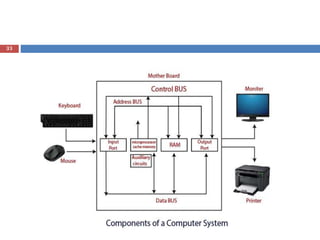
The document provides an introduction to computers, including definitions, characteristics, evolution, and components. It defines a computer as an electronic device that processes data according to instructions. Computers are characterized by their speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility, reliability, and multitasking abilities. The document outlines the five generations of computers from vacuum tubes to modern microprocessors. It also includes a block diagram showing the main components of a computer system including the CPU, memory, and input/output devices.