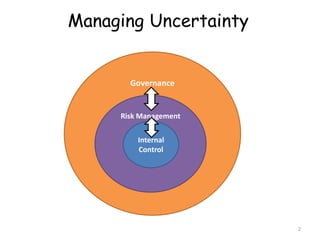
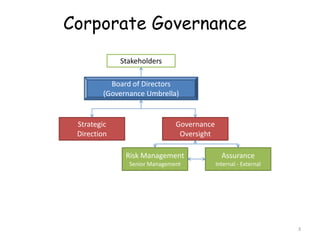
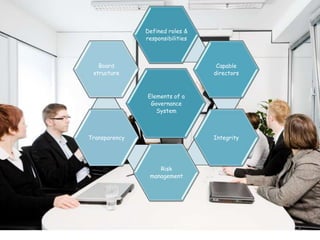
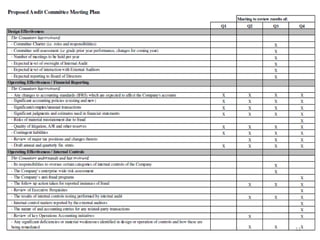
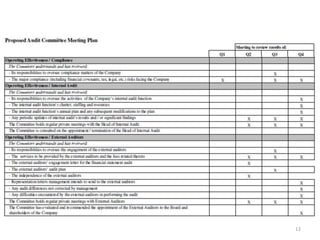
The document discusses corporate governance best practices. It provides an overview of governance structures and principles such as the roles of the board of directors and senior management in oversight, risk management, and internal controls. It also outlines common challenges for boards, governance pitfalls to avoid, and recommendations for establishing strong governance policies and practices in areas like transparency, accountability, and compliance. Sample agenda topics are given for both audit committee and board meetings.