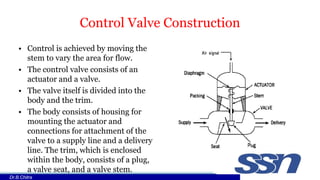
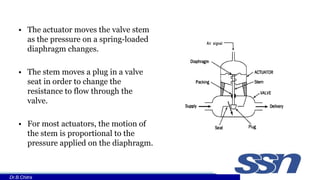
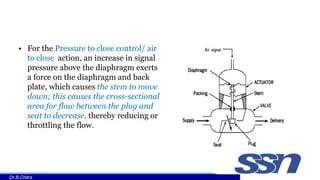
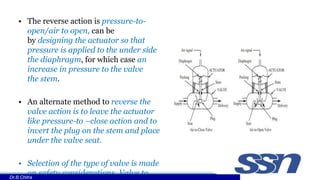
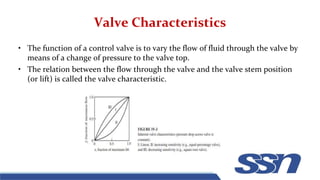
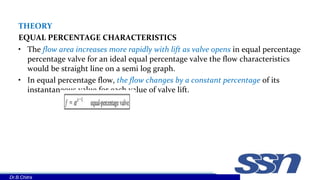
This document discusses control valves used in chemical processing. It describes how control valves work by varying the flow of fluids through changing the position of a plug within the valve body. Control valves have either linear, equal percentage, or quick opening flow characteristics depending on how the flow rate changes with valve stem position. The document focuses on pneumatic control valves as they are most commonly used and describes the typical components of a control valve including the actuator, body, trim, plug and seat. It also provides the equation used to size control valves based on flow rate, pressure drop, and a valve coefficient.