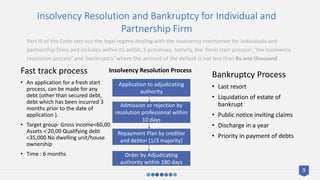
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 was introduced to consolidate existing insolvency laws in India, providing a structured framework for the resolution and liquidation processes for both corporate and non-corporate entities. It establishes the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India as the regulator and outlines processes for voluntary liquidation, fast track insolvency, and individual insolvency, aimed at early detection of financial failure and maximizing asset value. The code seeks to enhance the ease of doing business in India and improve the efficiency of debt recovery rates to revitalize the credit markets.