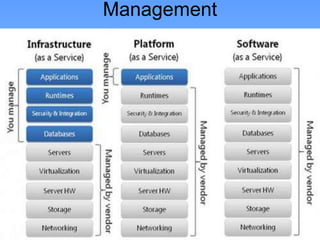
This document provides an overview of Software as a Service (SaaS) and Database as a Service (DBaaS). It defines SaaS as software deployed 100% over the internet, and notes it is the application layer of the cloud computing model. DBaaS delivers database functionality as a service internally or externally. SaaS offers advantages like access to unlimited resources paid for only as needed, decreasing costs, and increased vendor control. The document also discusses SaaS testing and security testing considerations.