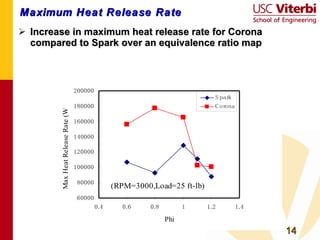
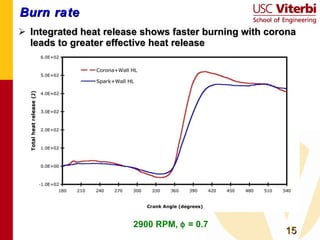
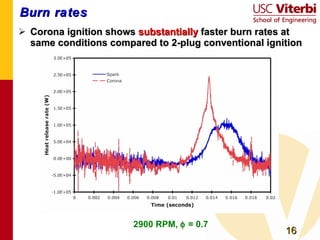
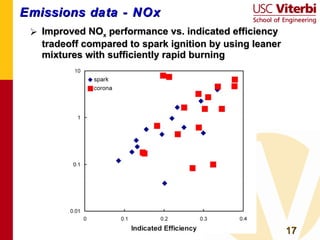
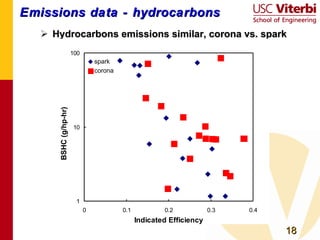
Transient plasma discharge ignition was tested as an alternative to spark ignition for internal combustion engines. On-engine experiments showed that transient plasma discharge ignition increased peak pressure, indicated mean effective pressure, and burn rates compared to spark ignition, especially for lean mixtures. It also decreased heat release times. Emissions of NOx, hydrocarbons, and CO were similar between the two ignition methods. Transient plasma discharge ignition shows potential for improving engine performance through enabling leaner, lower turbulence combustion with similar or reduced emissions. Future work includes improved electrode designs, multi-cylinder testing, and exploring applications to low turbulence engine designs.