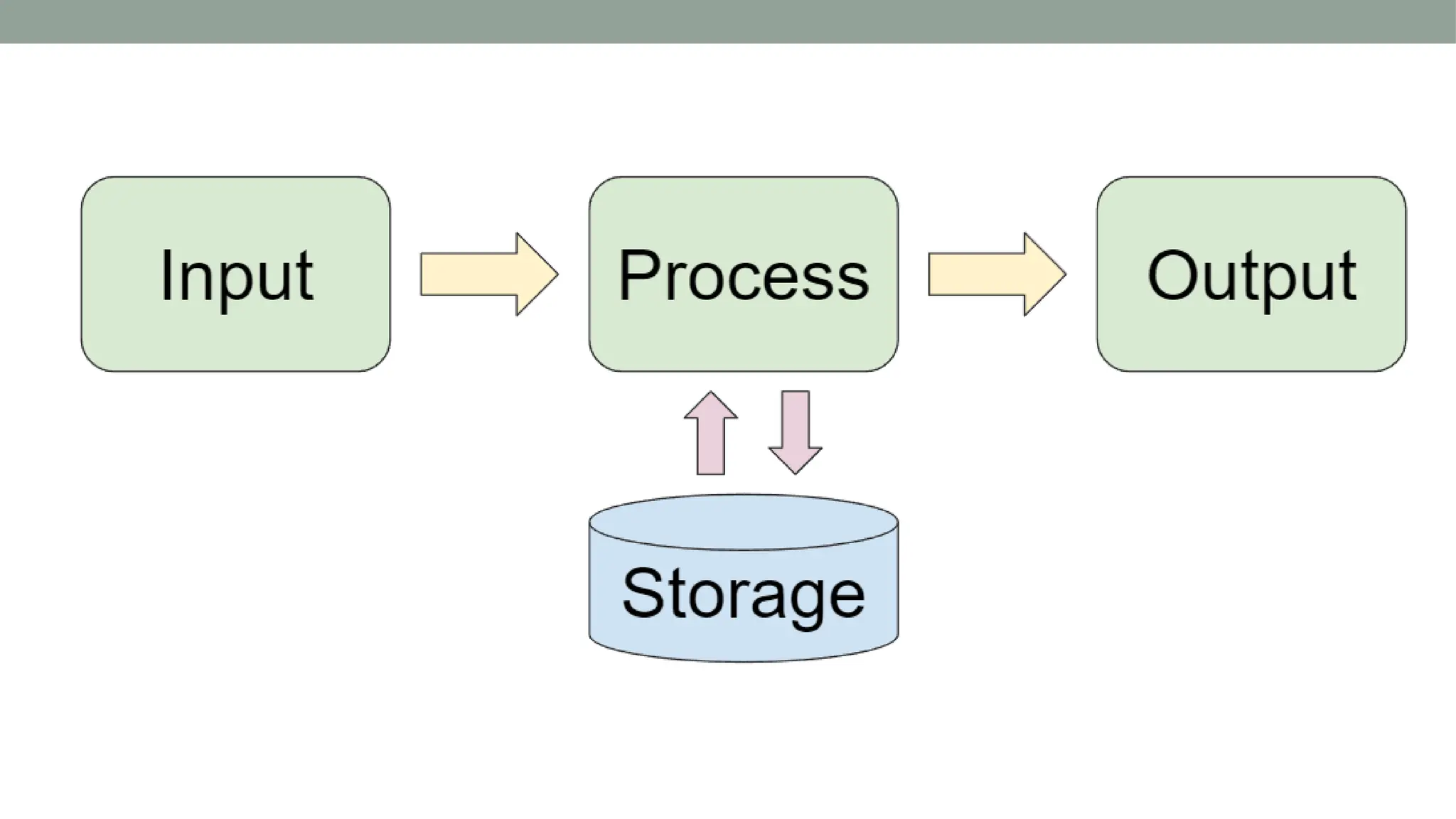
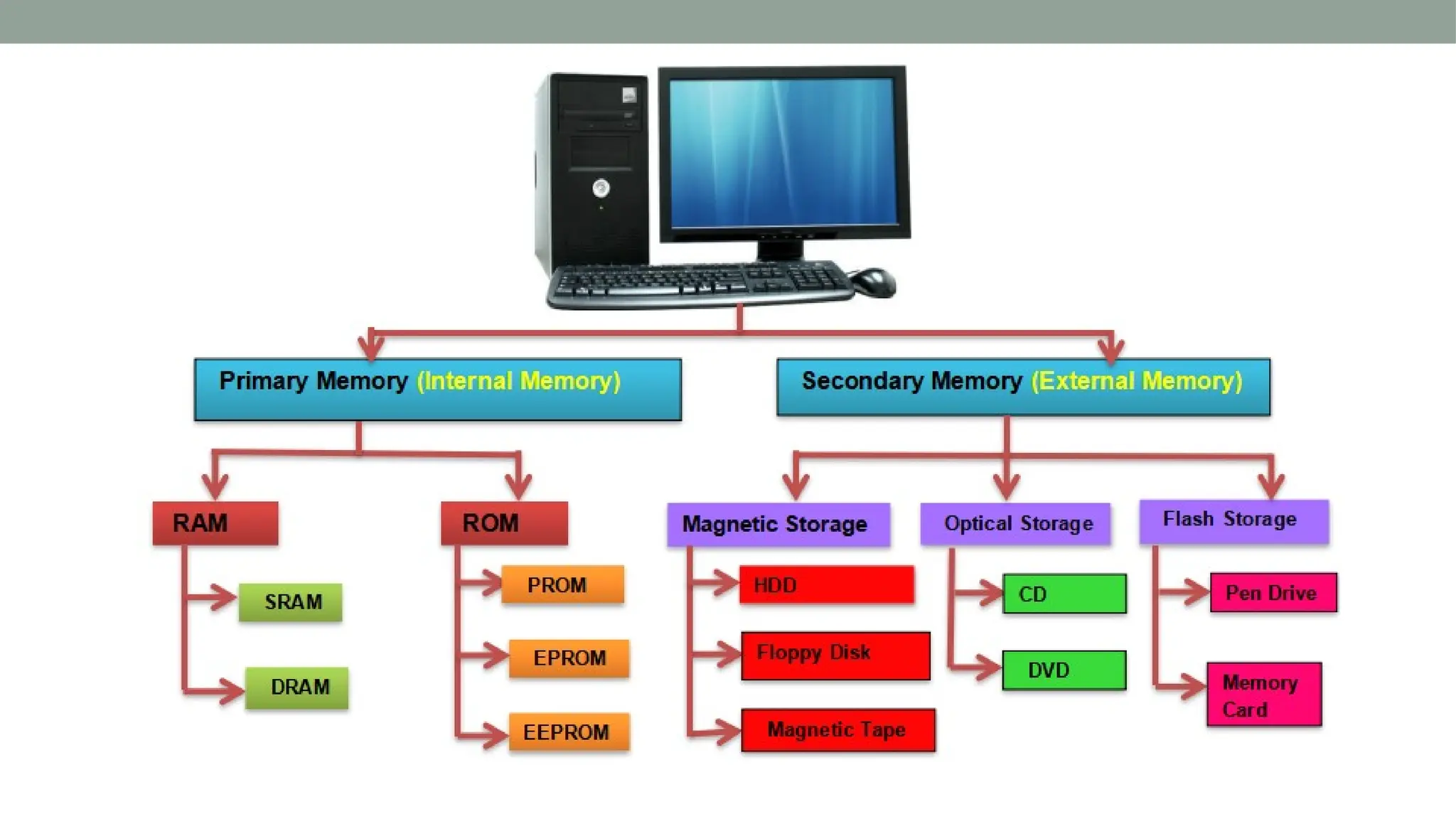
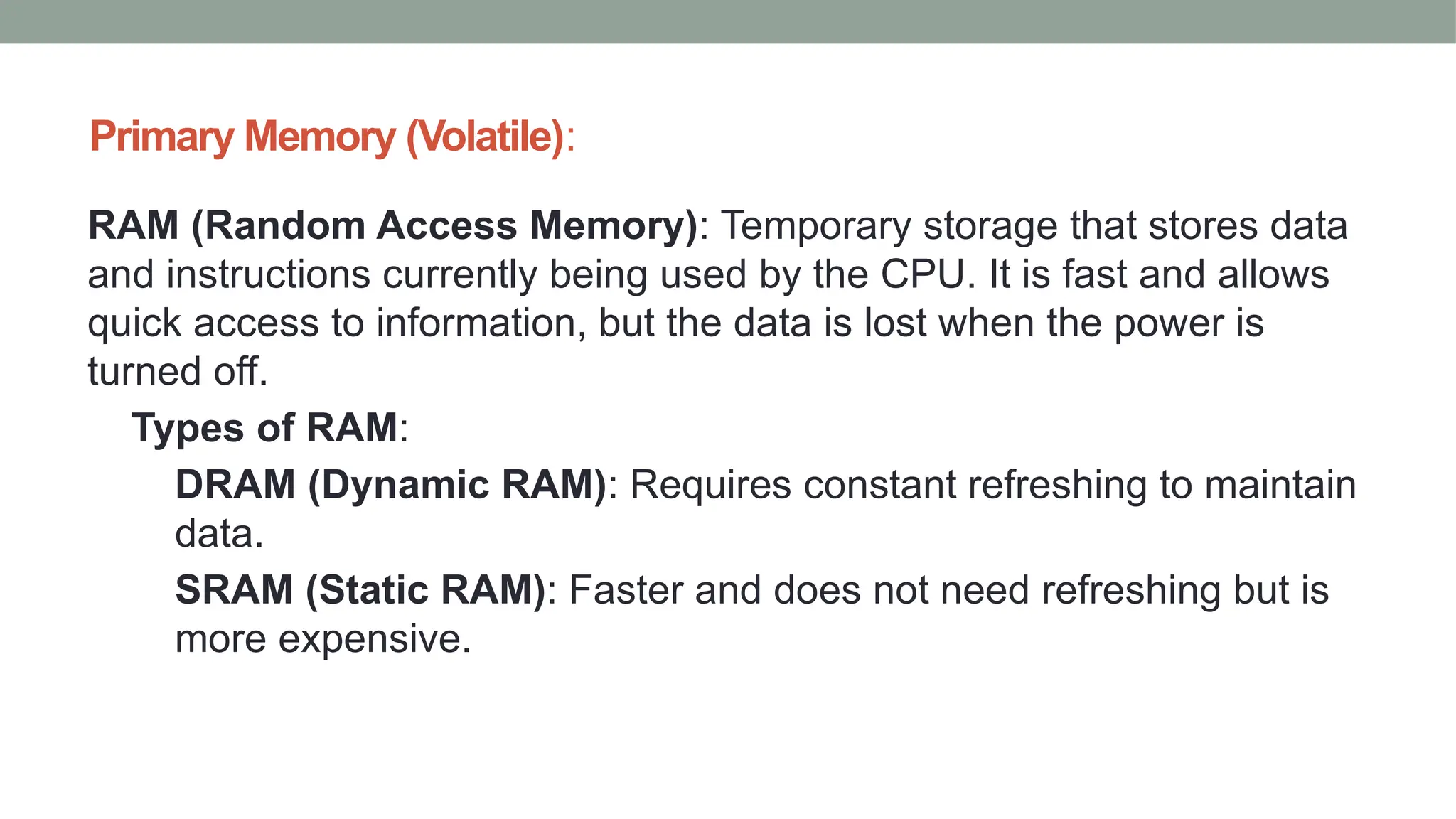
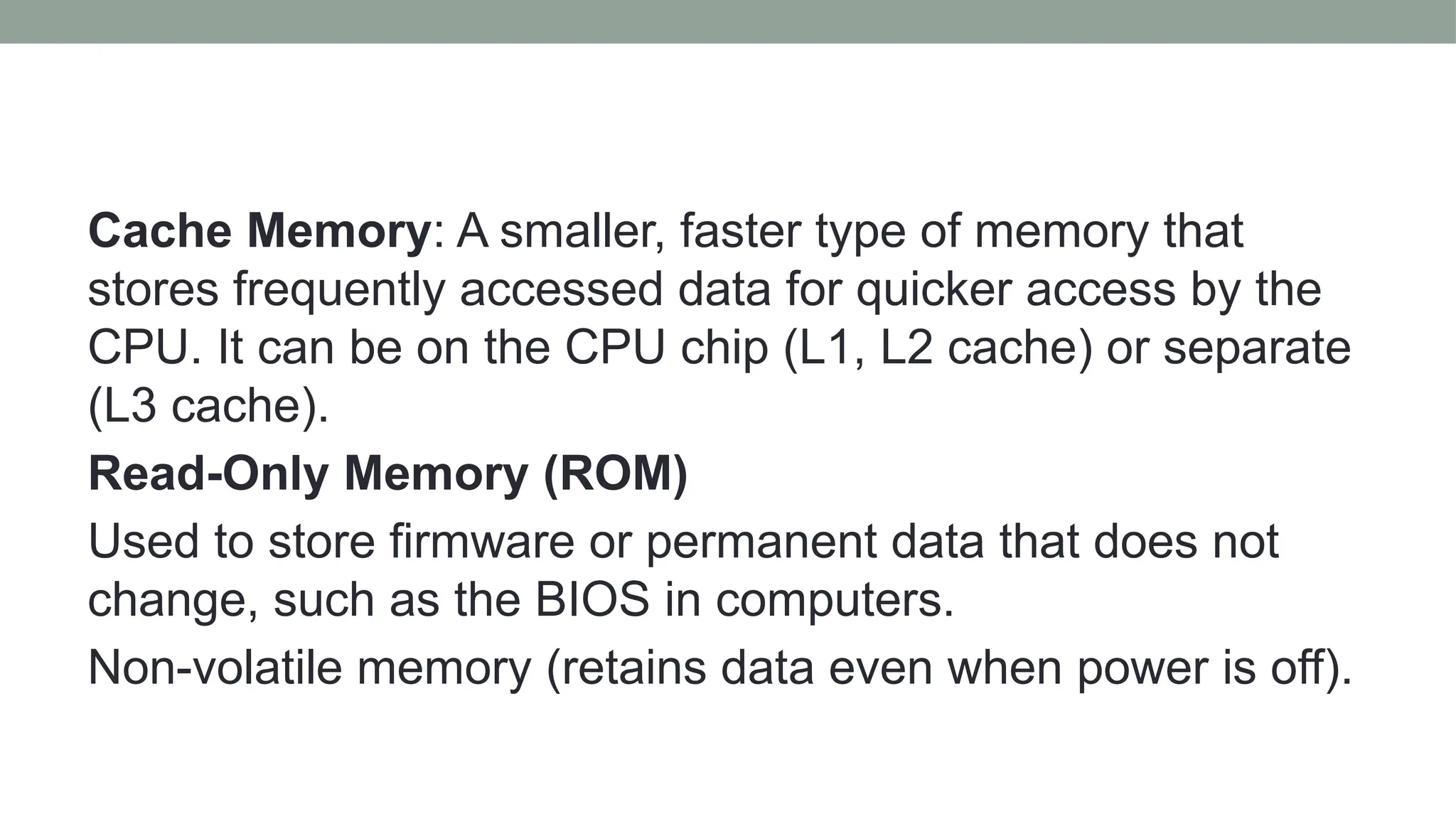
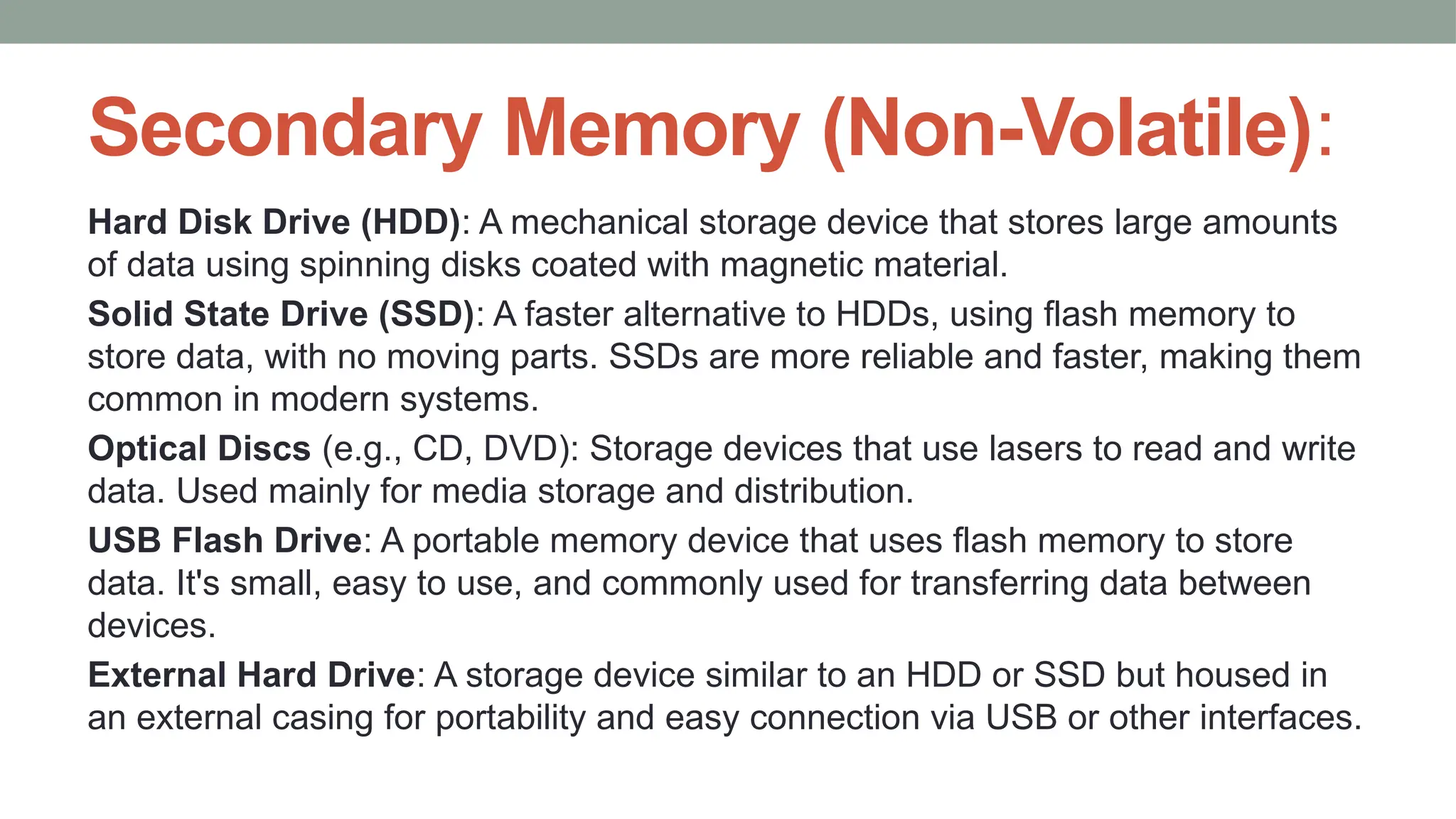
The presentation by P. Pavani Srija provides an overview of computer hardware, defining a computer as an electronic device that processes input, stores data, and produces output. It details the four main categories of computer hardware—input, processing, storage, and output—as well as various devices and technologies associated with each category, including keyboards, webcams, and storage types like HDDs and SSDs. Additionally, the document covers internal components like the power supply, motherboard, microprocessor, and memory types like RAM and ROM, emphasizing their roles in computer functionality.