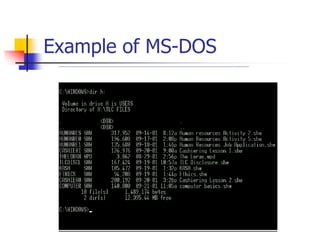
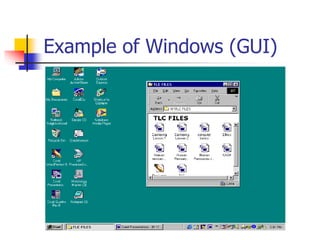
This document describes the major internal and external components of a computer system. It explains that computers contain hardware components like the central processing unit (CPU) and memory chips, as well as input/output devices. The CPU interprets and executes program instructions. Other hardware includes the computer case, monitor, keyboard, mouse, disk drives, network cards, and printers. The document also discusses software components like operating systems, which connect hardware and allow users to interact with programs. Examples of operating systems are MS-DOS and Windows.