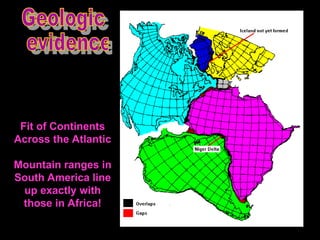
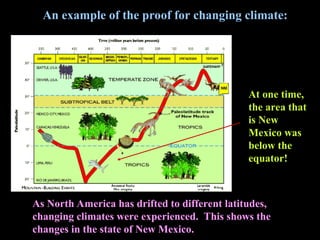
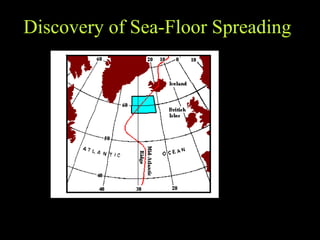
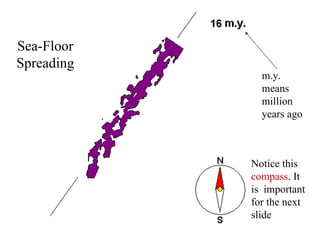
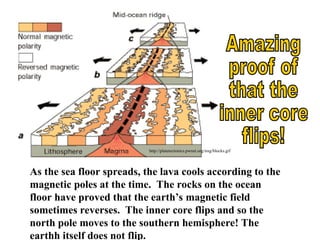
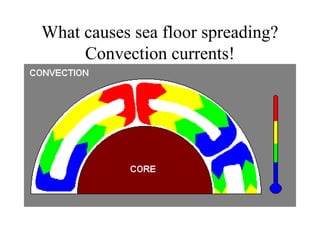
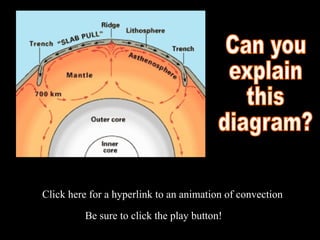
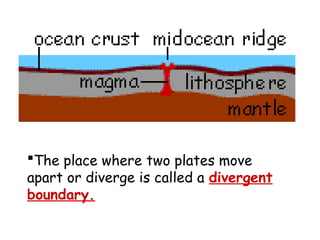
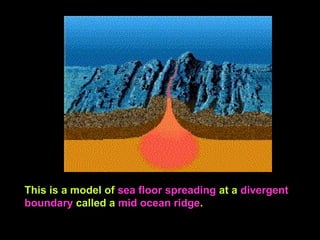
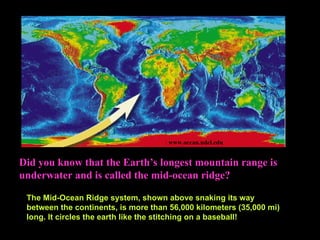
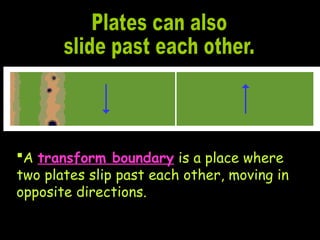
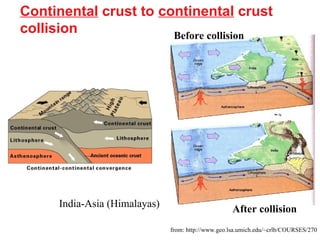
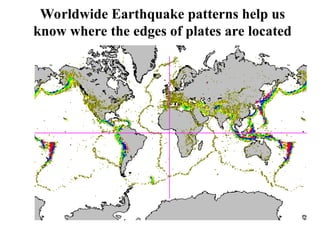
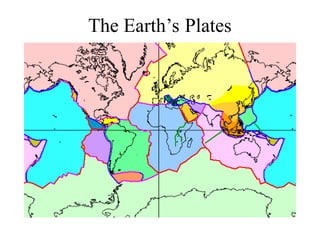
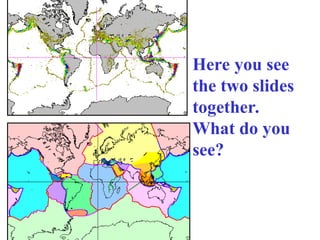
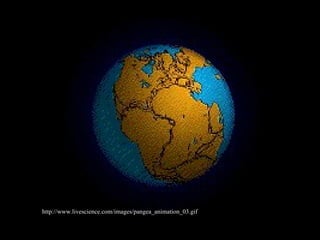
Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift, suggesting that all continents were once joined in a supercontinent called Pangaea but drifted apart over time, a hypothesis initially rejected due to lack of a mechanism. The advent of technology in the 1940s led to discoveries such as sea-floor spreading, providing evidence for plate tectonics, which describes the movement of Earth's plates and the formation of geological features. Different boundary types, including divergent, convergent, and transform, explain how tectonic plates interact and have formed major landforms like mountains and ocean ridges.