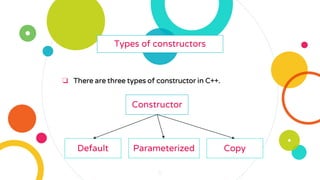
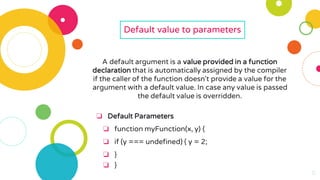
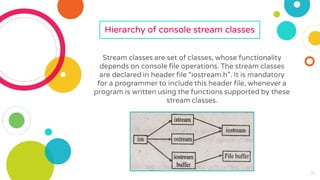
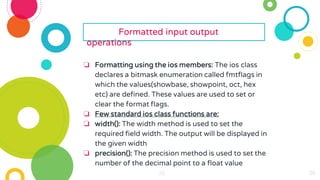
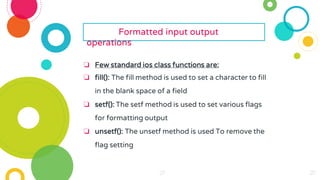
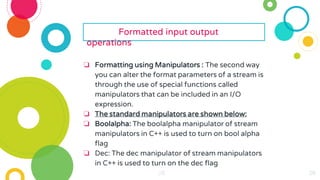
The document provides an overview of constructors and destructors in C++, detailing their roles, types, and properties. It explains constructors as special member functions that initialize objects and outlines different types such as default, parameterized, and copy constructors. Additionally, it discusses destructors, their invocation, and the importance of managing memory, along with formatted and unformatted input/output operations in C++.