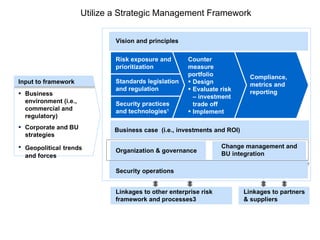
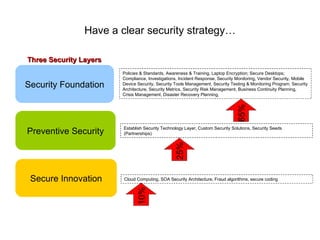
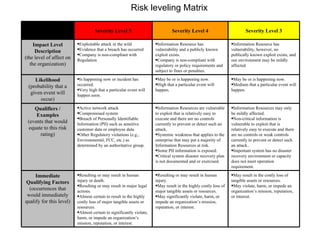
The document discusses the trends of technology, security risks, and the importance of having a clear security strategy and framework. It recommends converging security resources across an organization in a collaborative way to improve risk mitigation, operational effectiveness, and reduce costs. Key aspects include having a preventative security approach, leveraging security technologies, and ensuring security spending aligns with the most important business risks.












![Dave Tyson CISO PG&E 415 973-5455 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convergence-innovativeintegrationofsecurity-110901171722-phpapp02/85/Convergence-innovative-integration-of-security-16-320.jpg)