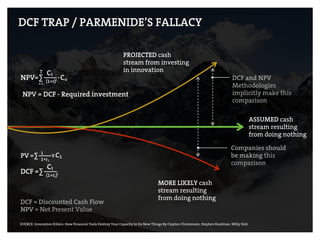
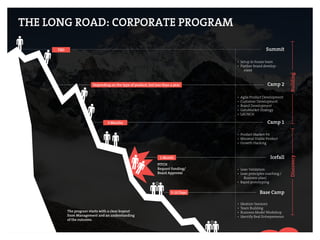
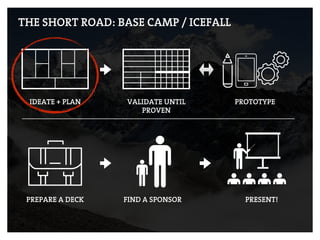
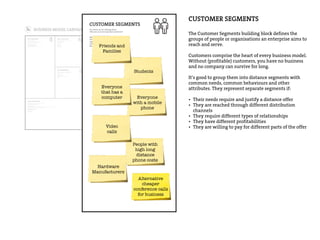
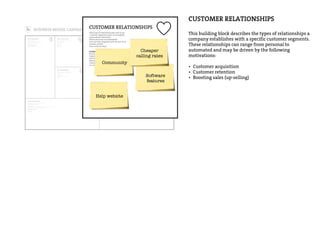
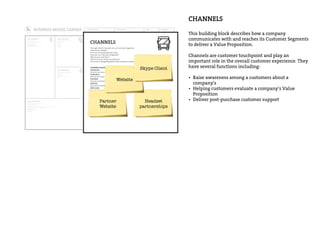
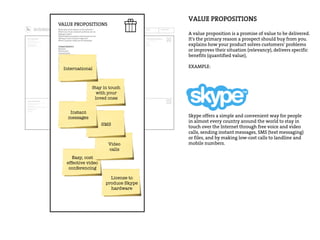
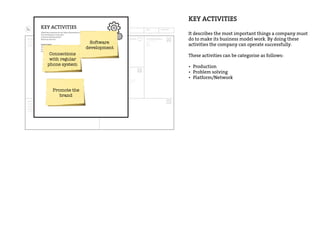
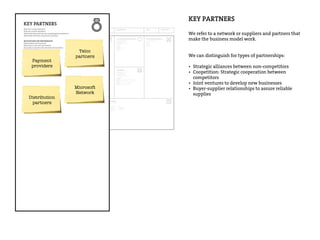
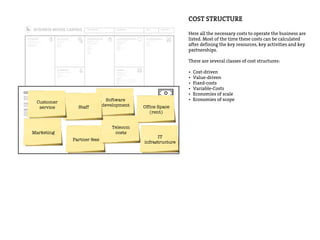
This document provides an agenda for a business design workshop. It includes introductions and hashtags for participants, an overview of corporate entrepreneurship and the business model canvas tool. The agenda covers introducing the business model canvas, forming groups to work on ideas using the canvas, and having group presentations. It encourages participants to think about opportunities as corporate entrepreneurs and provides facts about gender diversity in corporate leadership.