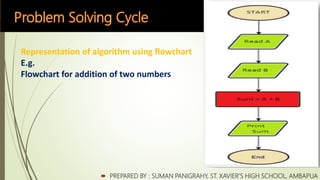
The document discusses computational thinking and problem solving. It introduces computational thinking as a problem solving process that uses computers. The key aspects of computational thinking covered are decomposing problems, recognizing patterns, and developing step-by-step solutions. The document then covers the main steps of the problem solving cycle: defining the problem, designing the solution through algorithms, flowcharts or pseudocode, and implementing the solution. It provides examples and differences between algorithms, flowcharts and pseudocode for representing solutions.