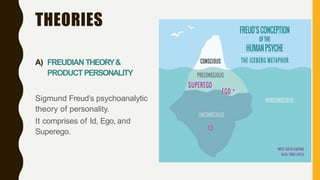
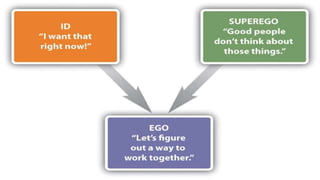
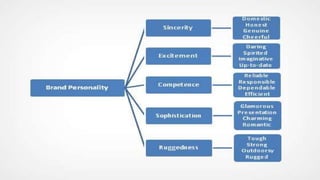
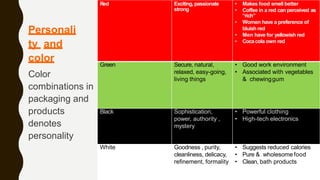
This document discusses personality and consumer behavior. It defines personality as inner characteristics that determine how individuals respond to their environment. Marketers have intuitively felt that personality influences consumer purchasing and consumption patterns. The document covers various personality theories and traits like Freudian theory, trait theory, and sensation seeking that relate to consumer innovativeness. It also discusses how cognitive factors, materialism, ethnocentrism, and brand personality impact consumer behavior. Understanding consumer personality diversity can help marketers better target different types of consumers.