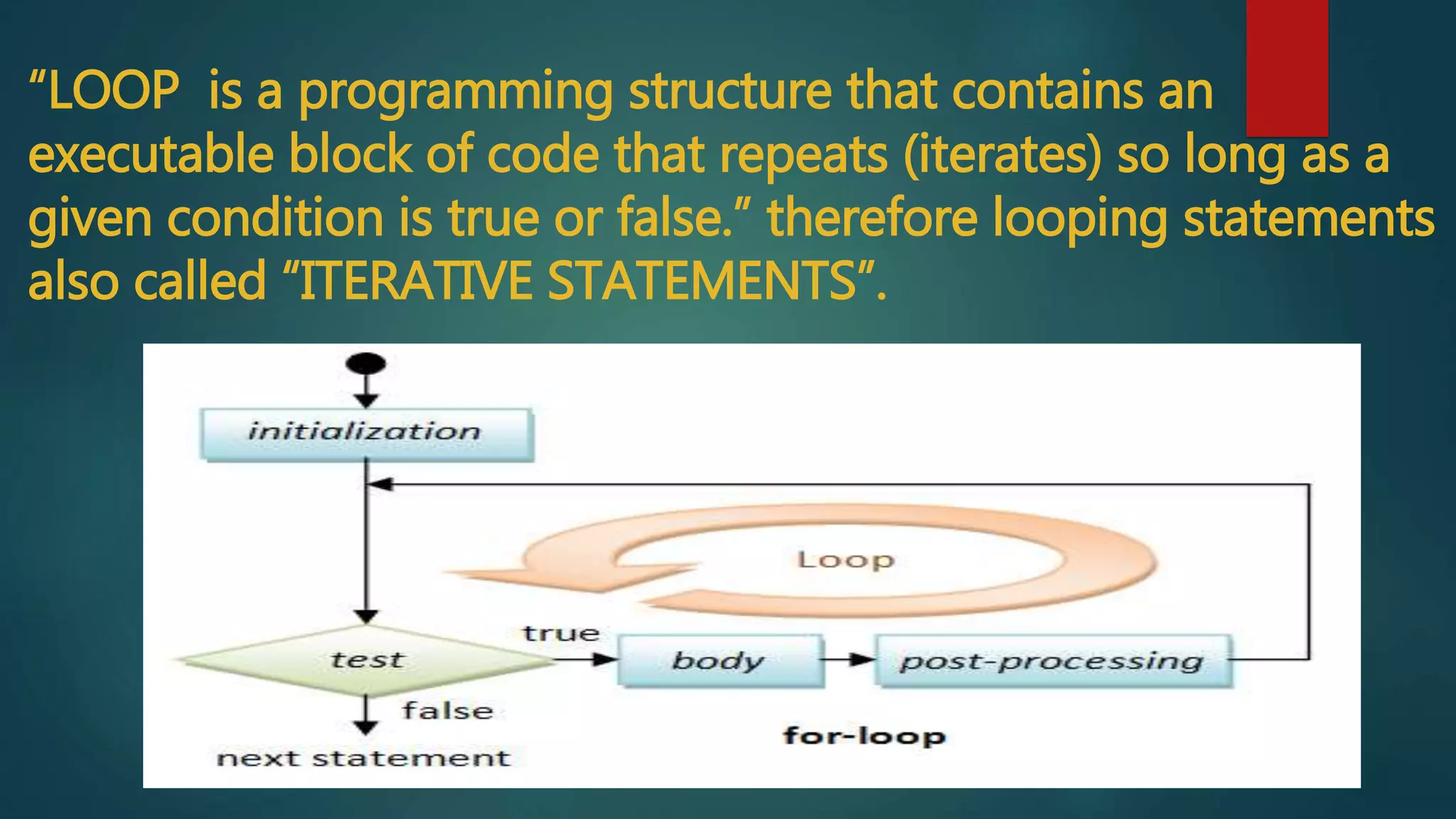
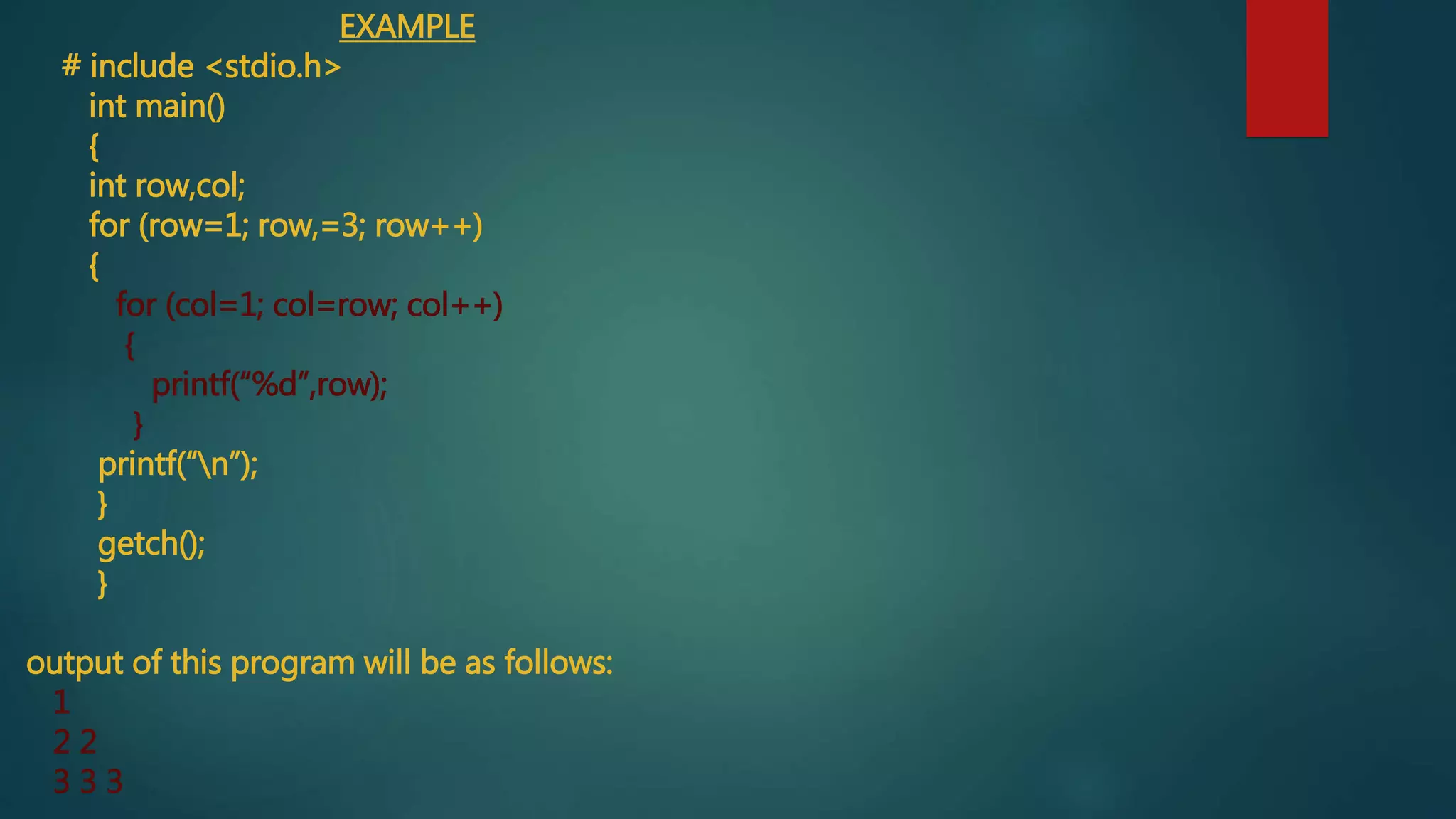
This document discusses different types of looping statements in programming. It begins by defining a loop as a programming structure that repeats a block of code as long as a condition is true or false.
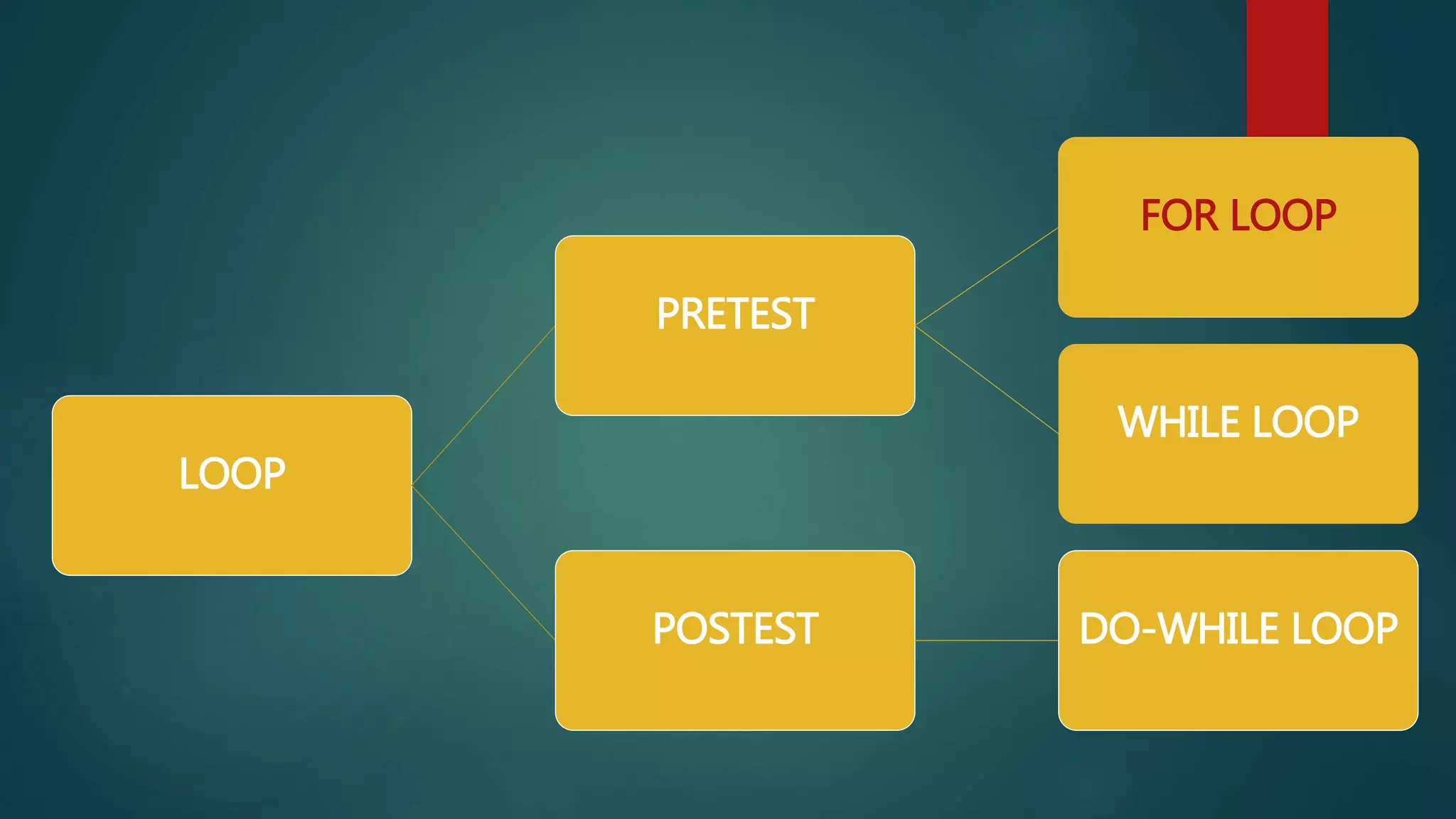
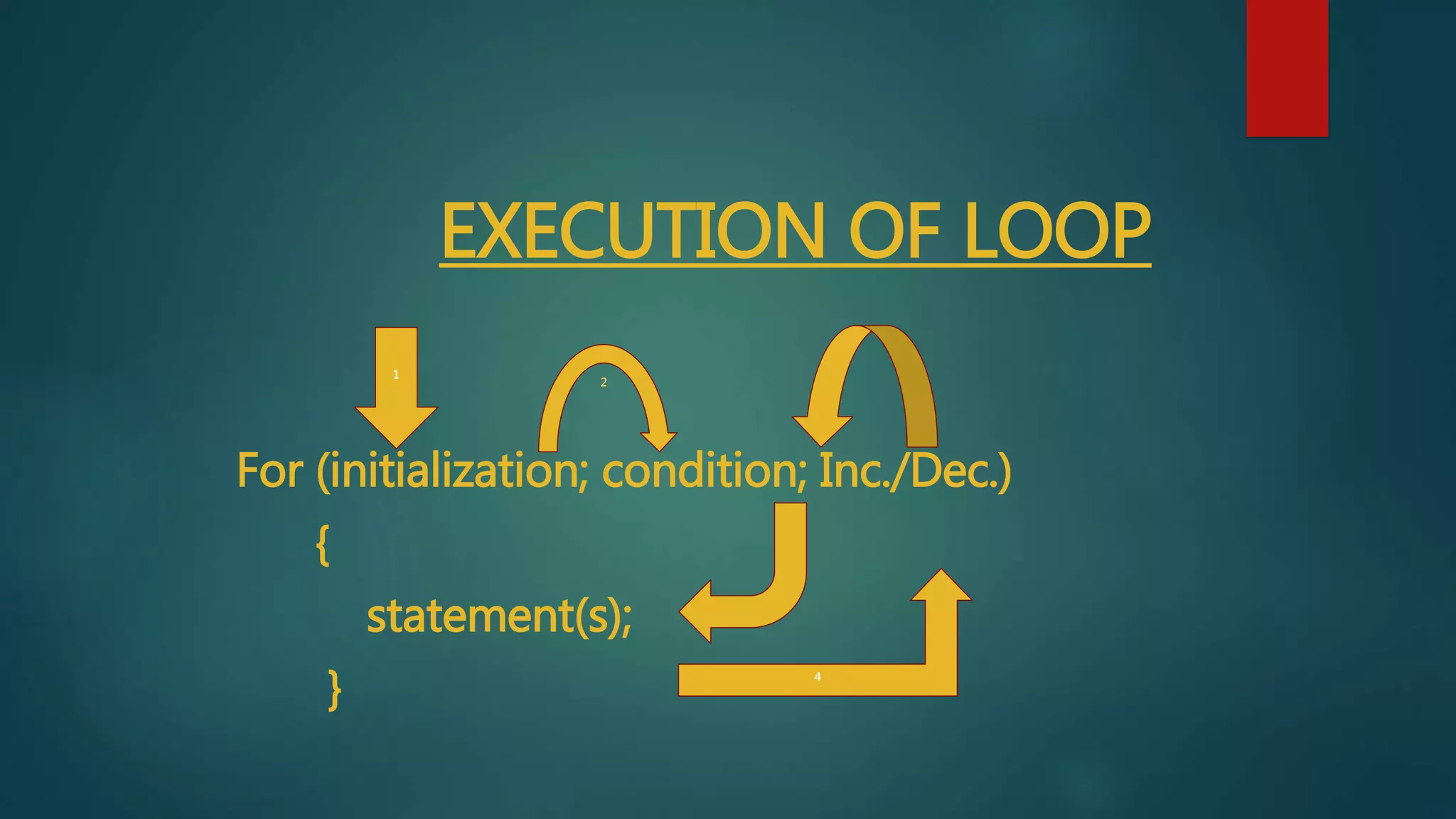
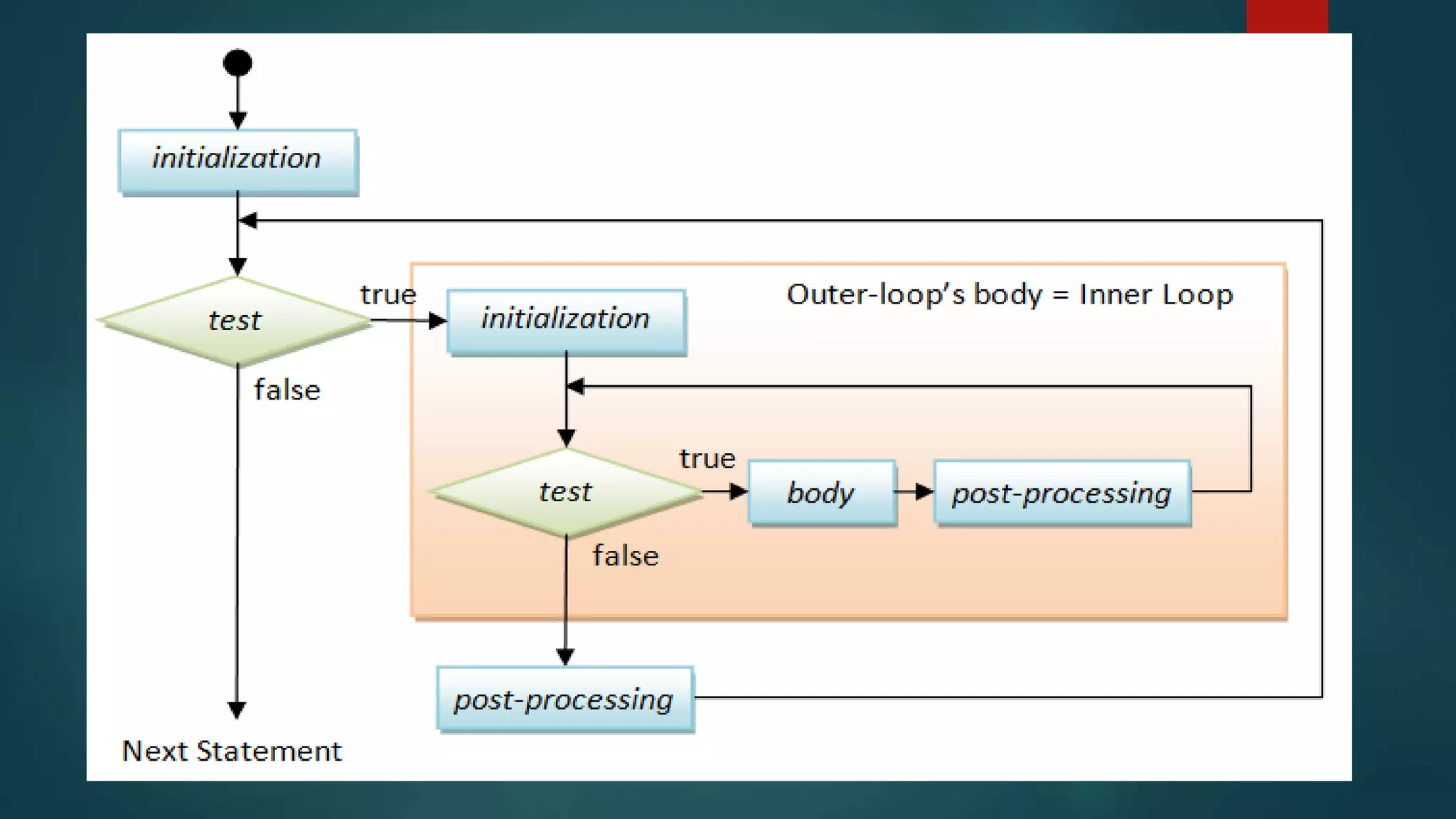
It then describes three common loop types: for loops, which check a condition before each iteration; while loops, which check at the end of each iteration; and do-while loops, which check at the end but run the code block at least once. Nested loops, where one loop is placed within another, are also discussed. Examples are provided to demonstrate how each loop type is written and functions.