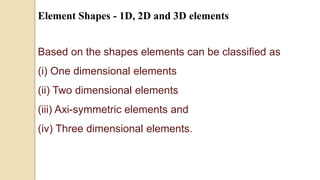
This document discusses computer aided engineering and finite element analysis. It introduces computer aided engineering tools like pre-processors, solvers, and post-processors used in product development. It also discusses one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional elements used in finite element analysis. Finally, it covers shape functions, coordinate systems, and nodal unknowns which are used to relate field variables within an element to the values at its nodal points.