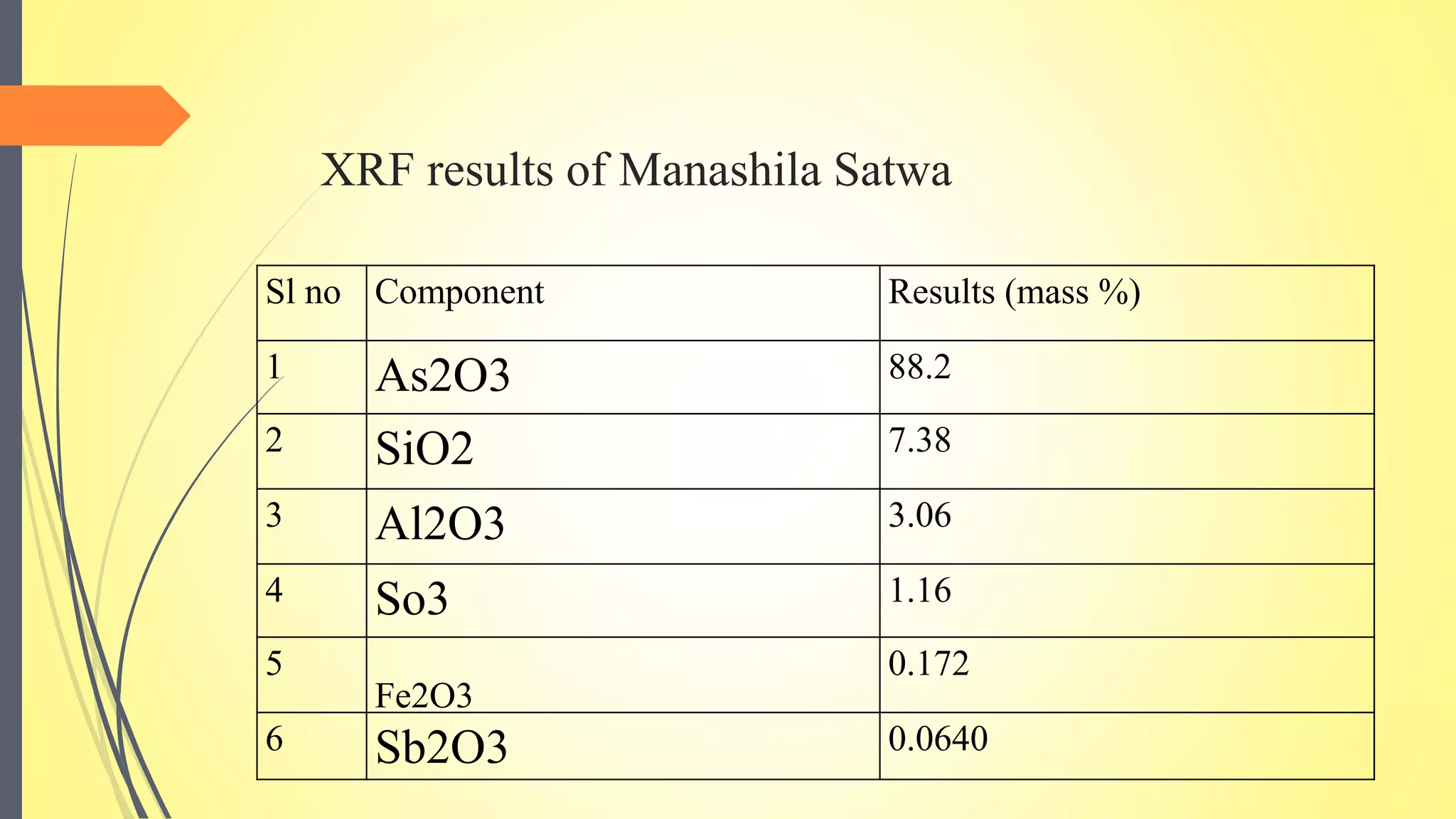
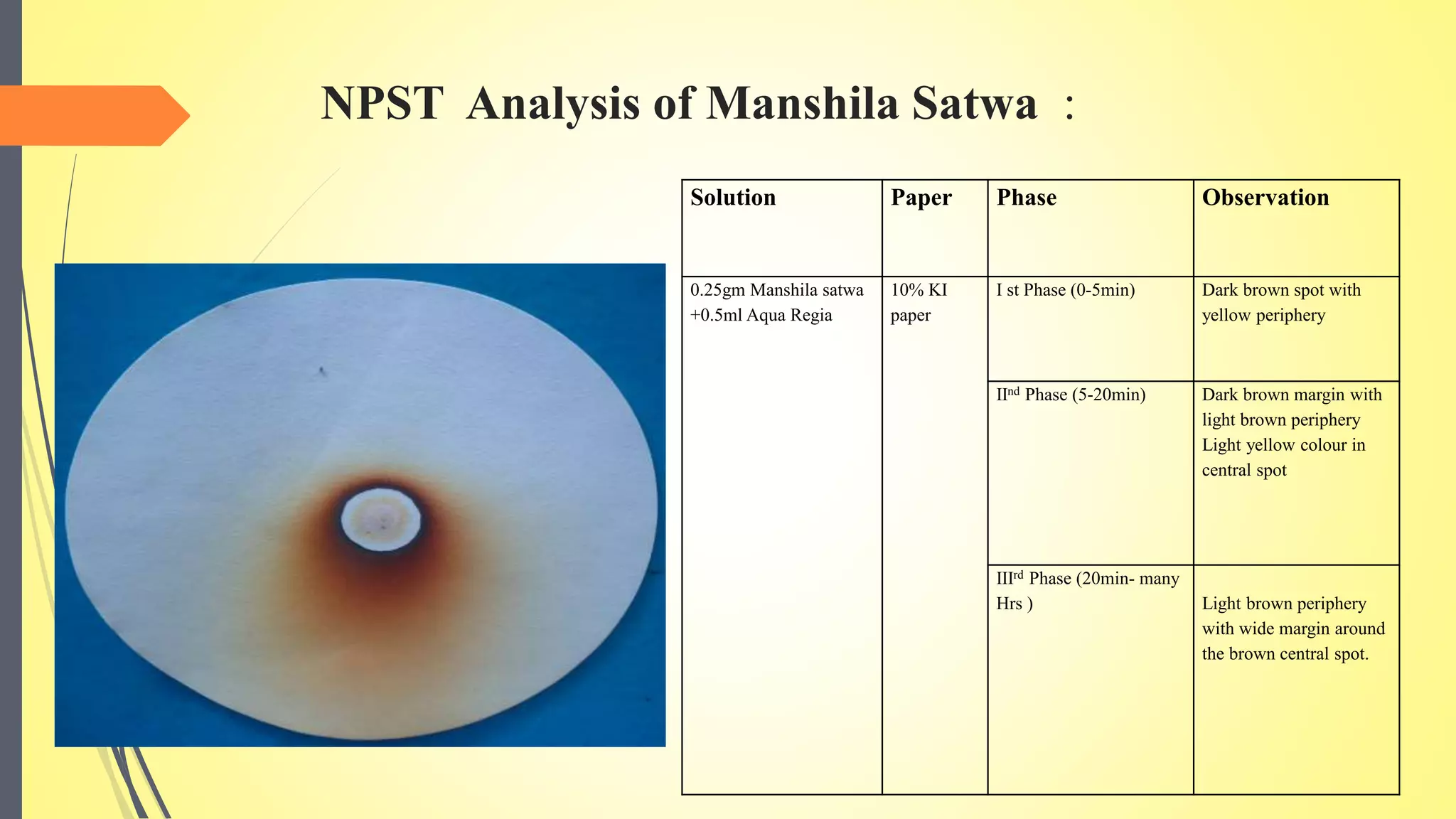
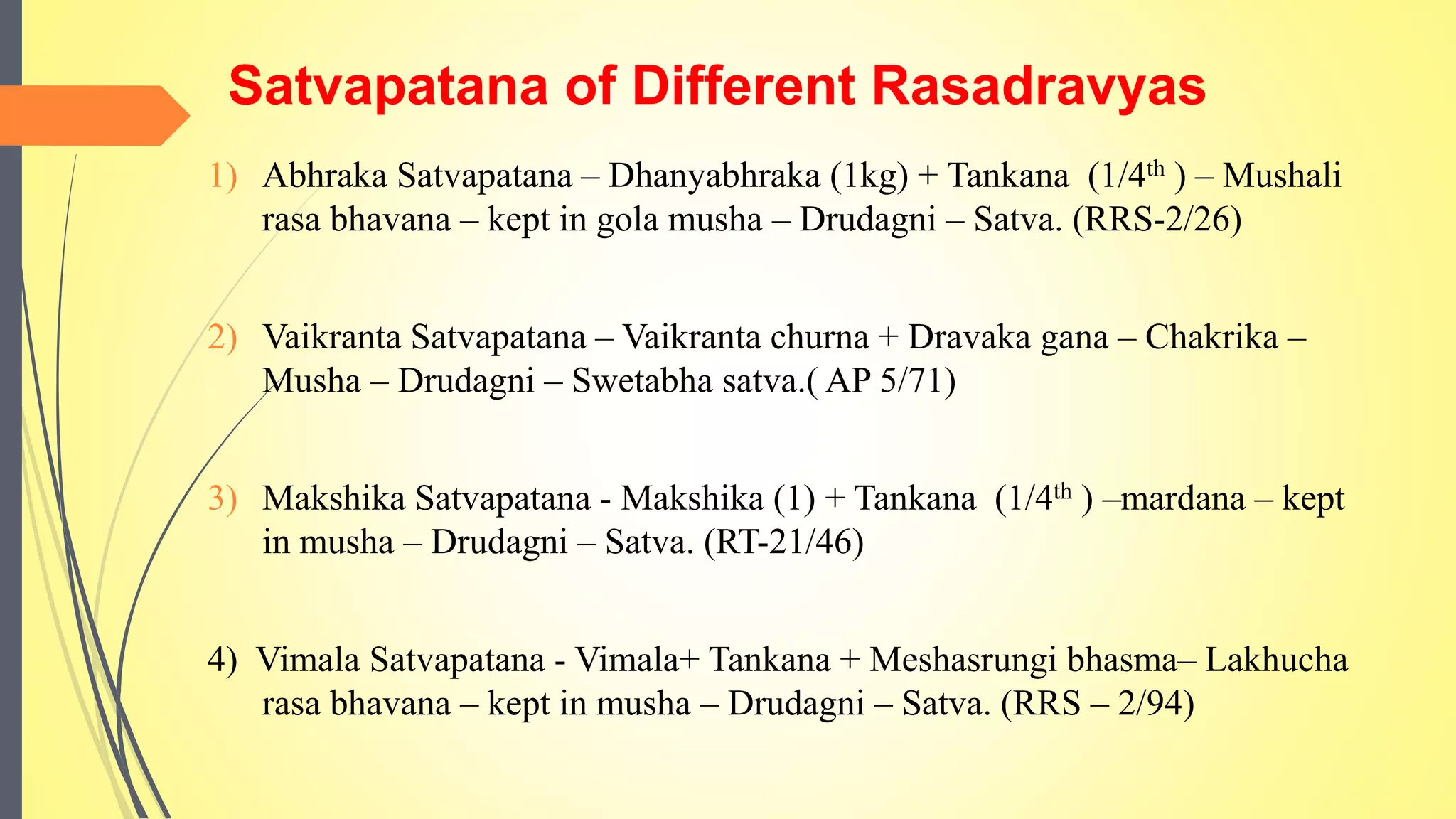
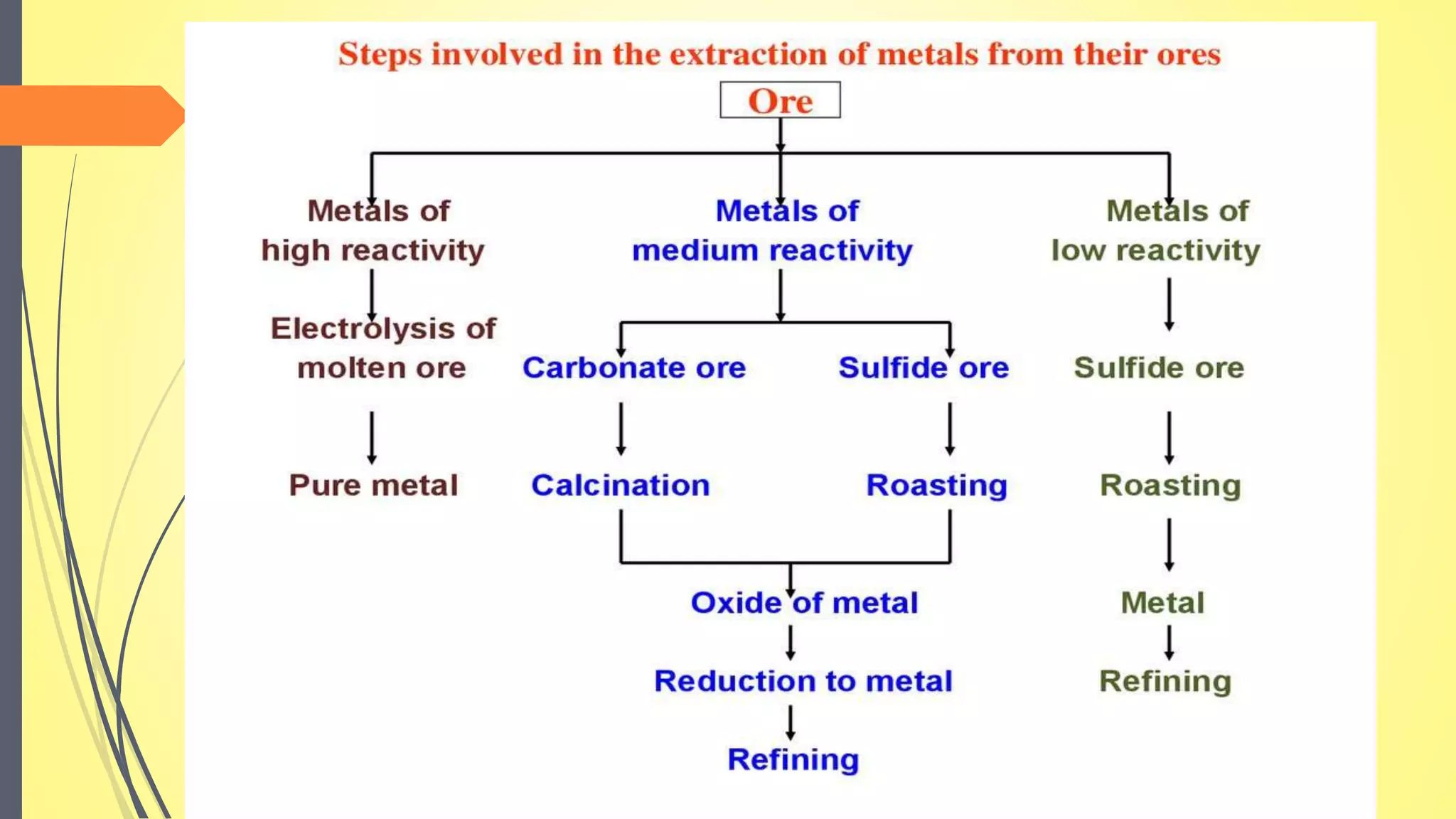
This document discusses the process of satvapatana, which is the extraction of the active principle or essence from minerals and metals. It begins by defining satvapatana and classifying it based on the form of satva extracted, the nature of the material, and the satva obtained. The document then outlines the aims, methods, equipment, and materials used in satvapatana like crucibles, fluxes, and heat sources. Specific extraction processes are provided for minerals like manahshila and metals. Analysis of the extracted satva is also presented. The conclusion differentiates satvapatana from metallurgy and emphasizes its therapeutic goal of obtaining an active principle.















![Before Satva is used for medicinal purpose, it has to be subjected
to other procedures as –
1) Mridukarana( Softening) – using Madhu, Taila, Vasa, Grita.
2) Nirmalikarana(Purification) – using shuddi varga dravyas –
Khacha(Lavana), Tankana, Souveera, Shipra(Muktha shuki or
Navasadara or Mahisha mutra) [ RRS 10]
3) Marana(Inciniration) – Bhasmikarana.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdl-200916085710/75/Concept-of-satvapatana-by-Dr-Mahantesh-Rudrapuri-17-2048.jpg)




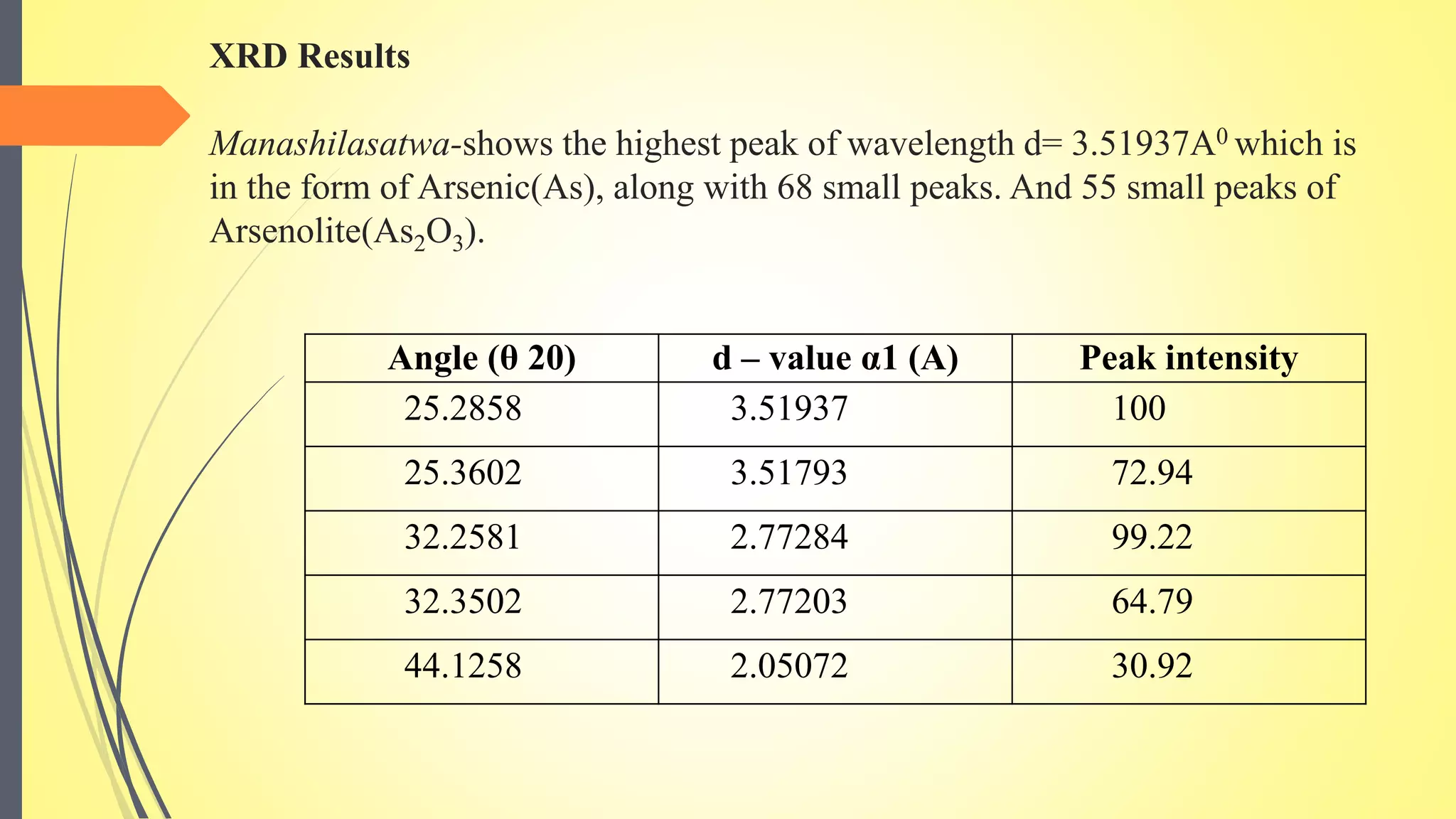
![Visible Ref.Code Score Compound Name Displ.[°2θ] Scale Fac. Chem. Formula
* 98-001-6518 68 Arsenic 0.000 1.005 As1
* 98-000-2114 55 Arsenolite 0.000 0.247 As2 O3
Position [°2θ] (Copper (Cu))
10 20 30 40 50 60
Counts
0
10000
20000
30000
40000
Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenic;Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
Arsenolite
Arsenic;Arsenolite
Arsenic
Arsenolite
3
Arsenic; As1
Arsenolite; As2 O3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdl-200916085710/75/Concept-of-satvapatana-by-Dr-Mahantesh-Rudrapuri-23-2048.jpg)