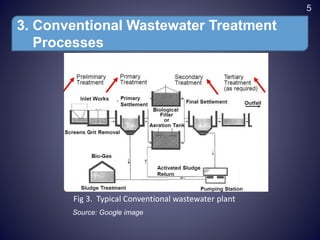
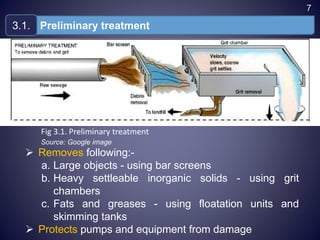
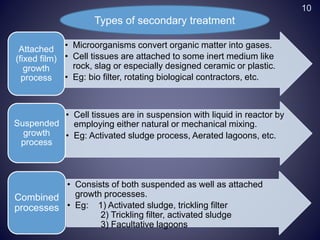
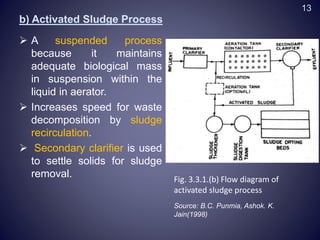
This document discusses conventional wastewater treatment processes and their applicability. It begins by outlining the objectives and presentation outline. The fundamental principles of conventional treatment are then described, including physical, chemical, and biological unit operations and processes. The main conventional treatment processes are explained in detail, including preliminary, primary, secondary, tertiary, and sludge treatment stages. Applications in Nepal are discussed. Strengths and limitations are provided. Finally, emerging alternative technologies are presented as potential solutions to challenges with conventional wastewater treatment.