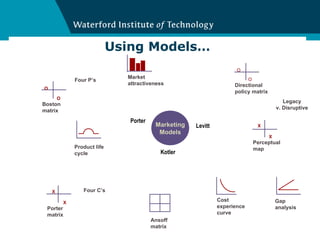
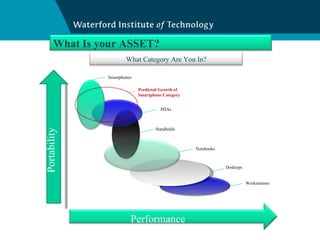
This document discusses challenging existing business models and designing new ones. It outlines four key things that matter for a successful business: 1) having a big market opportunity, 2) a defendable differentiated position, 3) a winning execution plan, and 4) sustainable profitability. The document provides several templates and frameworks to help analyze customers, competitors, routes to market, and financial projections to design an effective business model.
![Challenging your Business Model BizCamp Southeast June 12, 2010 Eugene Crehan Director of Programmes - CEDRE School of Business Waterford Institute of Technology [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bizcampse-eugenecrehan-100614091205-phpapp02/75/Eugene-Crehan-Understanding-Your-Business-Model-1-2048.jpg)


















![Good Luck & Thank you Eugene Crehan Director of Programmes Centre for Enterprise Development & Regional Economy School of Business Waterford Institute of Technology [email_address] www.seepp.ie Twitter & LinkedIn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bizcampse-eugenecrehan-100614091205-phpapp02/85/Eugene-Crehan-Understanding-Your-Business-Model-25-320.jpg)