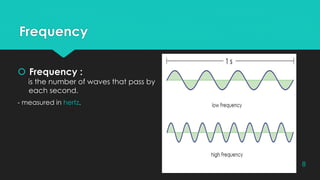
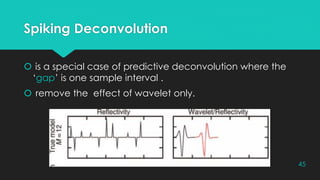
Convolution and deconvolution are processes used in seismic signal processing. Convolution describes how a seismic wavelet is modified as it passes through geological layers, producing a recorded seismic trace. Deconvolution aims to remove the effects of the source wavelet and recover the reflectivity series. There are two main types of deconvolution - deterministic deconvolution which can be used when the source wavelet is known, and statistical deconvolution which is used when no information about the source is available and aims to predict the wavelet. Common statistical deconvolution methods include predictive deconvolution and spiking deconvolution.