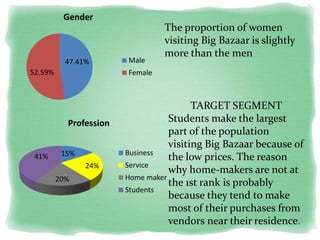
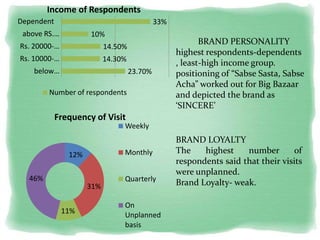
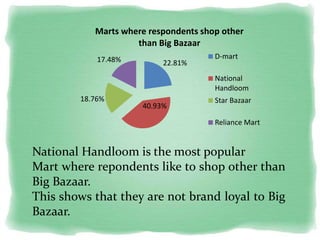
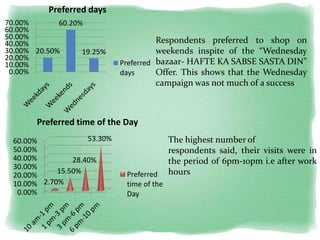
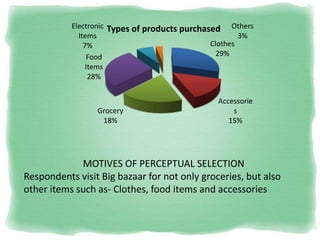
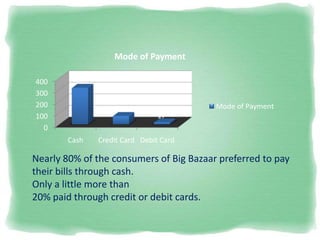
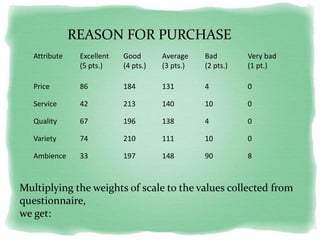
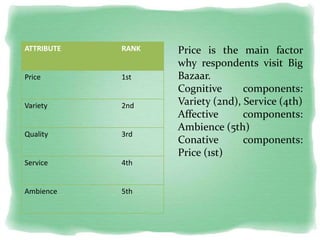
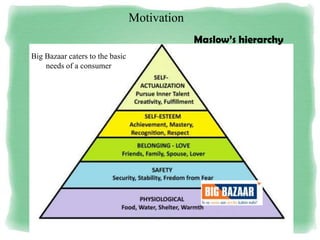
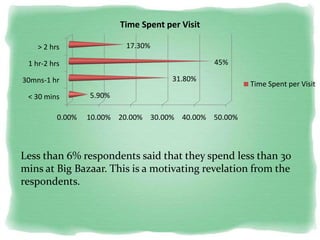
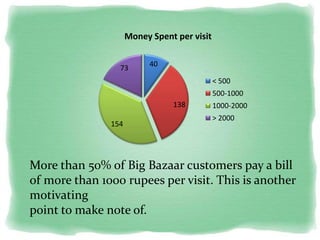
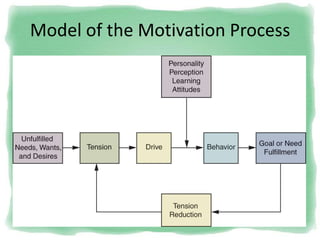
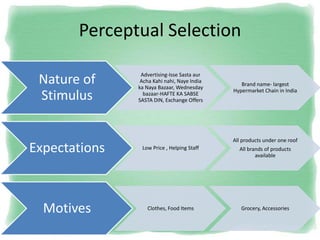
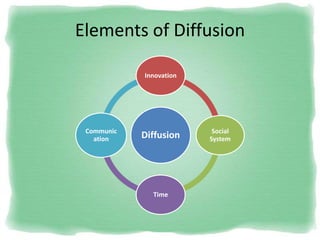
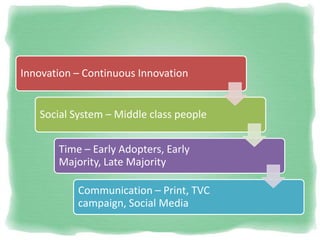
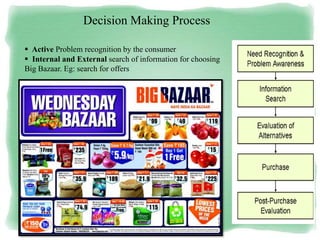
Big Bazaar is India's largest hypermarket chain known for its low prices. It targets middle-income customers, especially students, with promotions like "Wednesday Bazaar - Hafte ka Sabse Sasta Din." Research found most visitors are women aged 15-41 from service and business professions. Over half spend 1,000-2,000 rupees per visit. While price is the main reason for shopping at Big Bazaar, visitors also purchase clothes, food, and accessories. Most pay in cash and visit on weekends. Big Bazaar aims to meet customers' basic needs affordably while building a sincere brand known for variety, reliability and value.