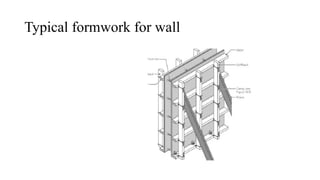
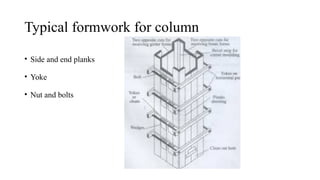
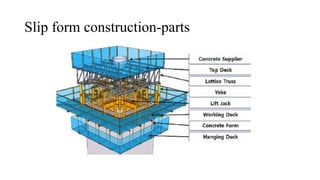
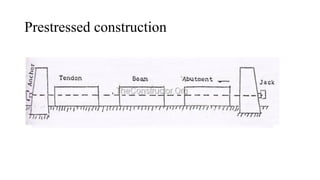
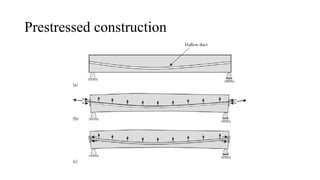
The document discusses various cost-effective construction technologies, emphasizing methods like rapid wall construction, soil-cement block masonry, voided slab technology, and filler slab technology. It highlights the benefits of these methods, such as reduced construction time, lower material usage, and environmental friendliness. Additionally, it covers scaffolding systems and prefabricated construction, explaining their advantages and limitations in modern building practices.