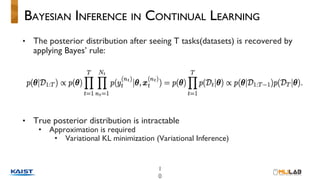
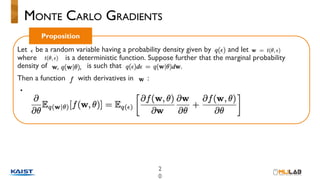
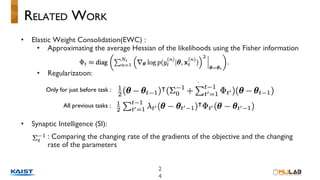
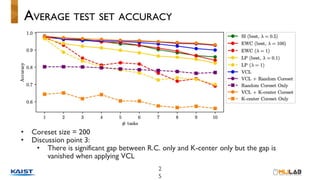
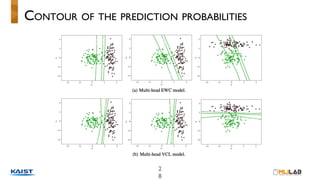
This document discusses variational continual learning for deep discriminative models. It covers continual learning backgrounds, variational inference for continual learning, the variational continual learning algorithm using a coreset, experiments comparing it to related methods, and discussion points. The variational continual learning algorithm uses a coreset to balance plasticity and stability when learning new tasks incrementally while avoiding catastrophic forgetting of old tasks. Experiments show it outperforms regularization-based methods on split MNIST and analyses the effect of coreset size and predictive uncertainty.