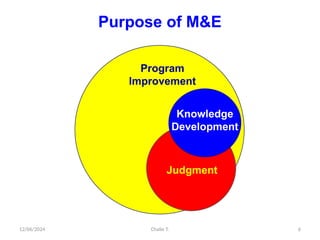
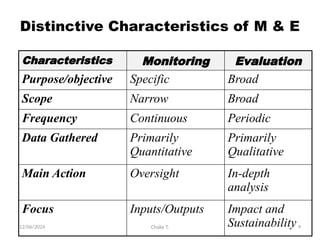
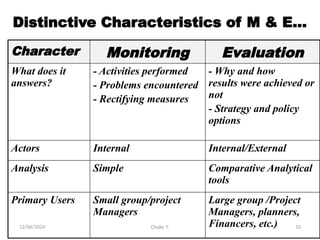
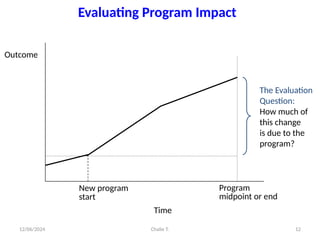
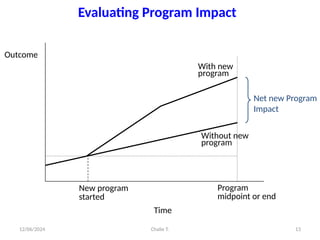
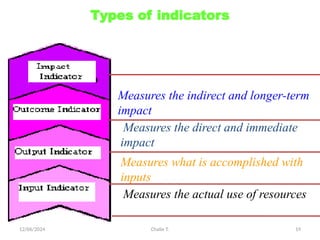
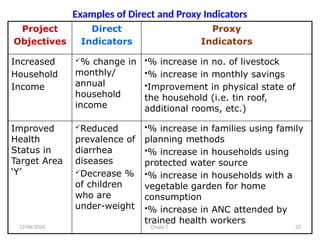
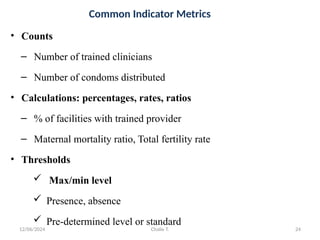
The document outlines the principles of controlling, monitoring, and evaluation (M&E) in project management, covering definitions, purposes, and steps involved. It distinguishes between monitoring and evaluation, highlighting their characteristics, types of indicators, and sources of information for effective assessment. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of indicators in measuring program impact and success, providing examples and characteristics of good indicators.