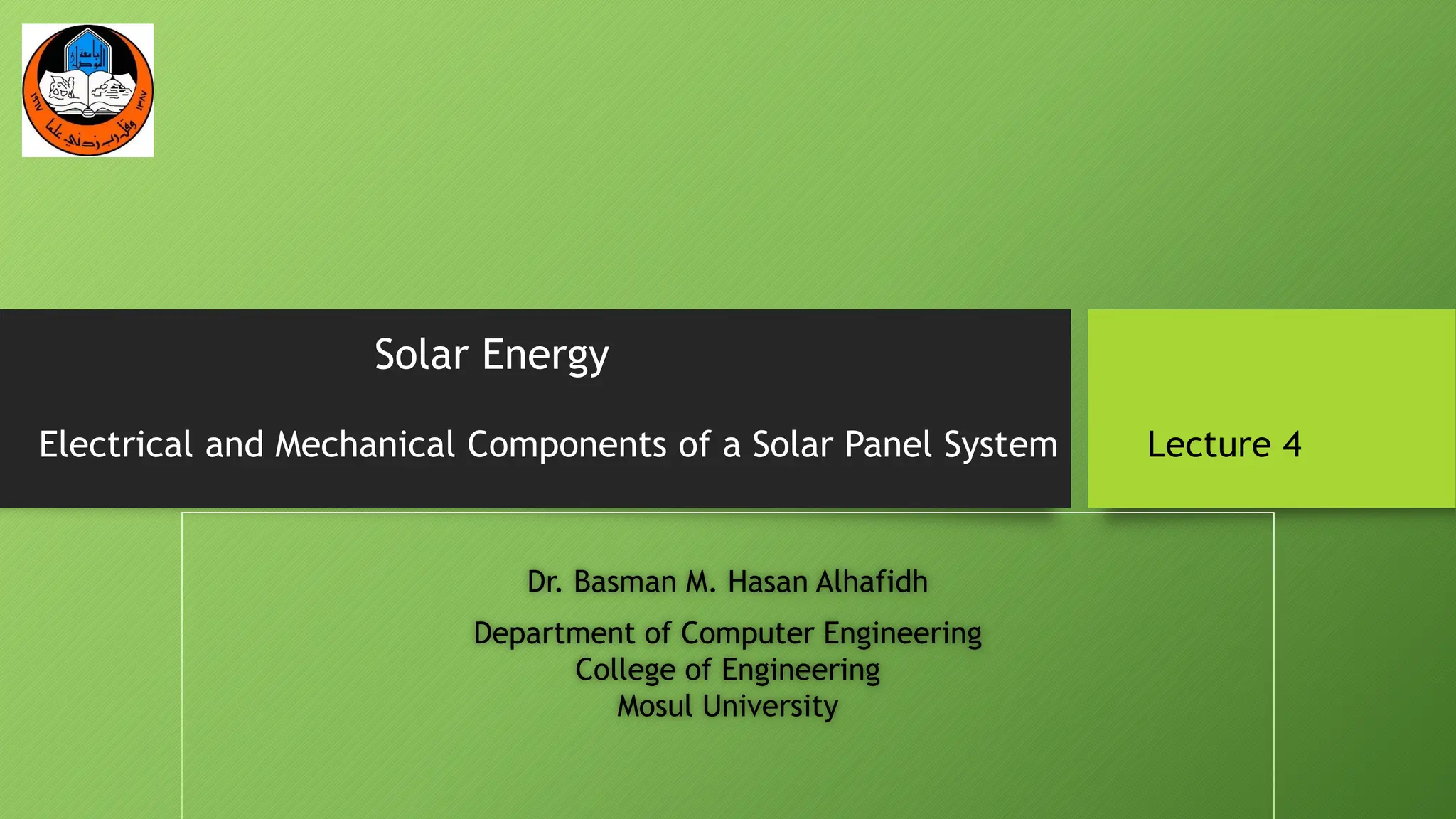
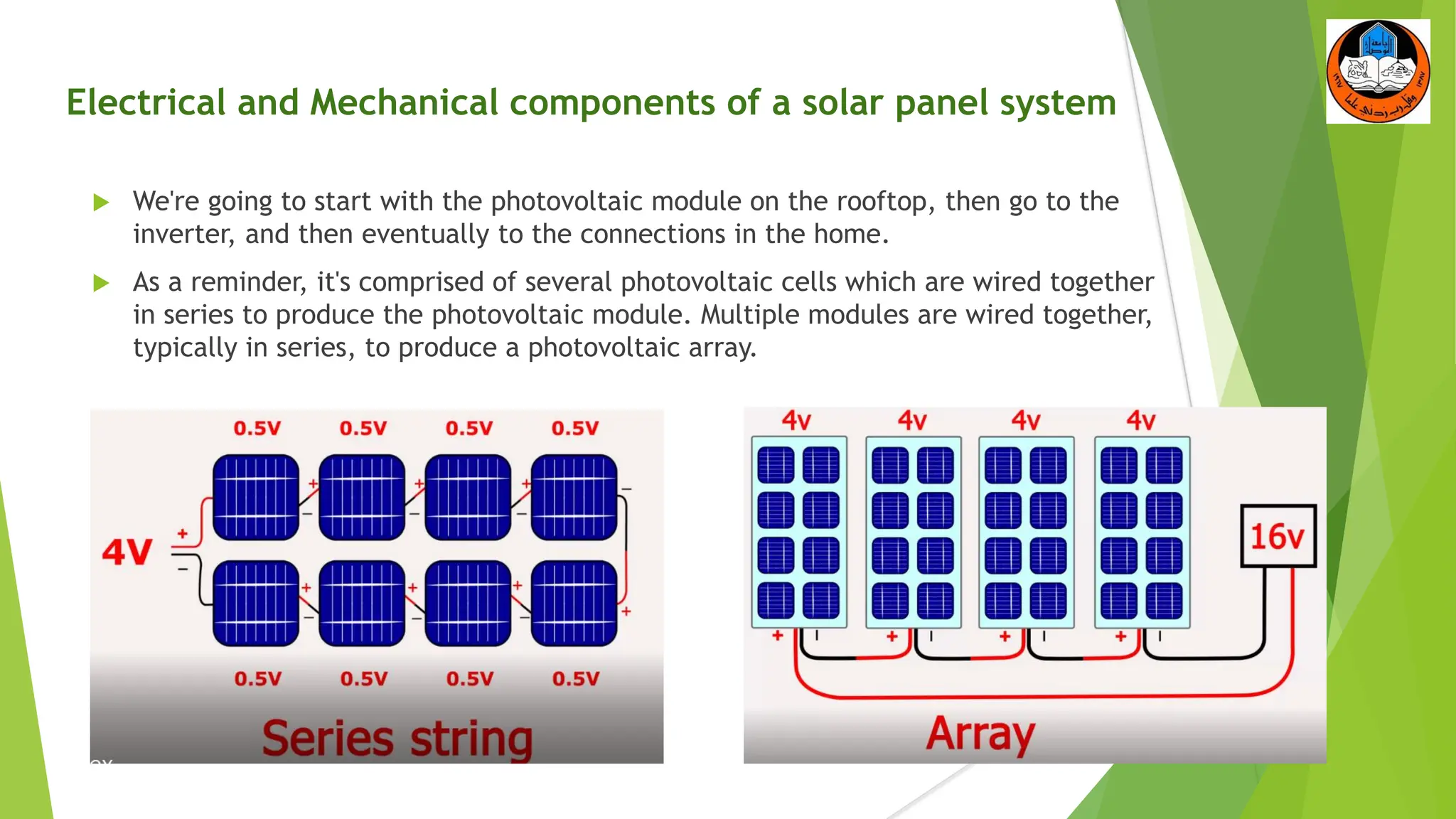
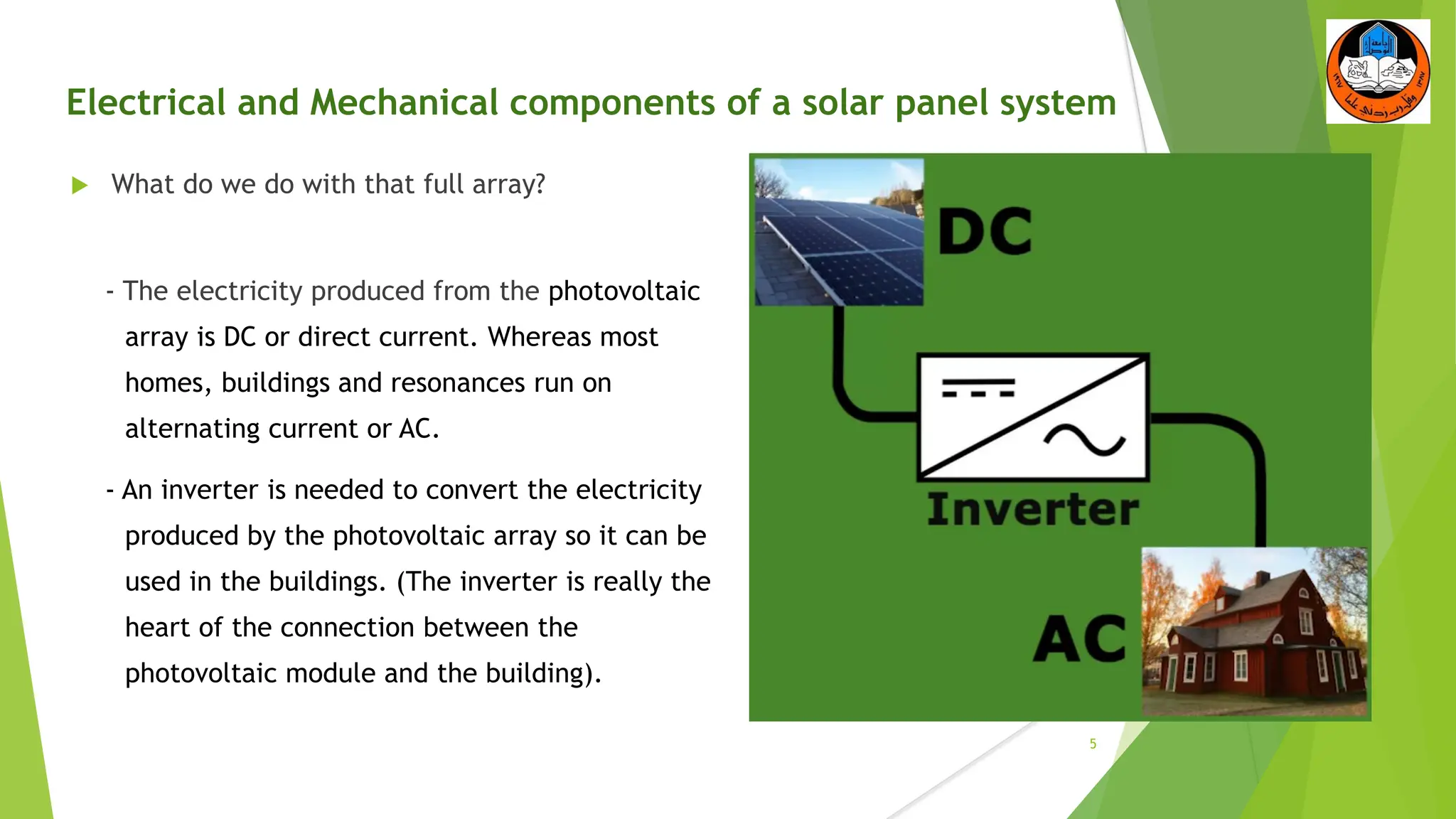
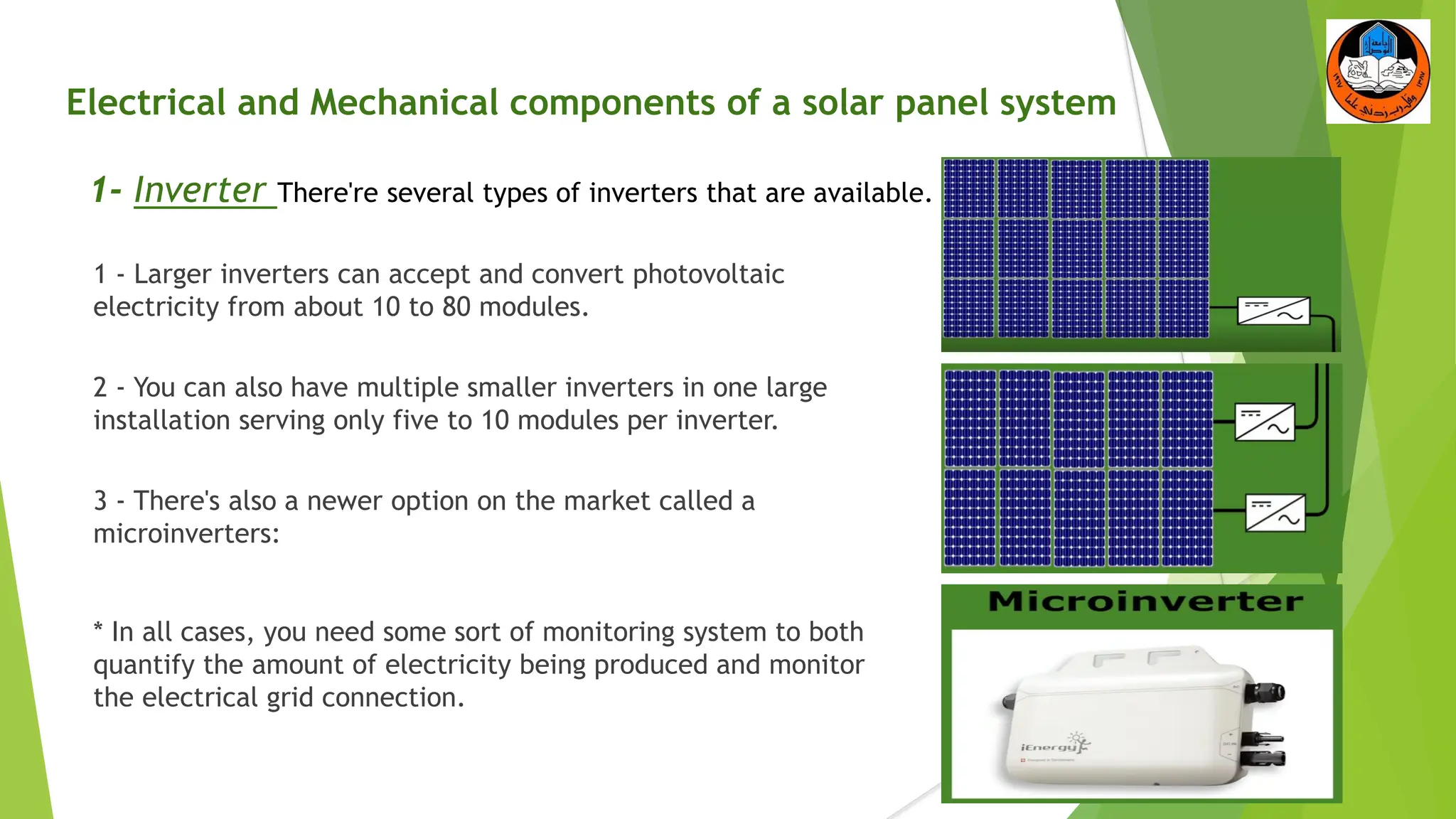
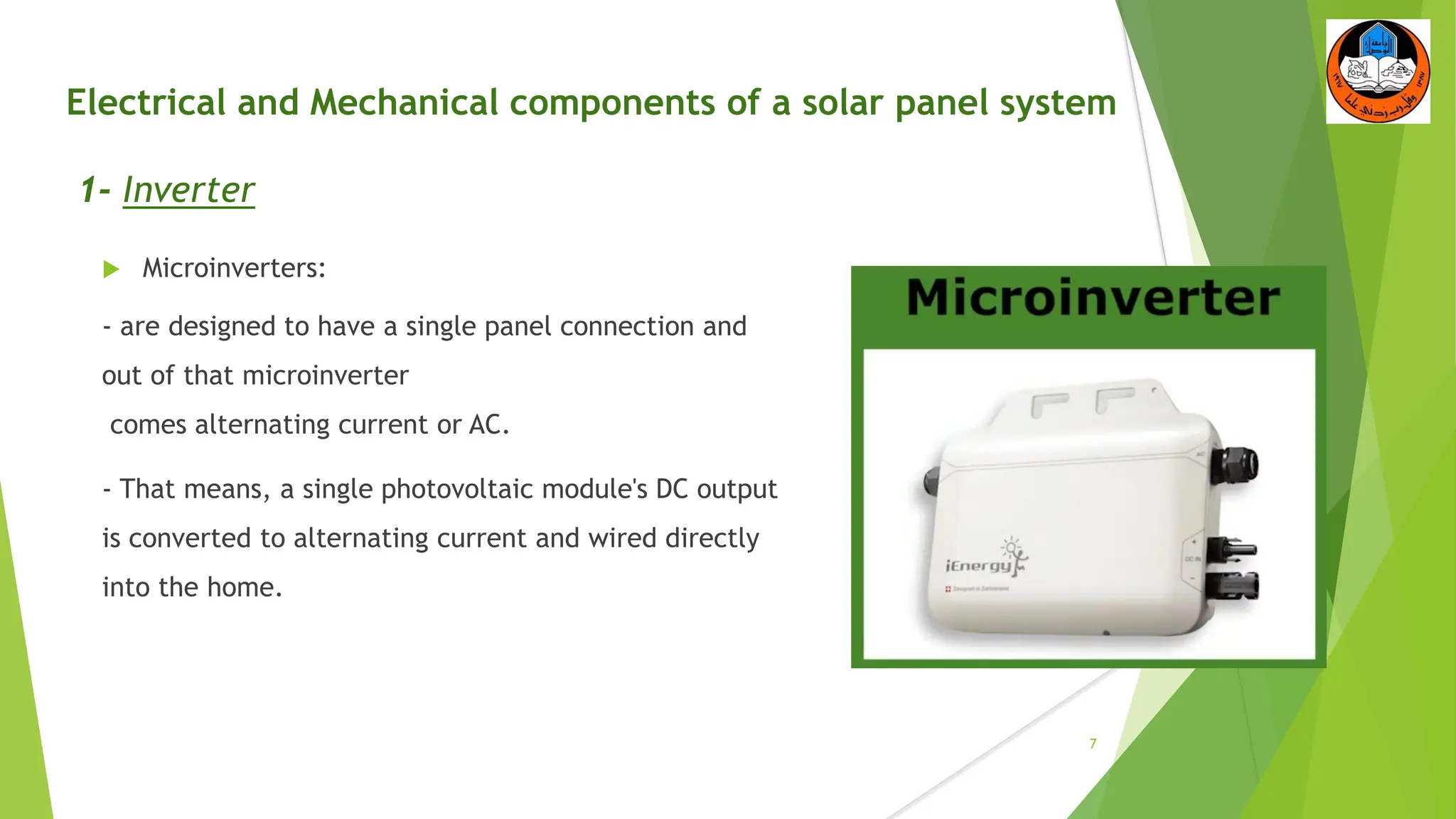
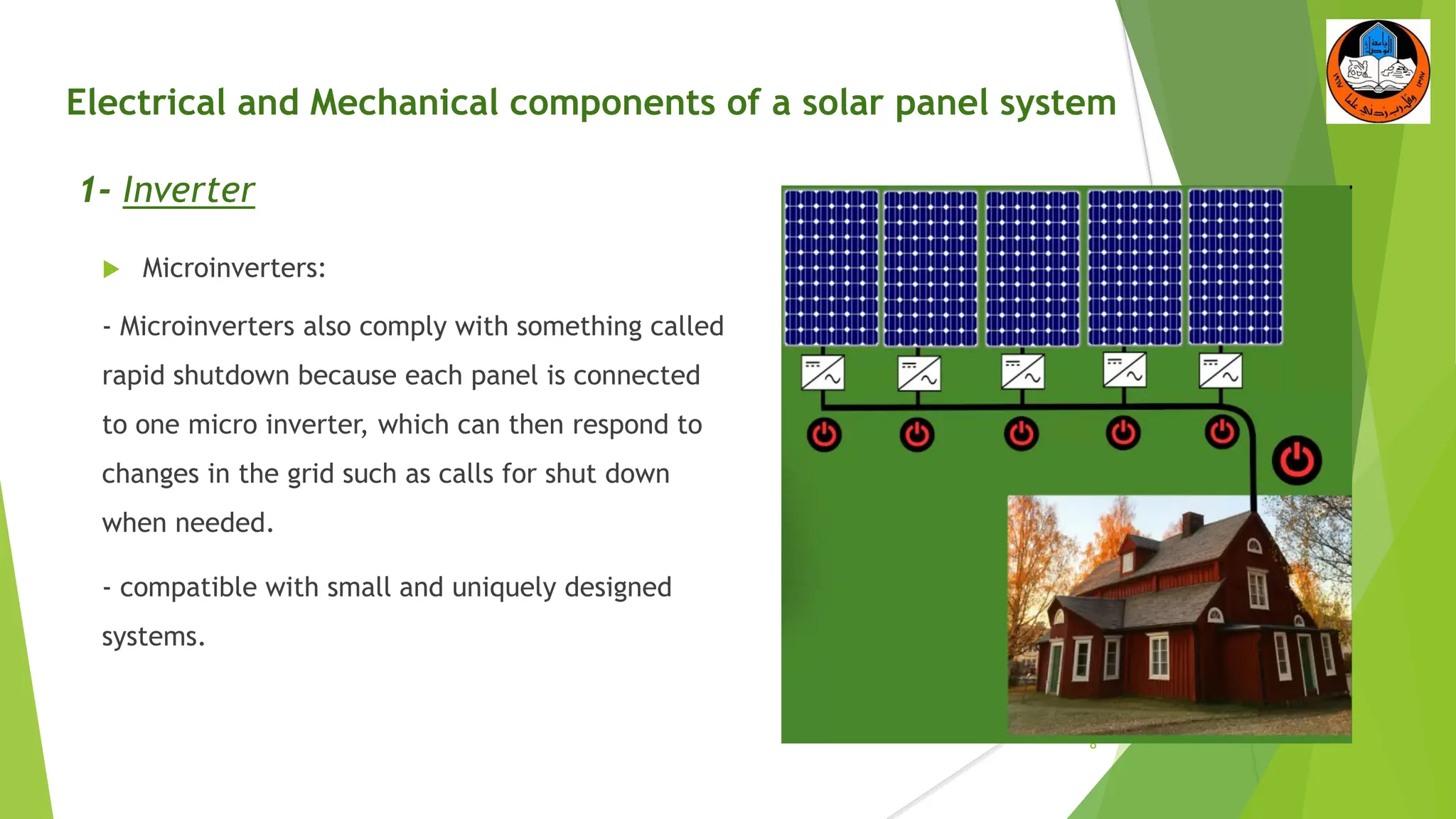
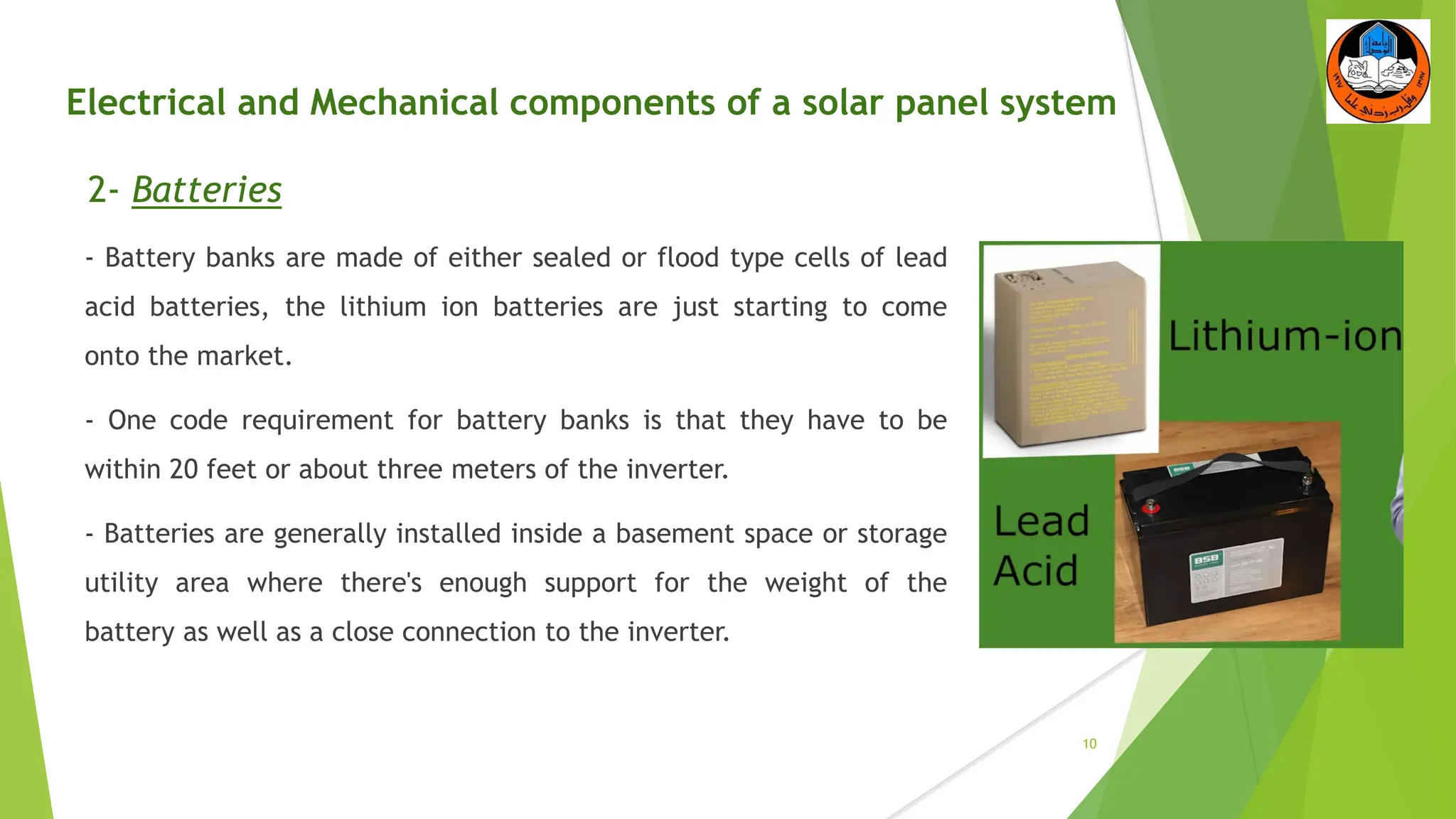
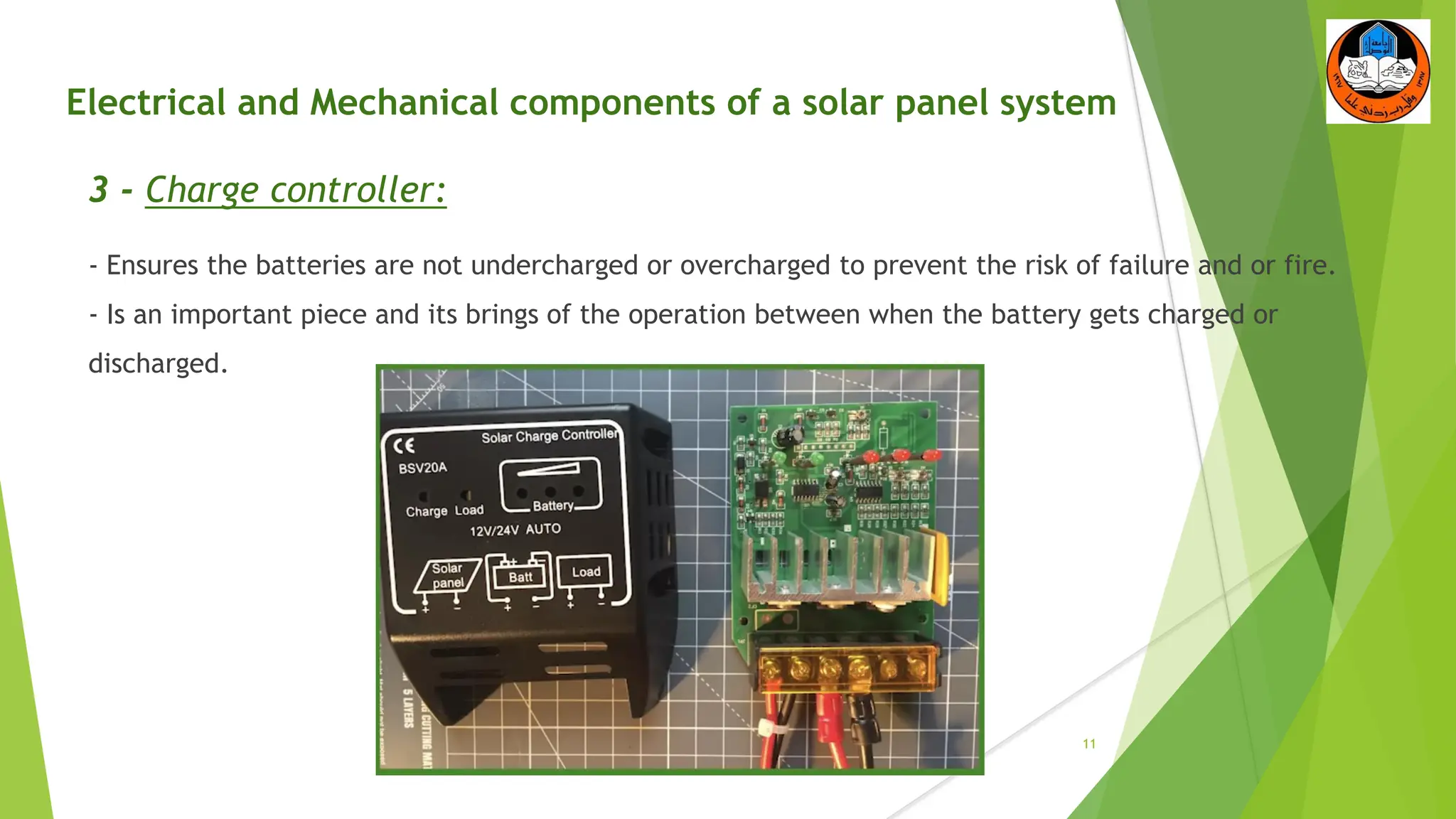
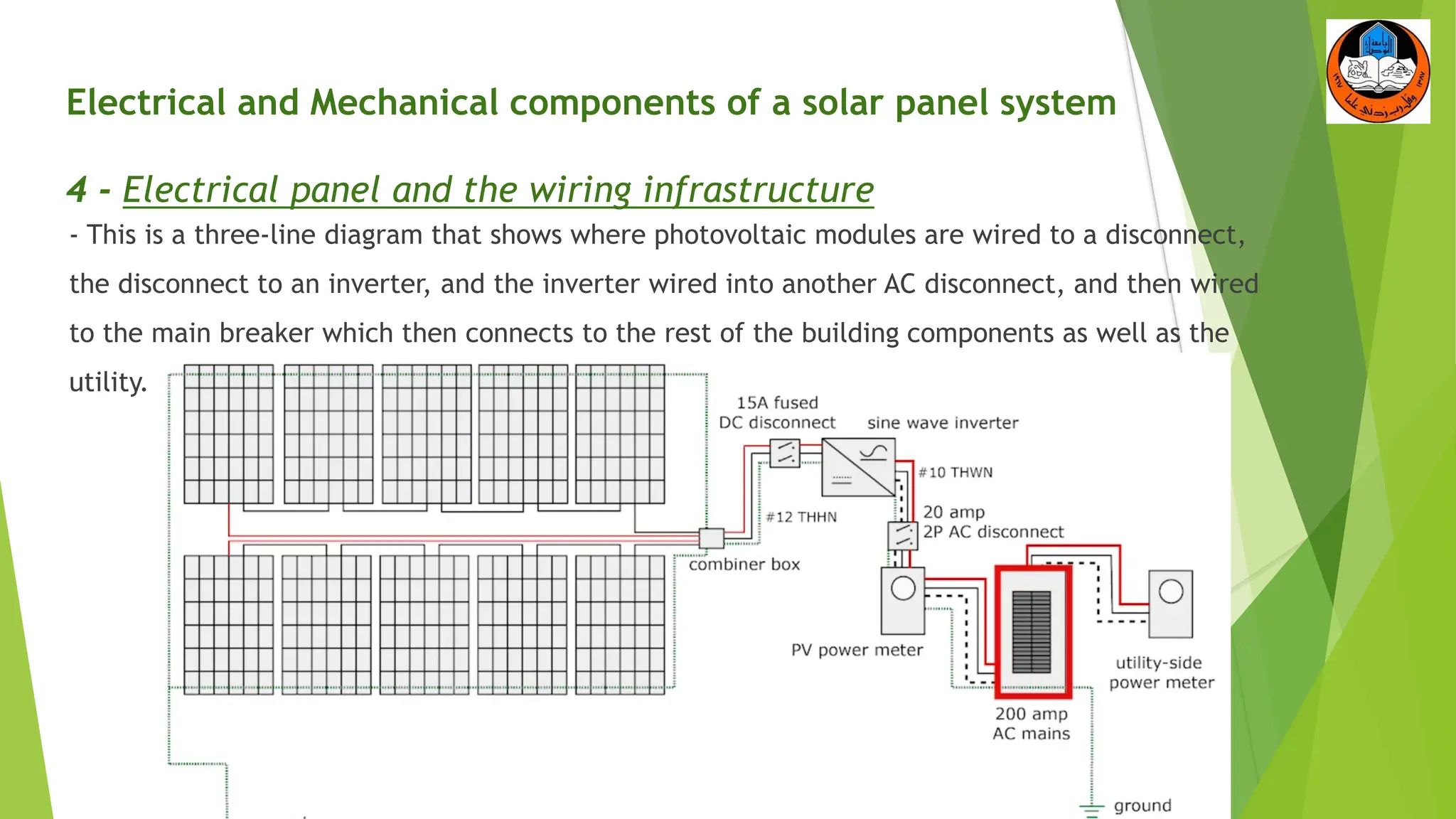
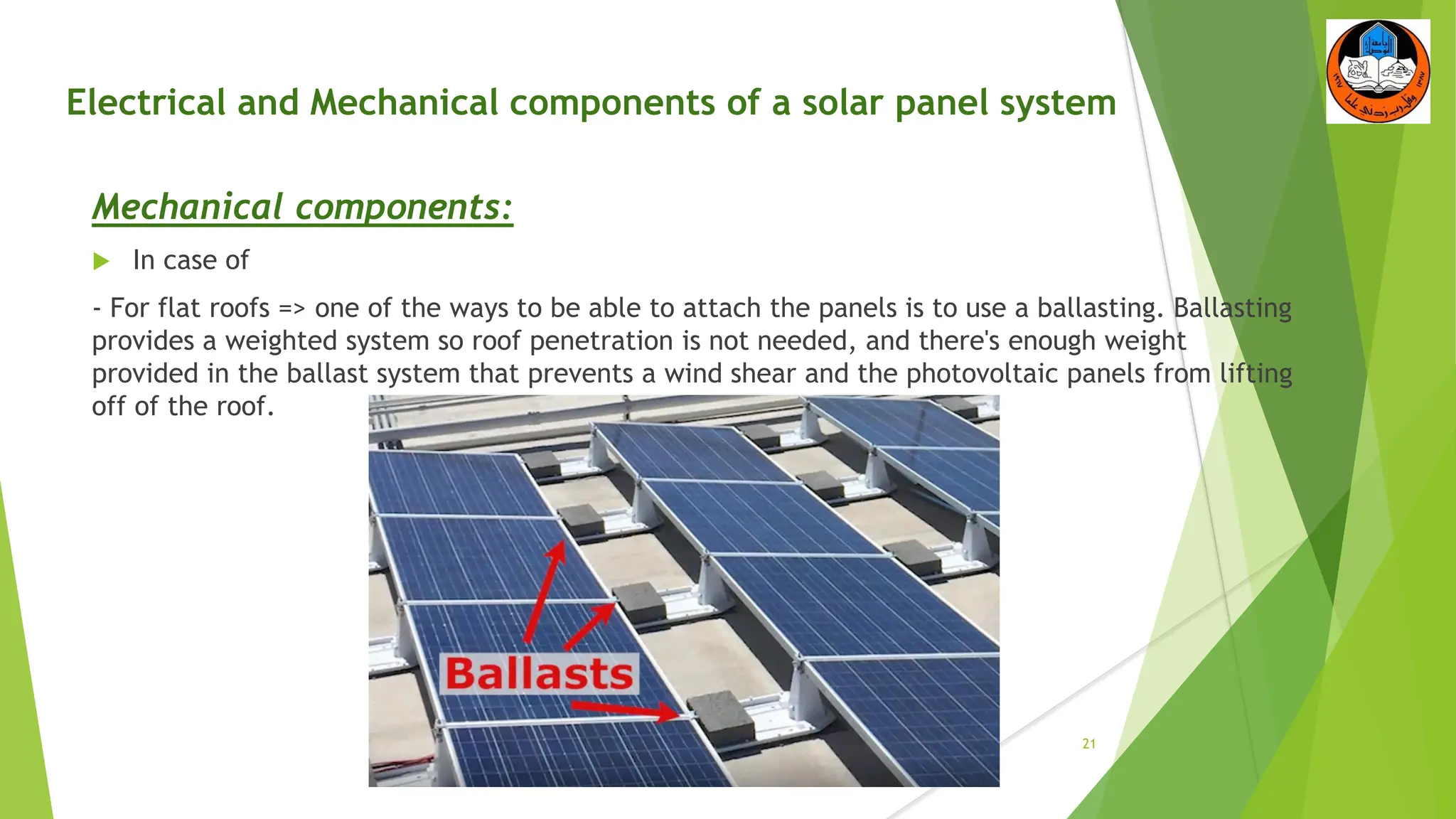
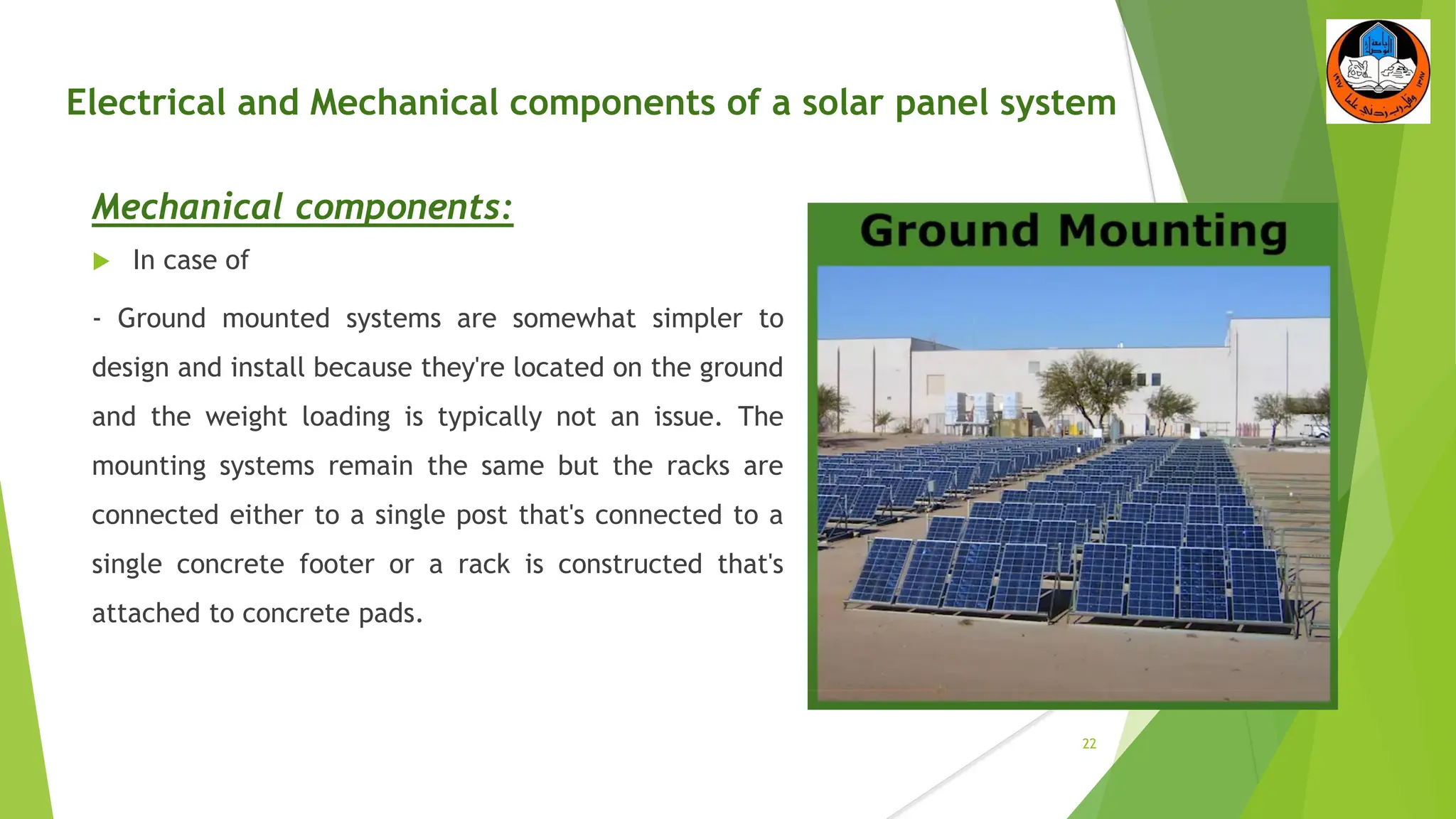
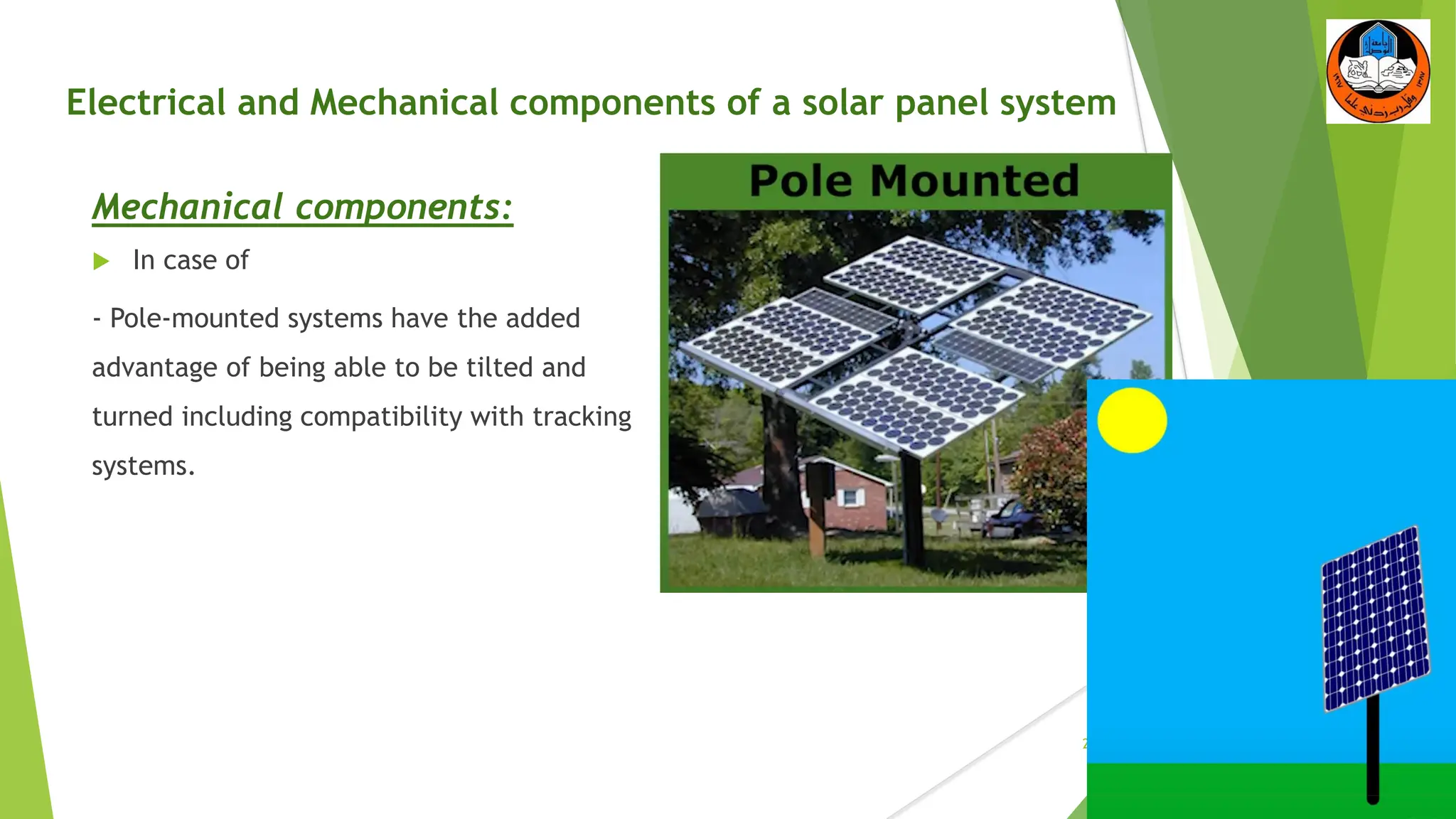
The document discusses the electrical and mechanical components of a solar panel system. It identifies the major photovoltaic components as the solar panel, inverter, battery, and charge controller. The inverter converts the direct current from the solar panels to alternating current used in homes. Other components include the mounting system that attaches the solar panels to the roof or ground, wiring that connects all the parts, and electrical protections required by code. Proper installation of both the electrical and mechanical components is needed to safely implement a functioning solar energy system.