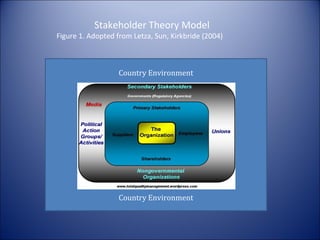
This document discusses corporate governance best practices and identifies areas for improvement. It begins with definitions of corporate governance and examines the role of businesses and stakeholders. Trends in corporate governance are outlined, including increasing transparency and accountability. The document identifies potential red flags, such as compromised board independence, and recommends best practices for boards to increase their effectiveness. These include ensuring diversity, director independence, and competency. Other topics covered include strategic planning, risk management, social media governance, and performance evaluation. The document concludes that corporate governance is an ongoing process that should focus on strategy, compliance, and creating sustainable shareholder value.