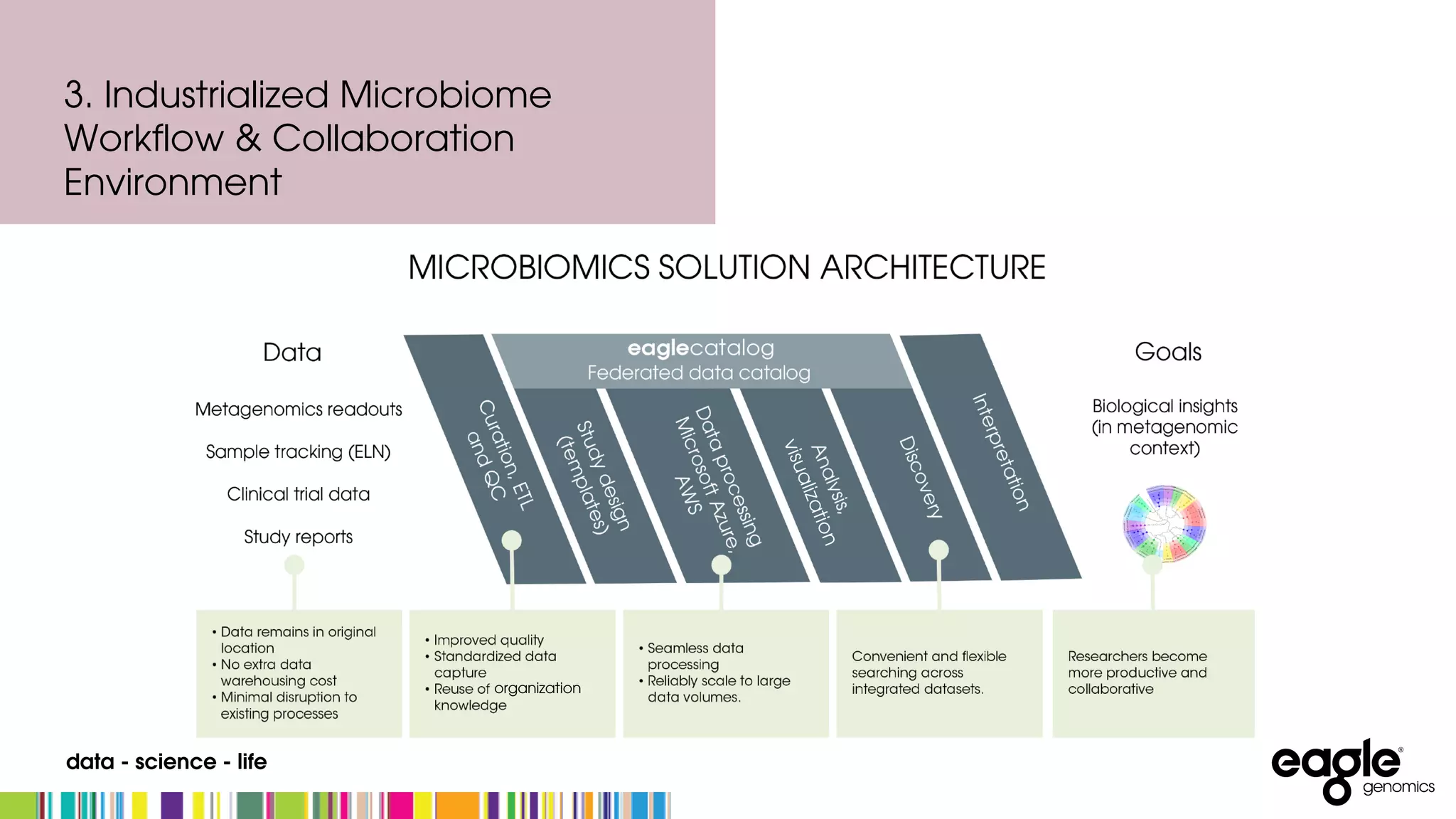
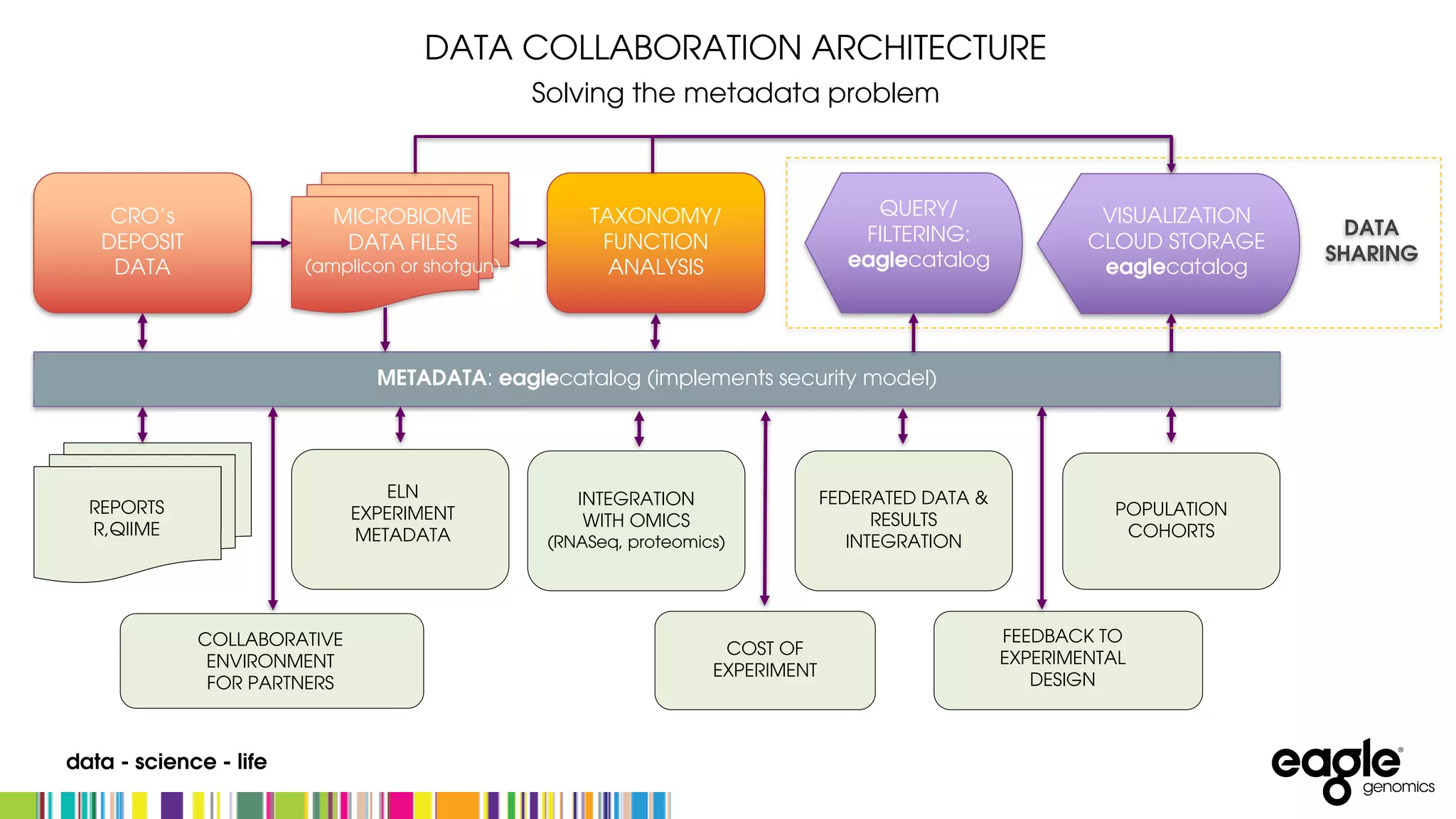
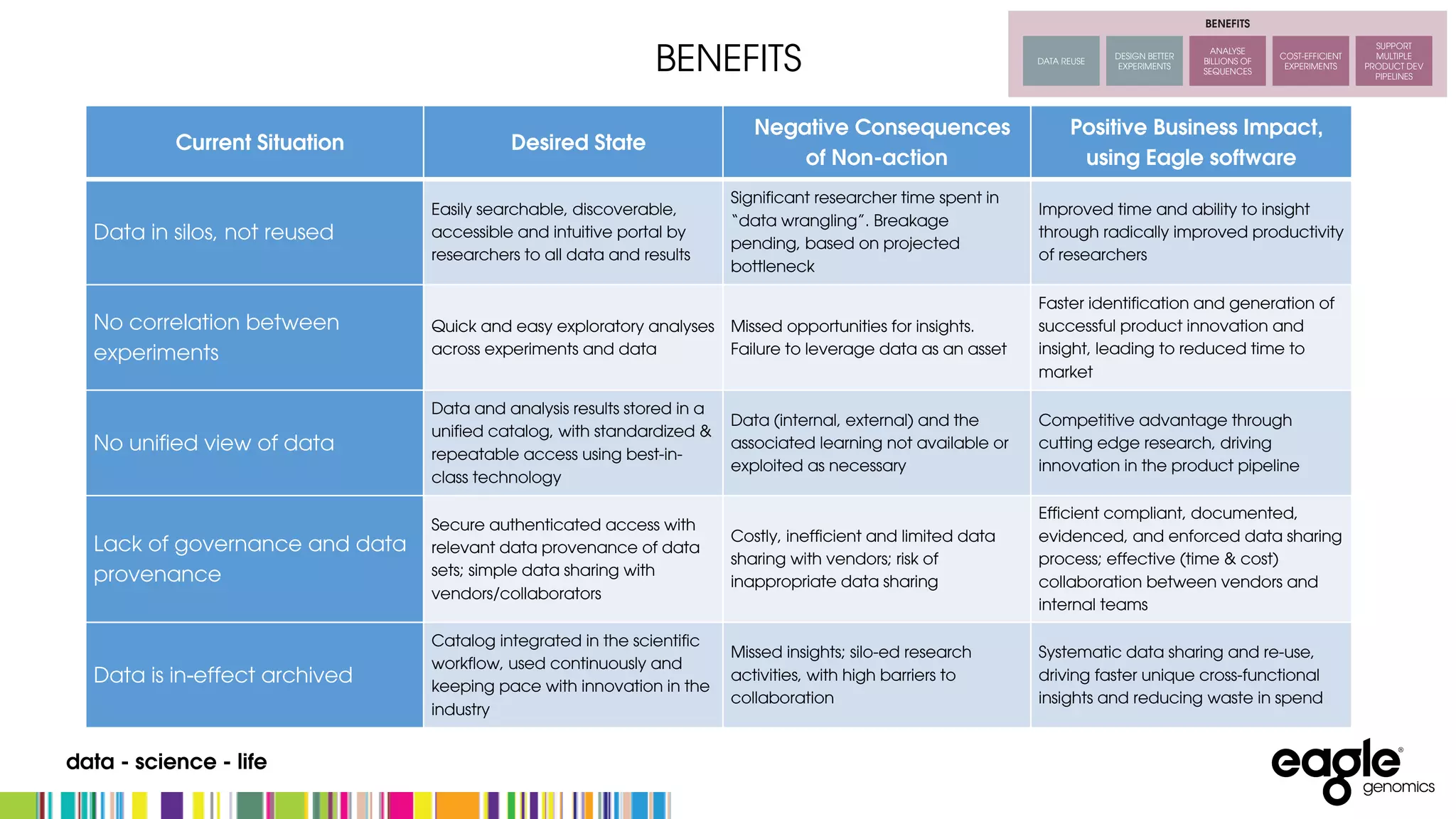
The document discusses the complexities and challenges in developing an end-to-end microbiome workflow, highlighting intrinsic factors, maturity of the field, and business value. It emphasizes the need for effective metadata management and robust compute resources, alongside advancements in industrialized microbiome workflow solutions. Eagle Genomics offers tools to streamline data collaboration, improve researcher productivity, and enhance data utilization in microbiome research.