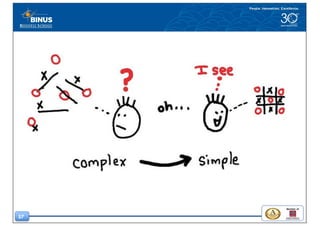
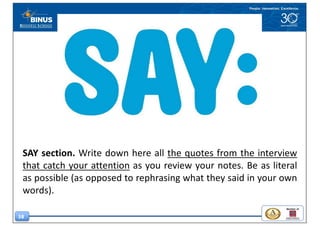
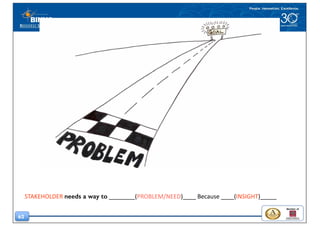
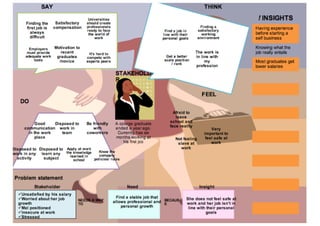
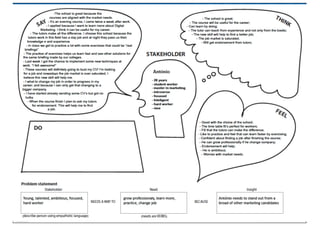
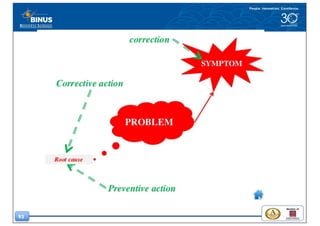
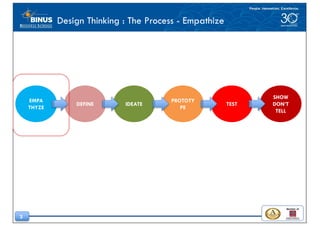
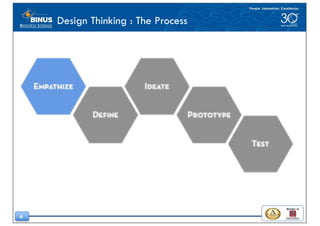
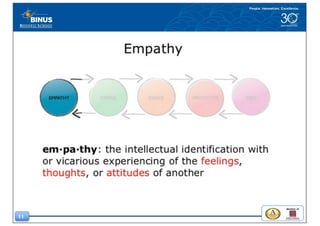
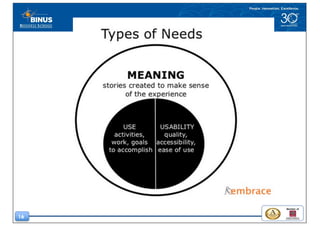
This document discusses the design thinking process of empathizing. It explains that empathizing involves understanding users by observing them, engaging with them, and experiencing their perspective. Methods discussed include conducting interviews, creating empathy maps to understand users' thoughts and feelings, using camera studies where users document their experiences, and assuming a beginner's mindset to understand users without biases. The goal of empathizing is to translate observations into insights about users' needs in order to design products and services that improve their lives.

































![38
Empathize: User Camera Study – How ?
1. Identify subjects whose perspective you are interested in learning more about.
2. Briefly explain the purpose of the study, & ask if they would be willing to
take photographs of their experiences. Get permission to use images they take.
3. Provide a camera to your subject & instructions such as:
•“We would like to understand what a day in your life feels like. On a day of your
choosing, take this camera with you everywhere you go, & take photos of experiences
that are important to you.” Or, you could try:
•“Please document your [morning routine] experience with this camera.” Or,
•“Take pictures of things that are meaningful to you in your kitchen.”
Frame your request a little broader than what you believe your problem space
might be, in order to capture the surrounding context. Many insights can emerge
from that surrounding space.
4. Afterwards, have your subject walk you through the pictures & explain the
significance of what they captured. Return to a good empathetic interviewing
technique to understand the deeper meaning of the visuals & experience they
represent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convertingneedintodemand-171203231427/85/Converting-need-into-demand-38-320.jpg)