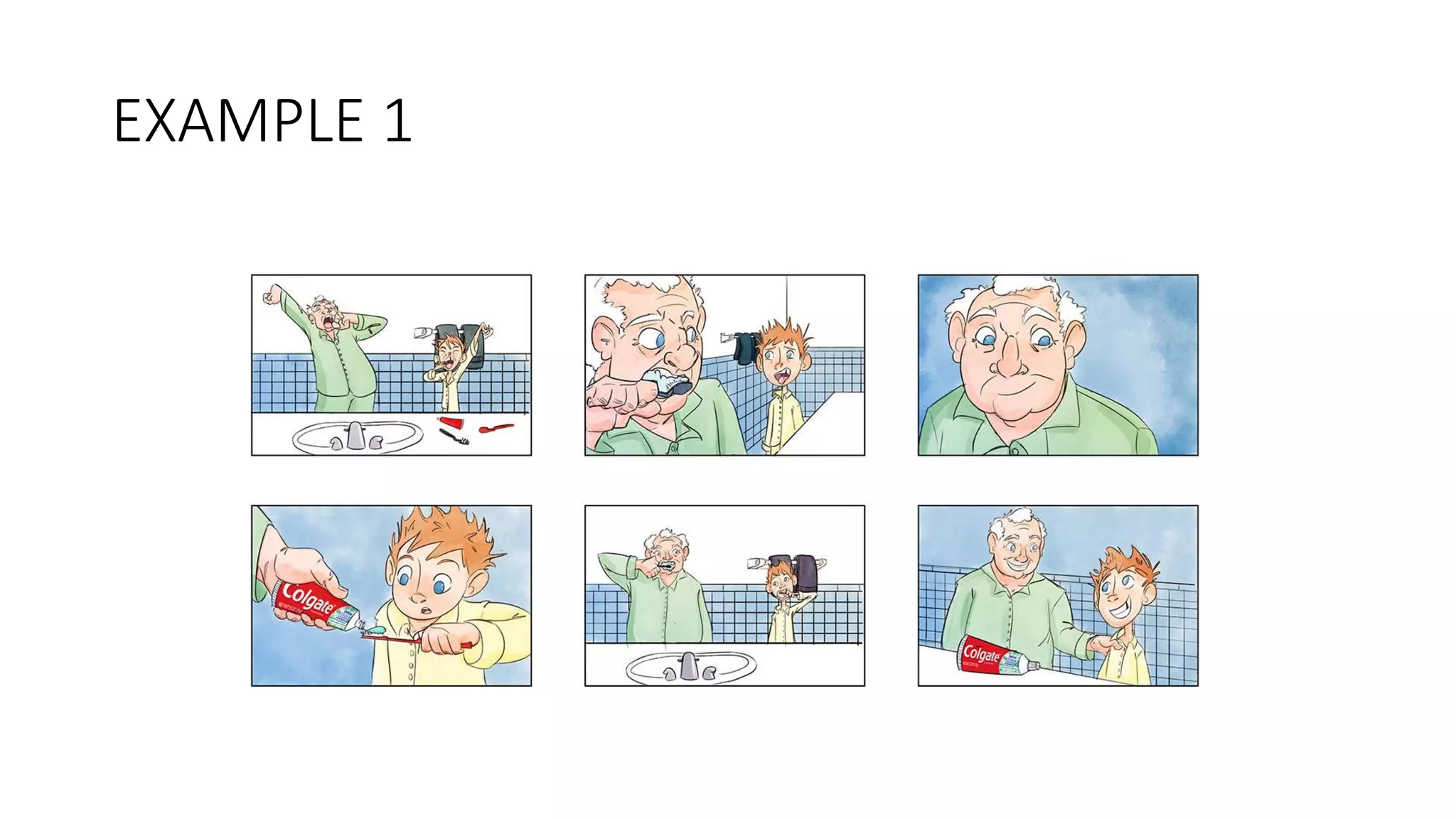
The document provides guidelines for writing copy for various media including print, television, outdoor, radio, and digital. It discusses key elements of effective copywriting across different formats. For print, it describes elements like headlines, subheads, images, body copy, and calls to action. For television, it covers storyboards, balancing words and visuals, and formats like demonstration and narrative. Outdoor guidelines emphasize brevity and identity. Radio tips stress simplicity, repetition, and entertainment. Digital writing should be keyword-rich, concise, and scannable.