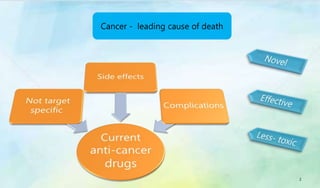
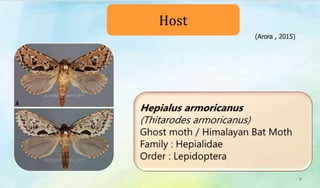
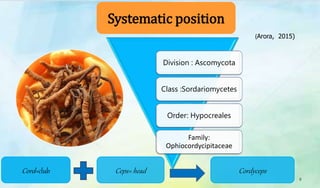
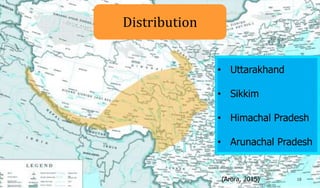
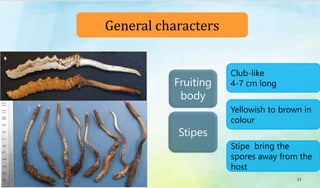
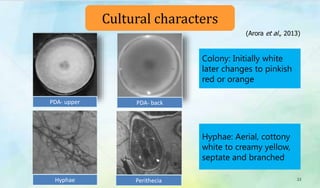
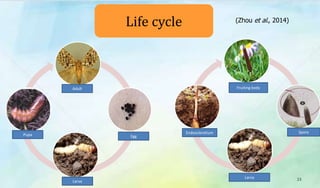
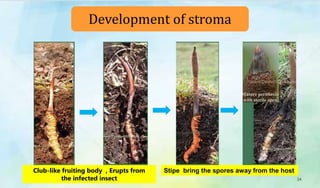
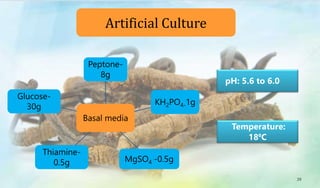
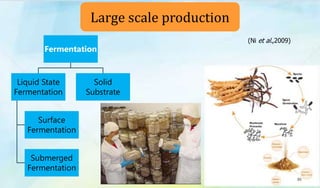
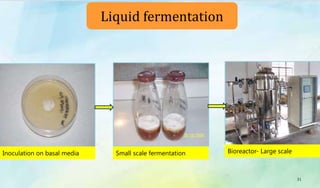
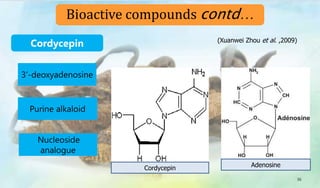
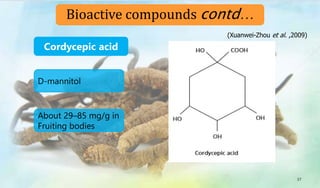
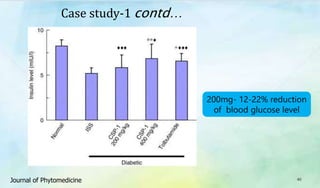
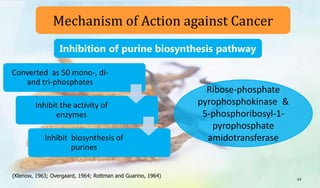
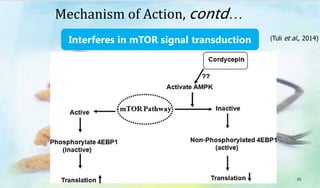
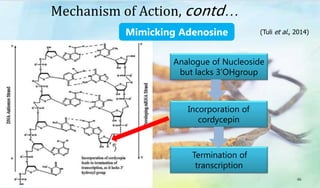
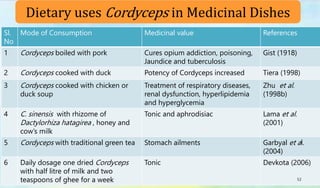
The document discusses Ophiocordyceps sinensis, a highly valued medicinal fungus known for its health benefits, including anti-cancer, anti-aging, and hypoglycemic properties. It covers its history, biological characteristics, cultivation methods, nutritional factors, and mechanisms of action, emphasizing its importance in traditional Chinese medicine and potential commercial applications. Future research directions include exploring its medicinal properties and optimizing production methods.