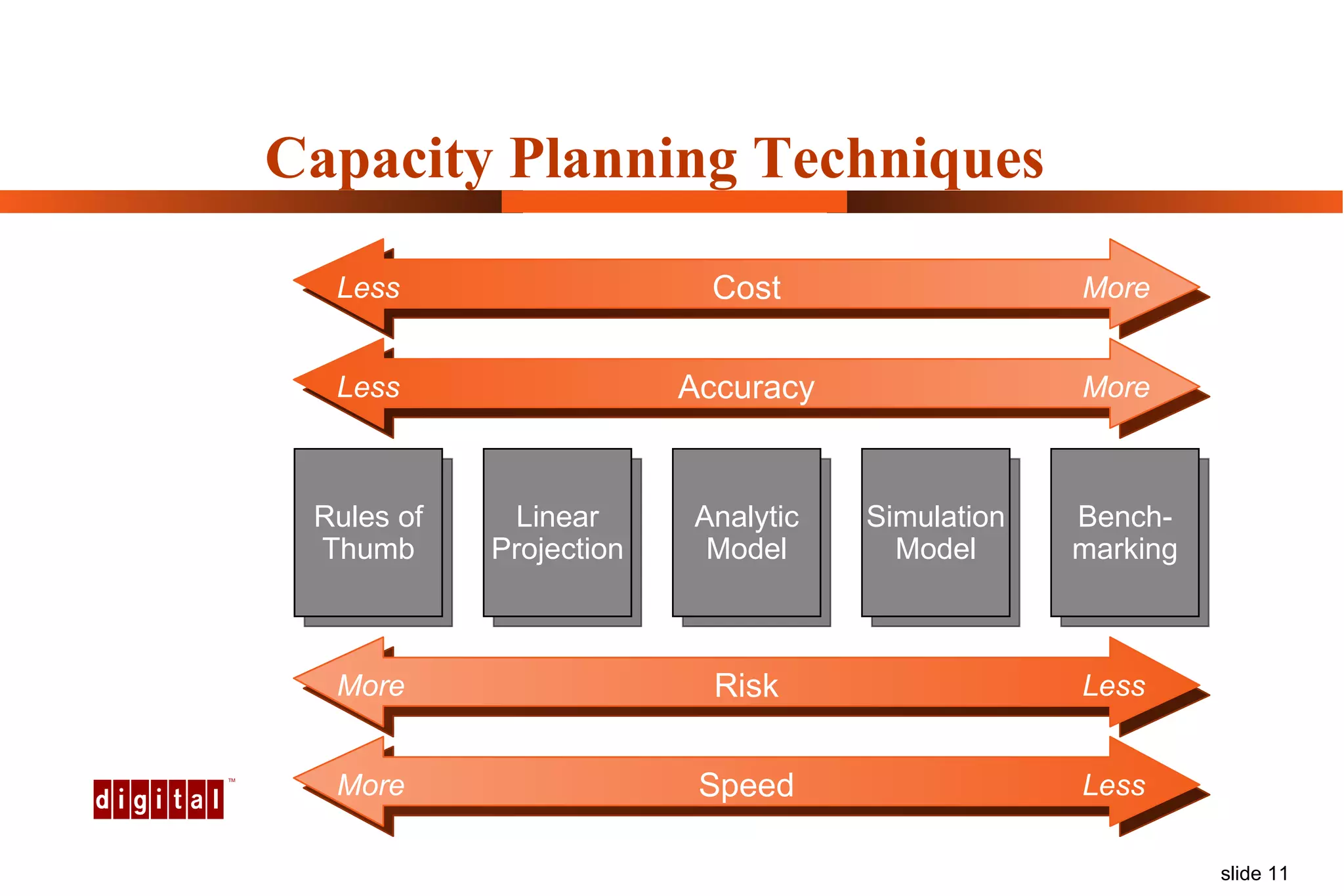
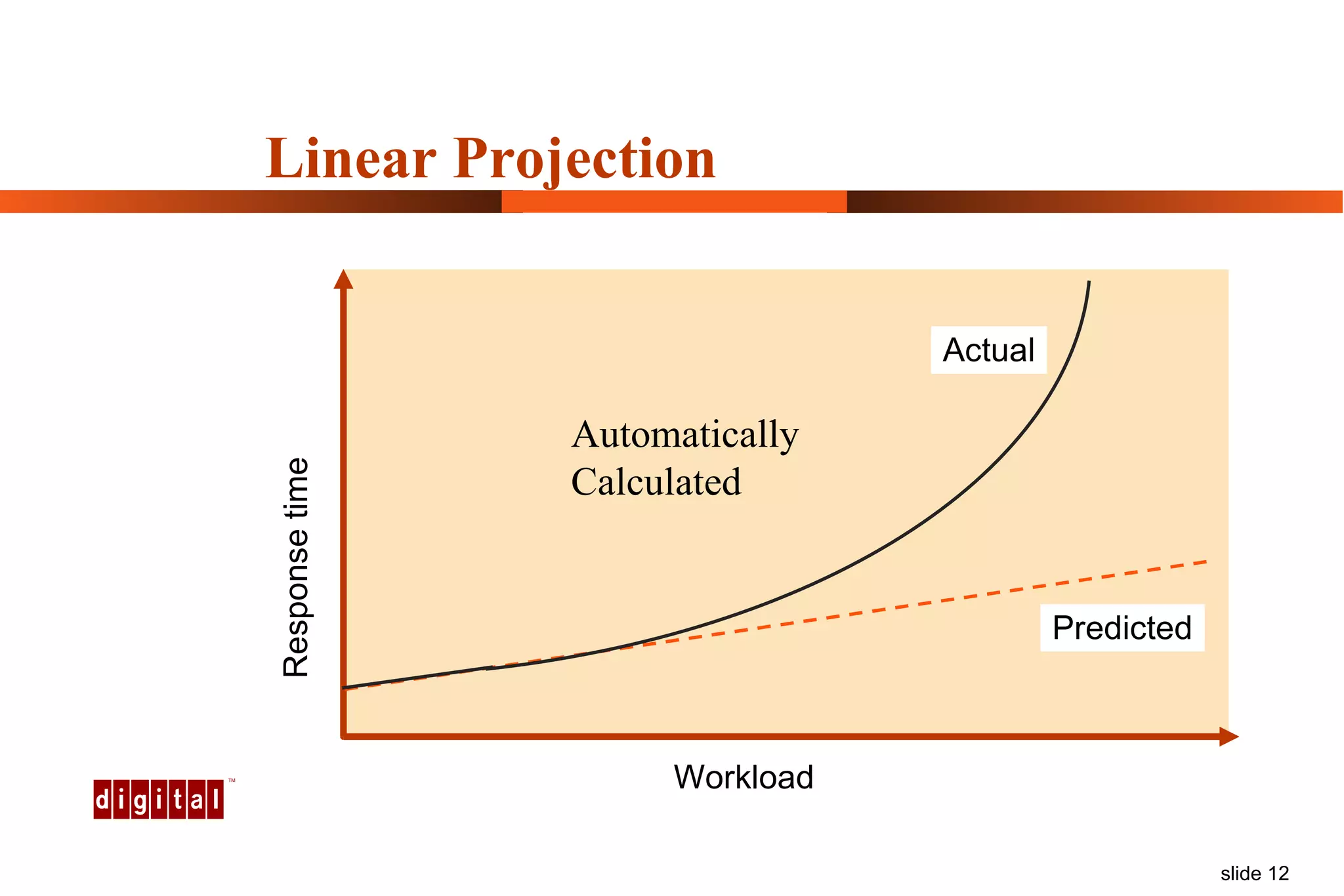
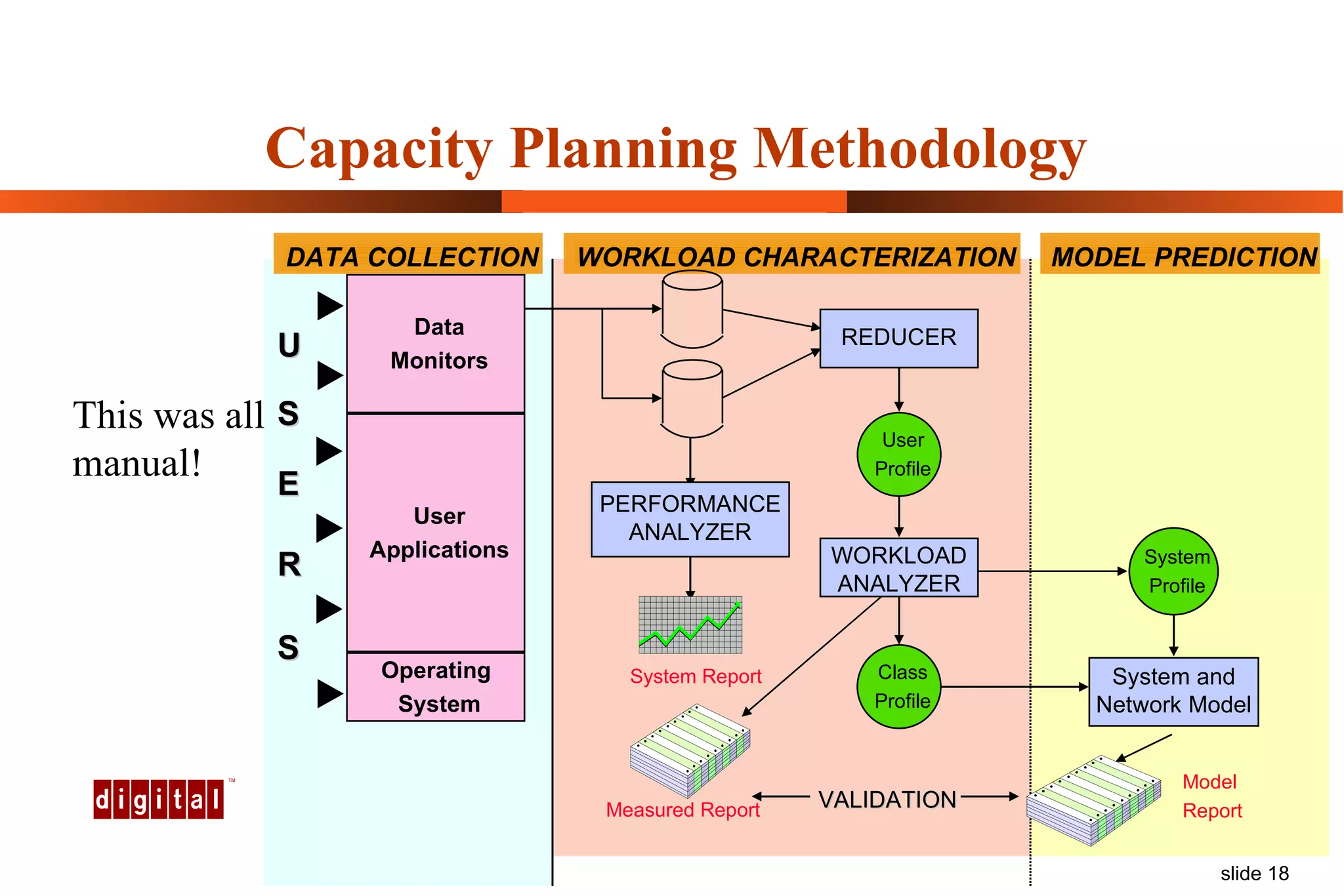
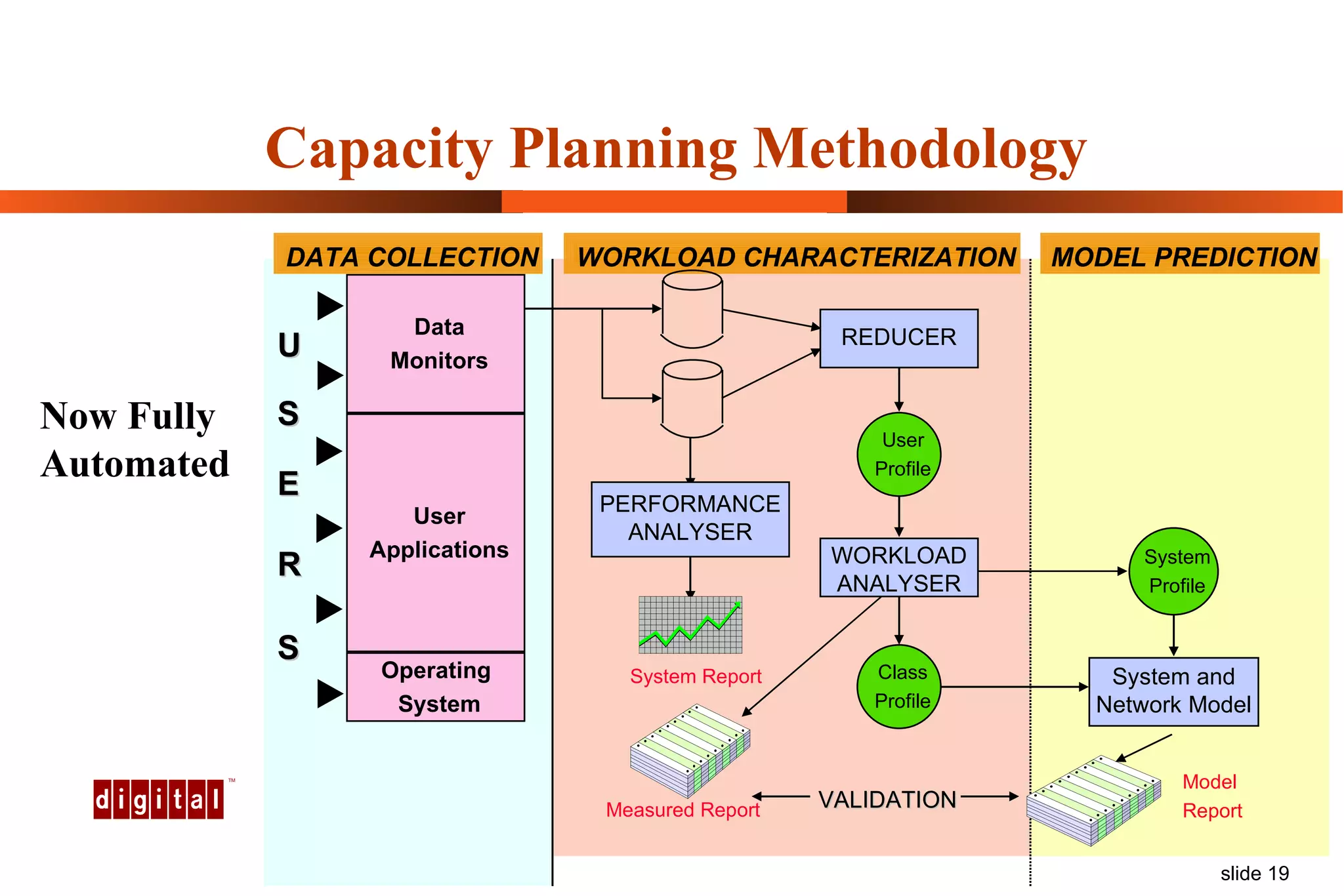
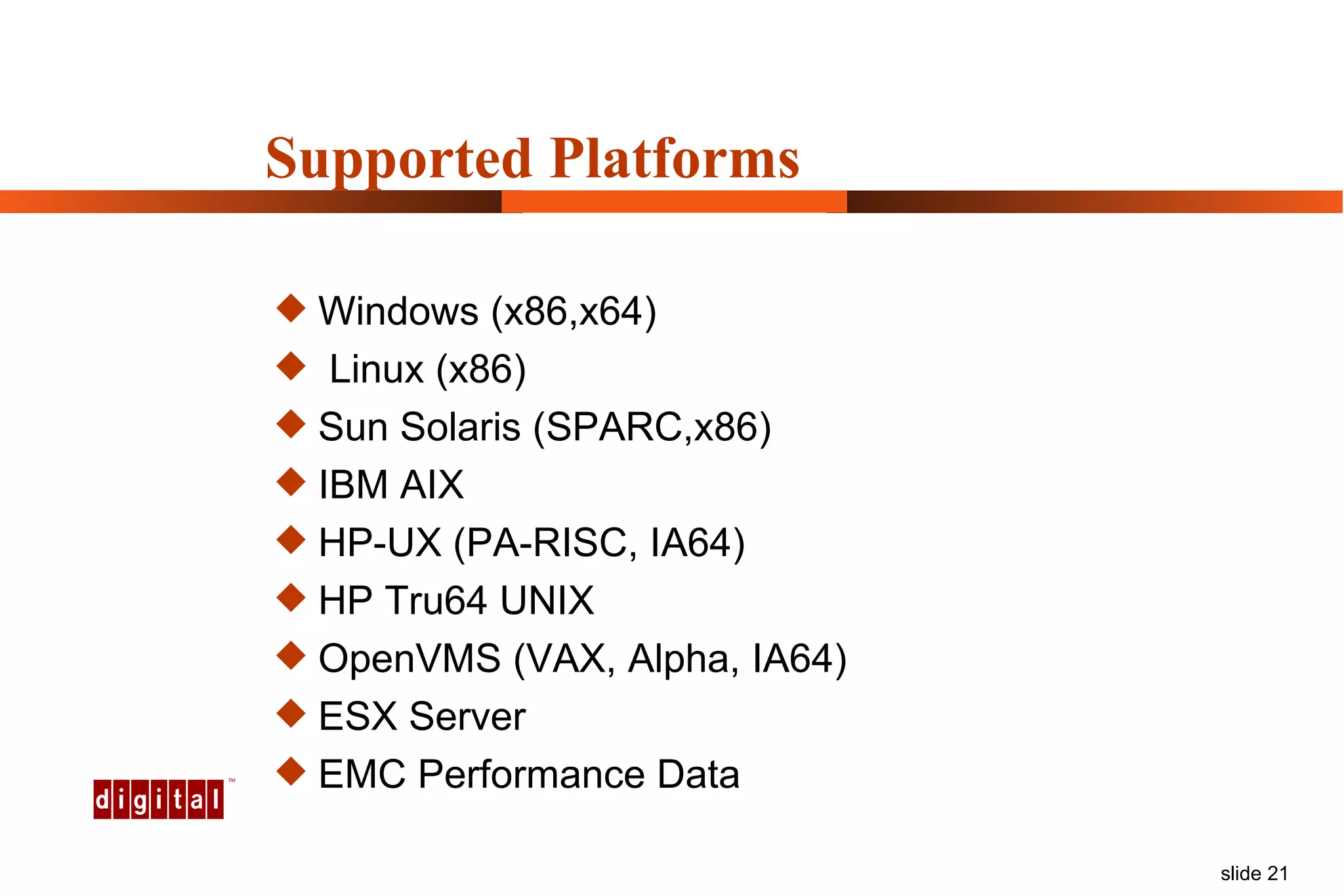
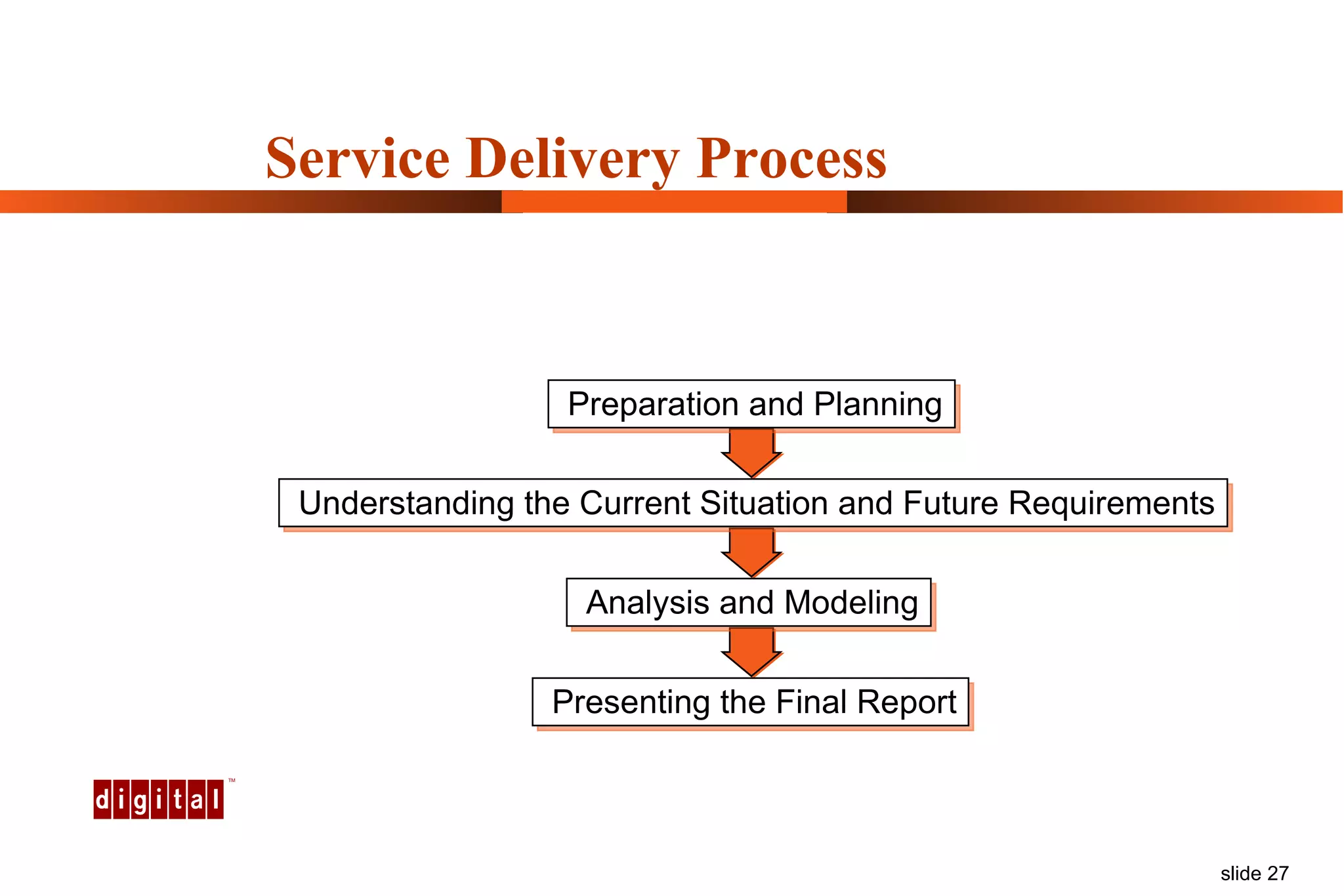
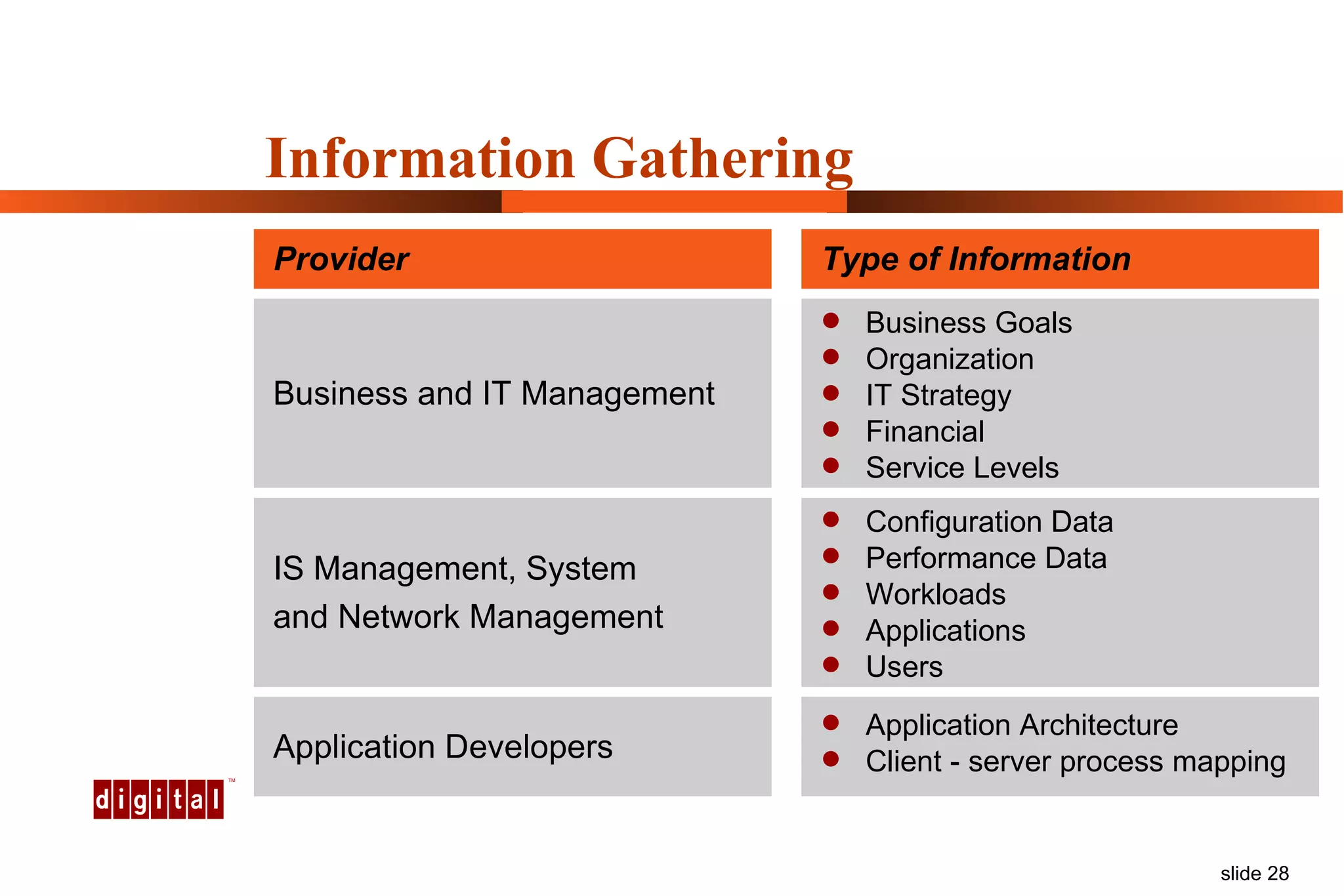
Capacity management involves planning IT capacity to support business needs. It aims to provide decision-makers with tools to timely acquire and provision IT resources. Key challenges include regaining control of infrastructure, matching IT investments to business needs, and maintaining service levels during changes. Capacity management approaches include reactive, responding to current needs, and proactive planning using tools to analyze current performance, future workloads, and IT strategies to develop capacity plans.