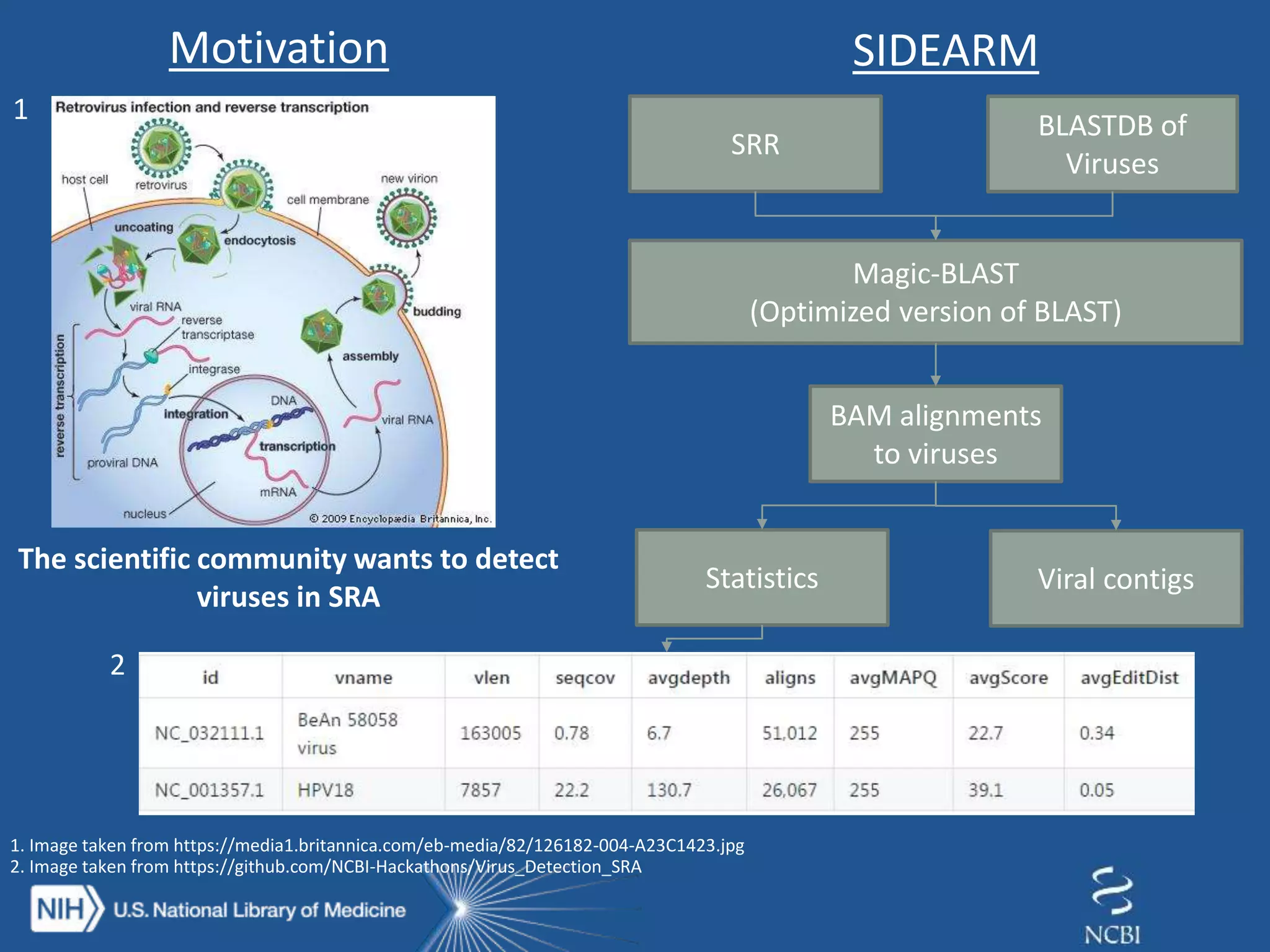
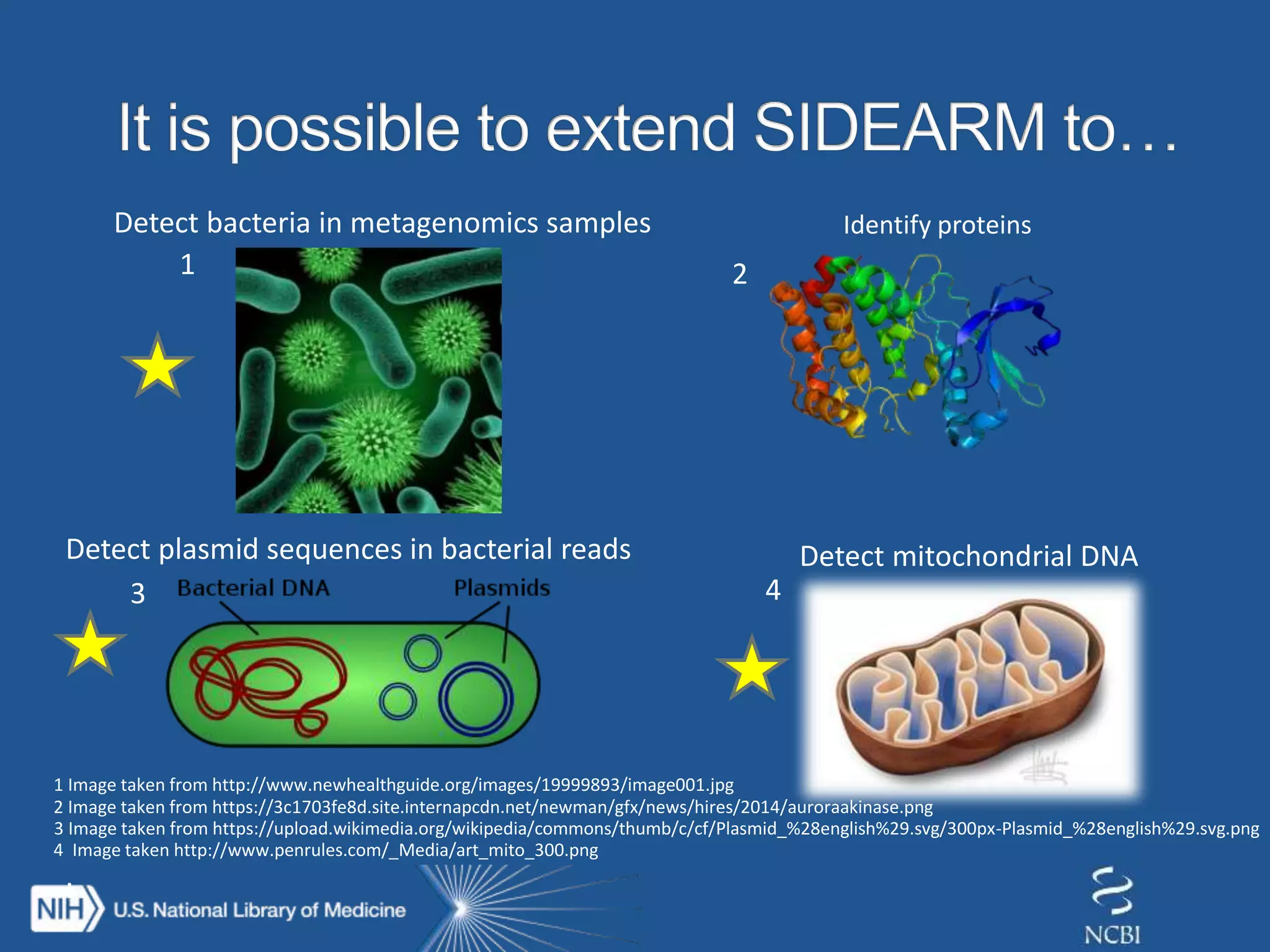
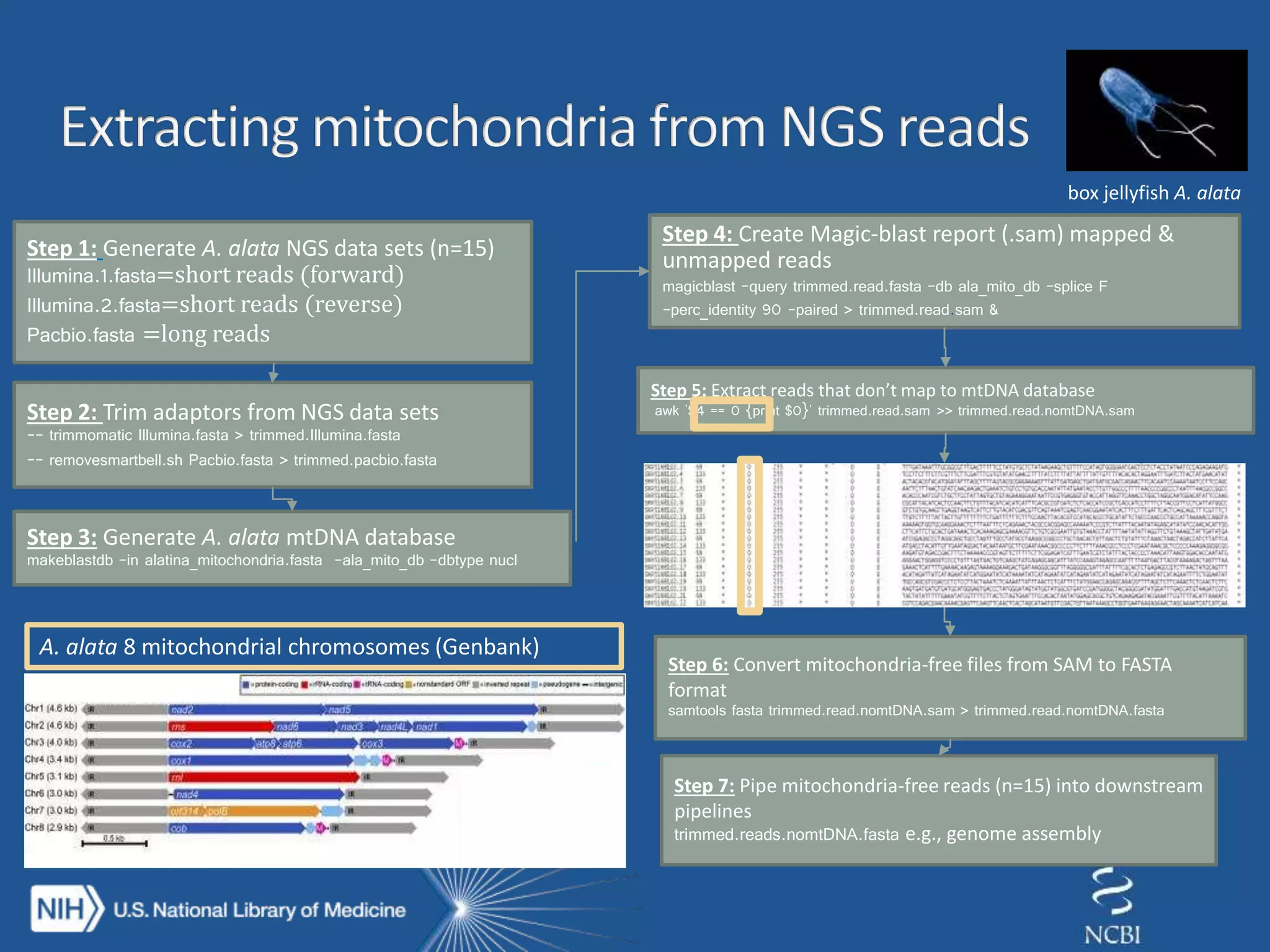
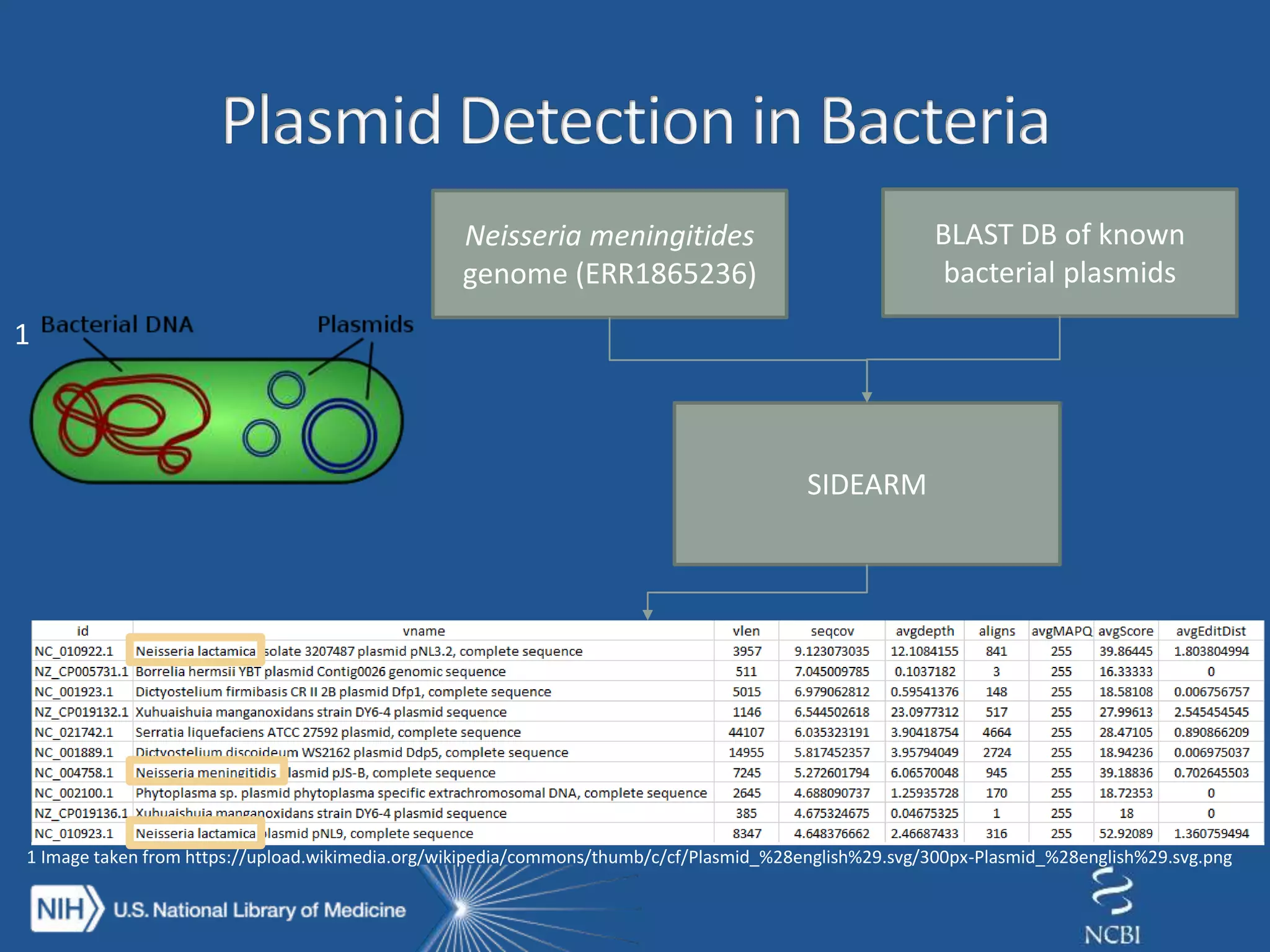
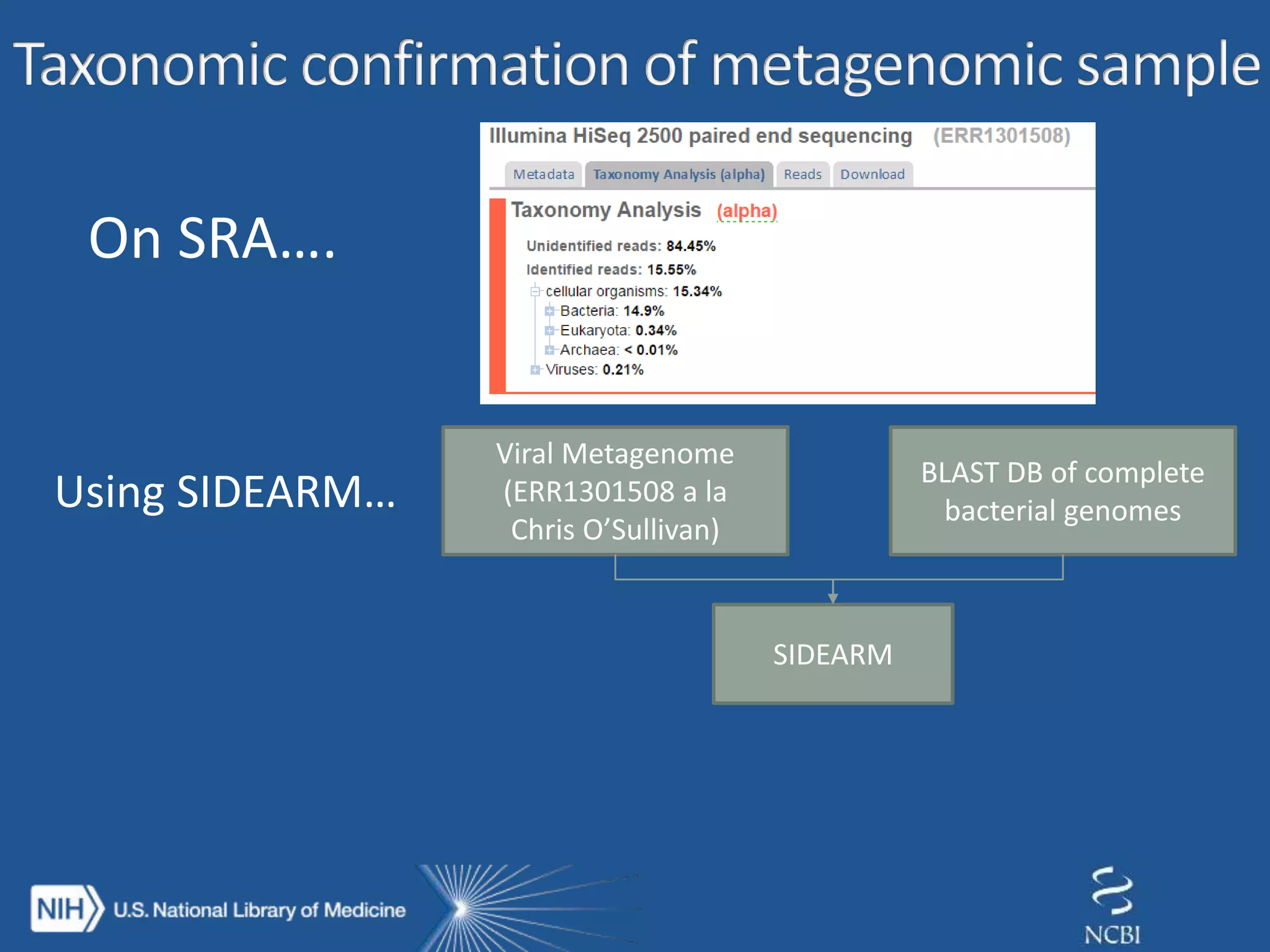
The document discusses methodologies for detecting viruses and bacteria in genomic data, primarily using tools such as magic-blast and samtools. It outlines a step-by-step process for data processing, including generating databases and trimming reads, as well as the creation of specific downstream analyses. The research involves extracting mitochondrial DNA and analyzing metagenomic samples to identify proteins and plasmid sequences.