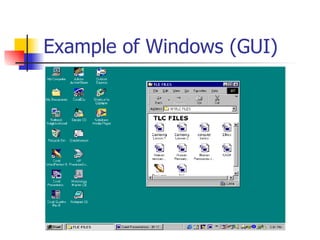
The document describes the major hardware and software components that make up a computer system. It explains that hardware refers to the physical parts like the processor, memory, input/output devices, and storage devices. The CPU or processor is the central component that interprets and executes instructions. Other hardware includes the computer case, monitor, video card, keyboard, mouse, drives, hard disk, RAM, printer, and networking components. The document also introduces software programs like the operating system which provides instructions to the CPU and allows users to interact with the computer and its components.