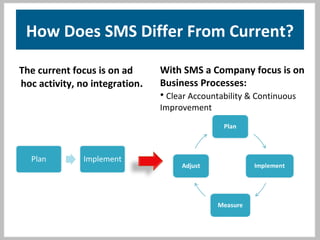
The document discusses physical security systems and security management systems. It provides information on the goals of physical security systems, which are to employ security in depth through deterrence, detection, assessment, delay, and response. It then describes key aspects of a security management system, including identifying assets and risks, analyzing vulnerabilities, evaluating risk, analyzing improvements, and making recommendations. The document argues that a security management system provides benefits like reducing losses and costs while protecting reputation, and that senior management commitment is important for sustainability.