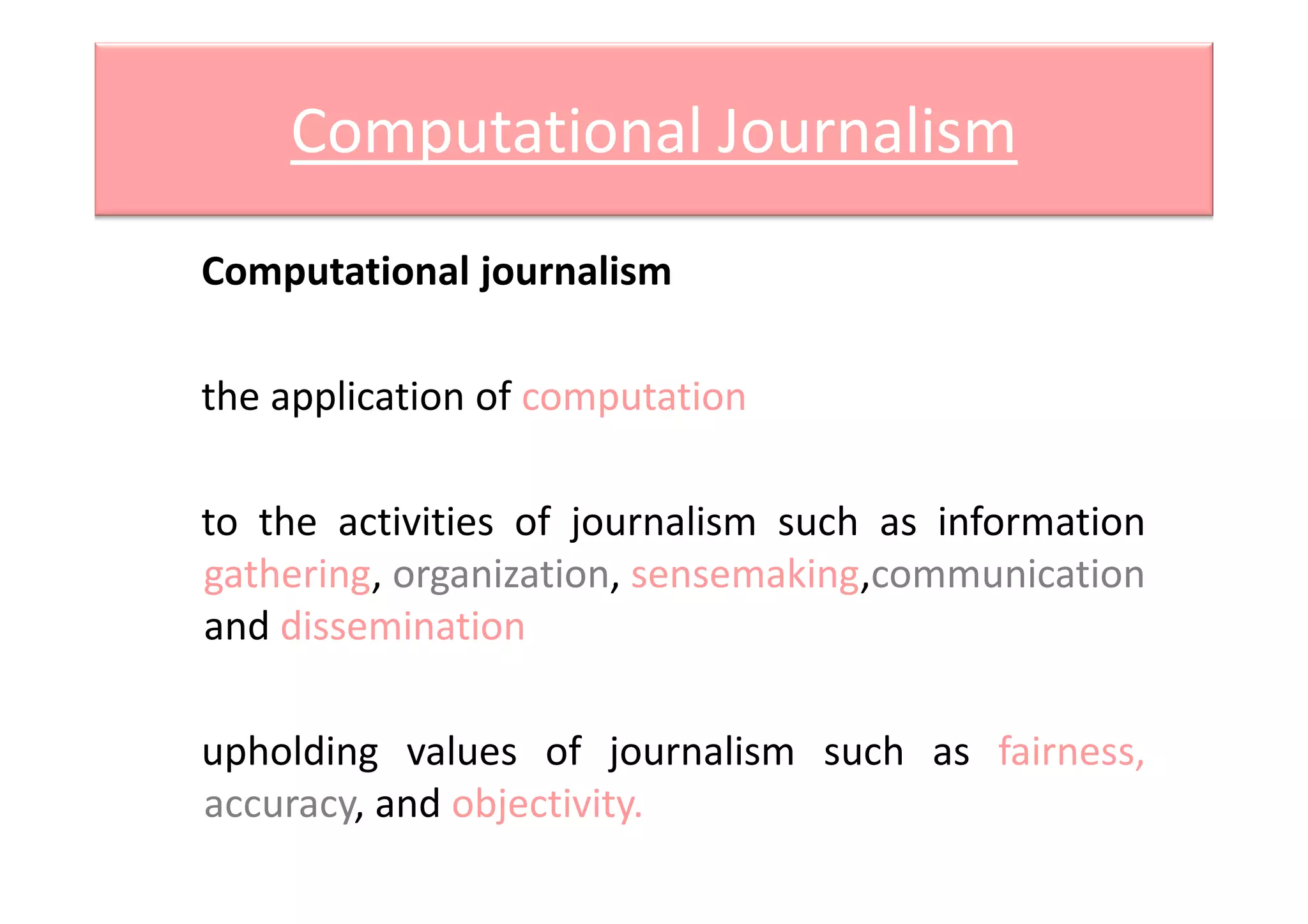
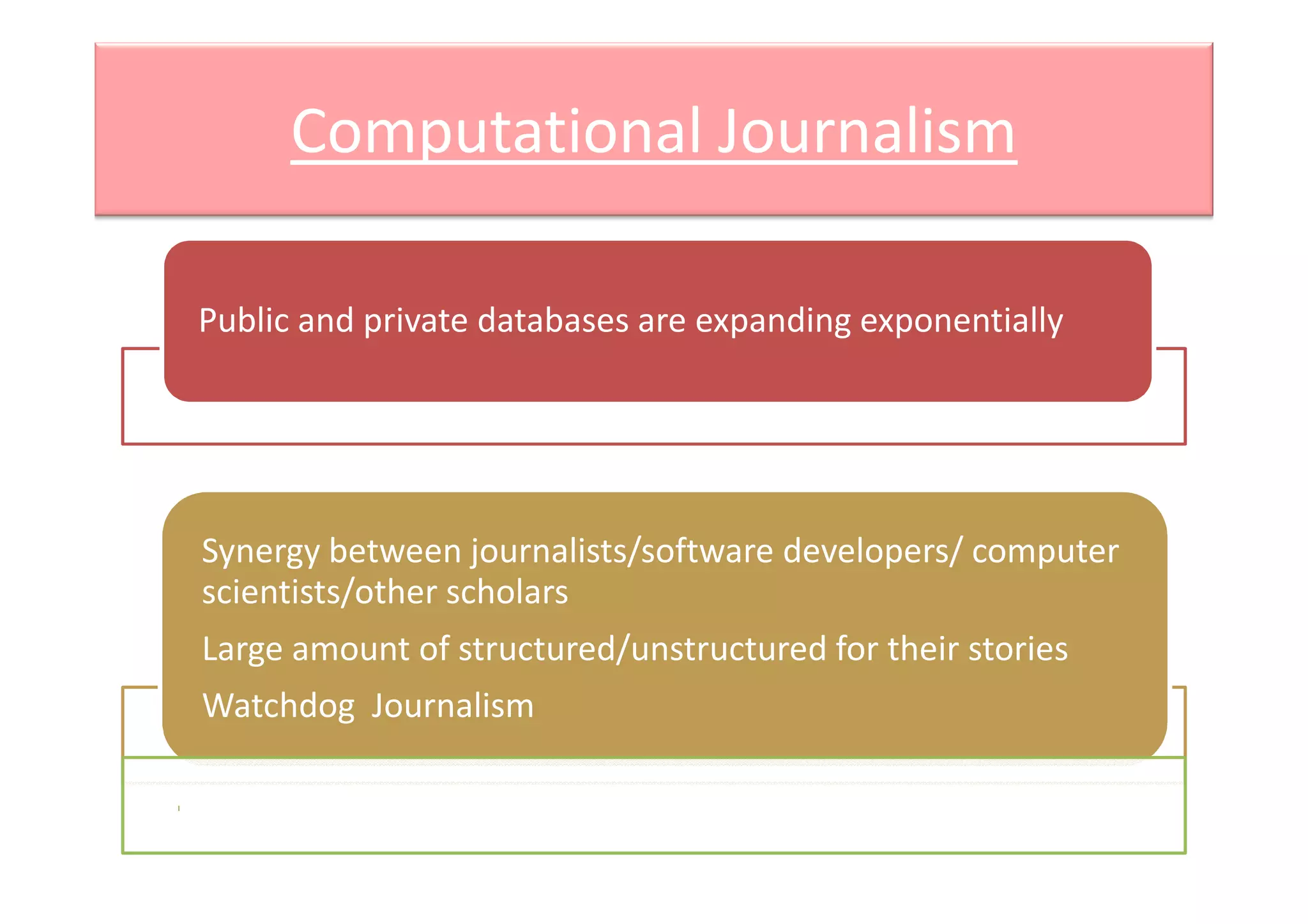
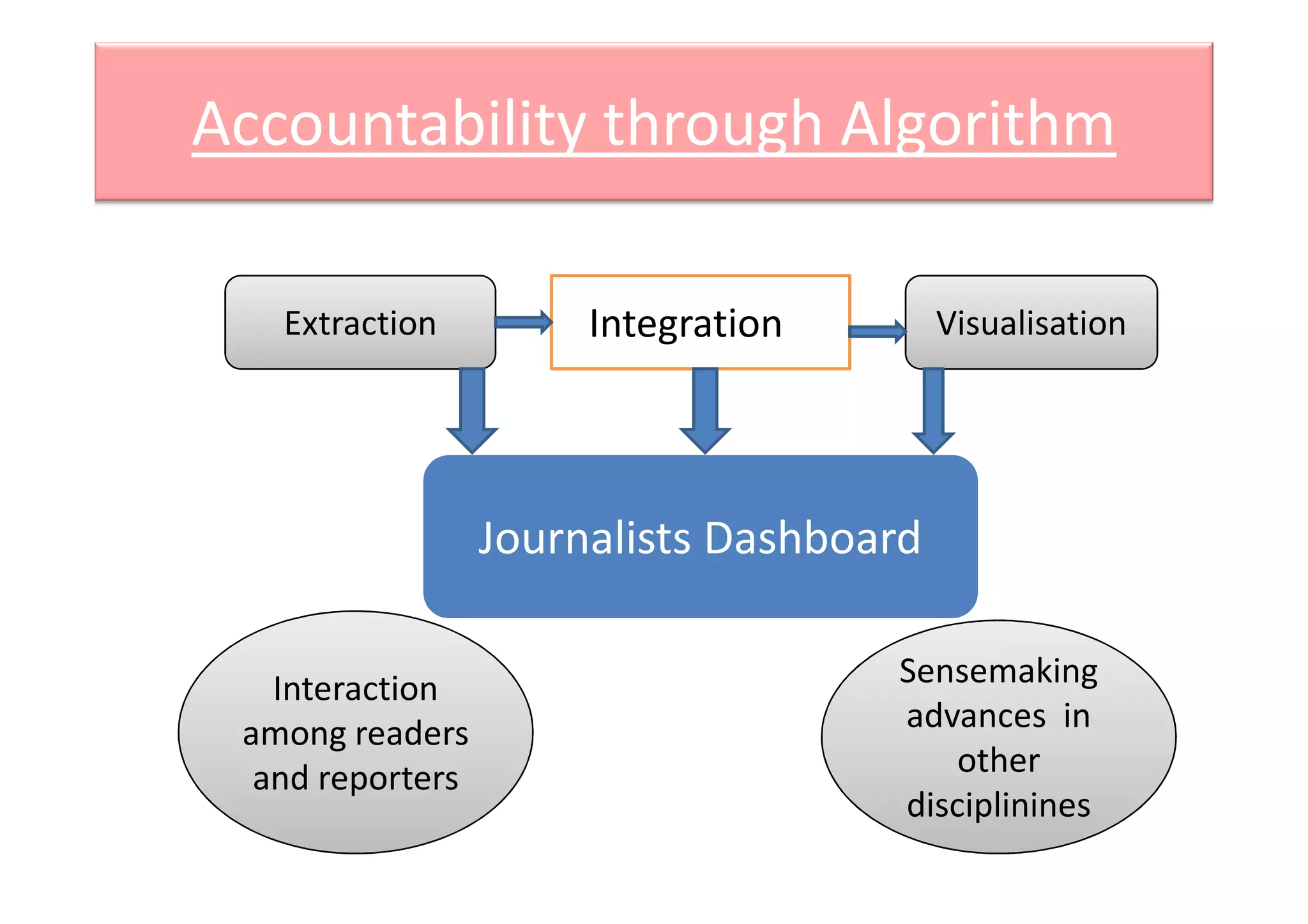
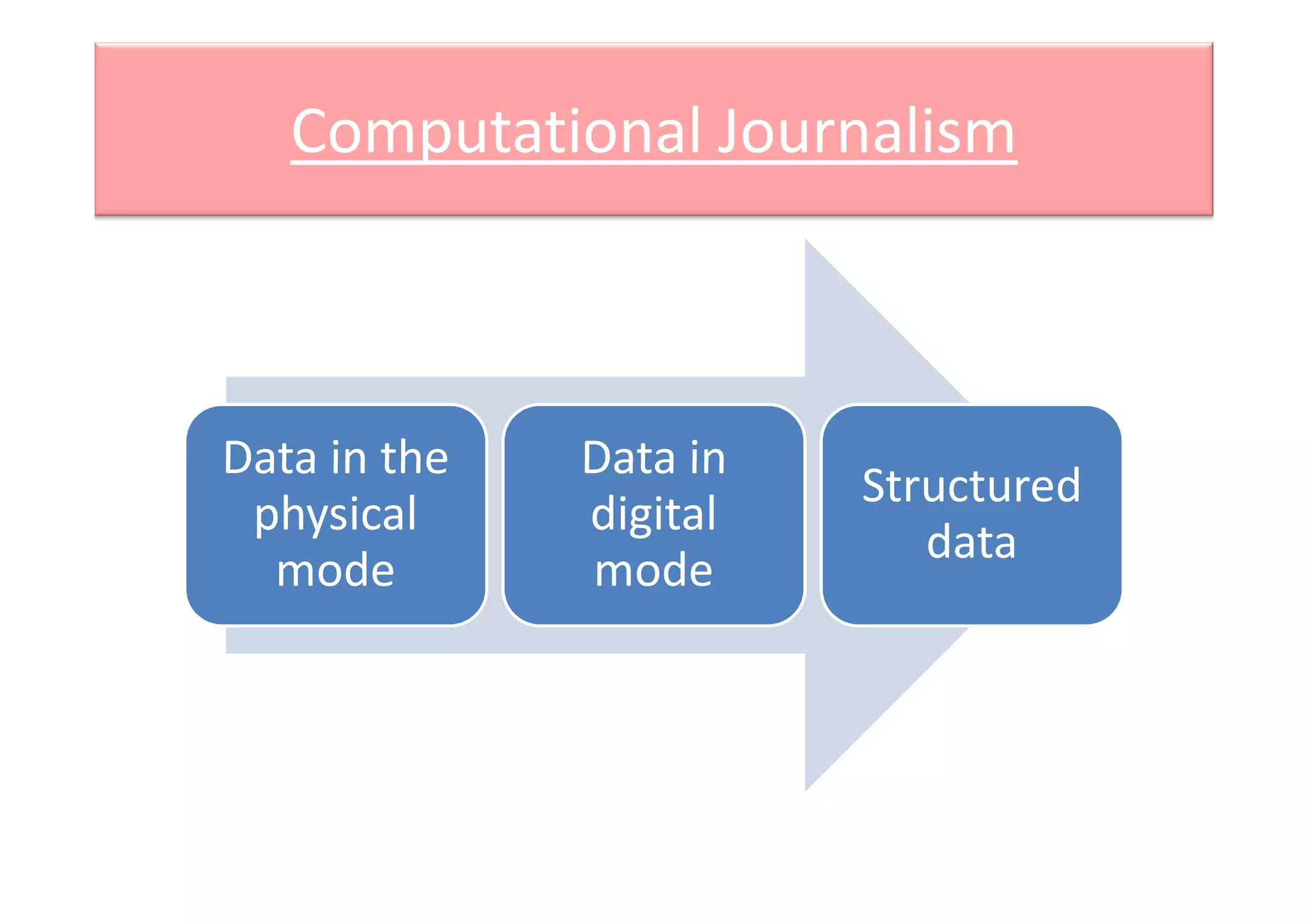
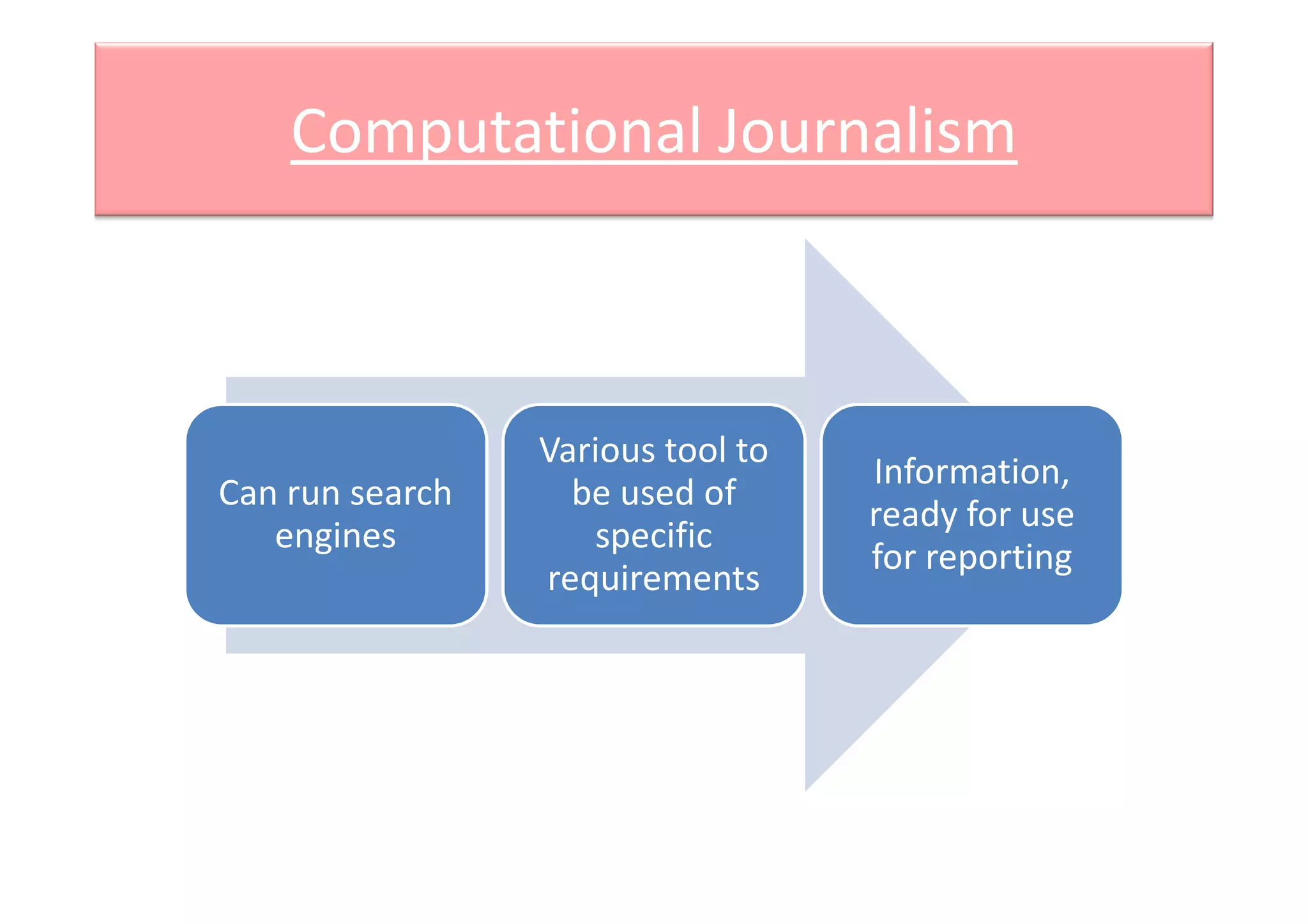
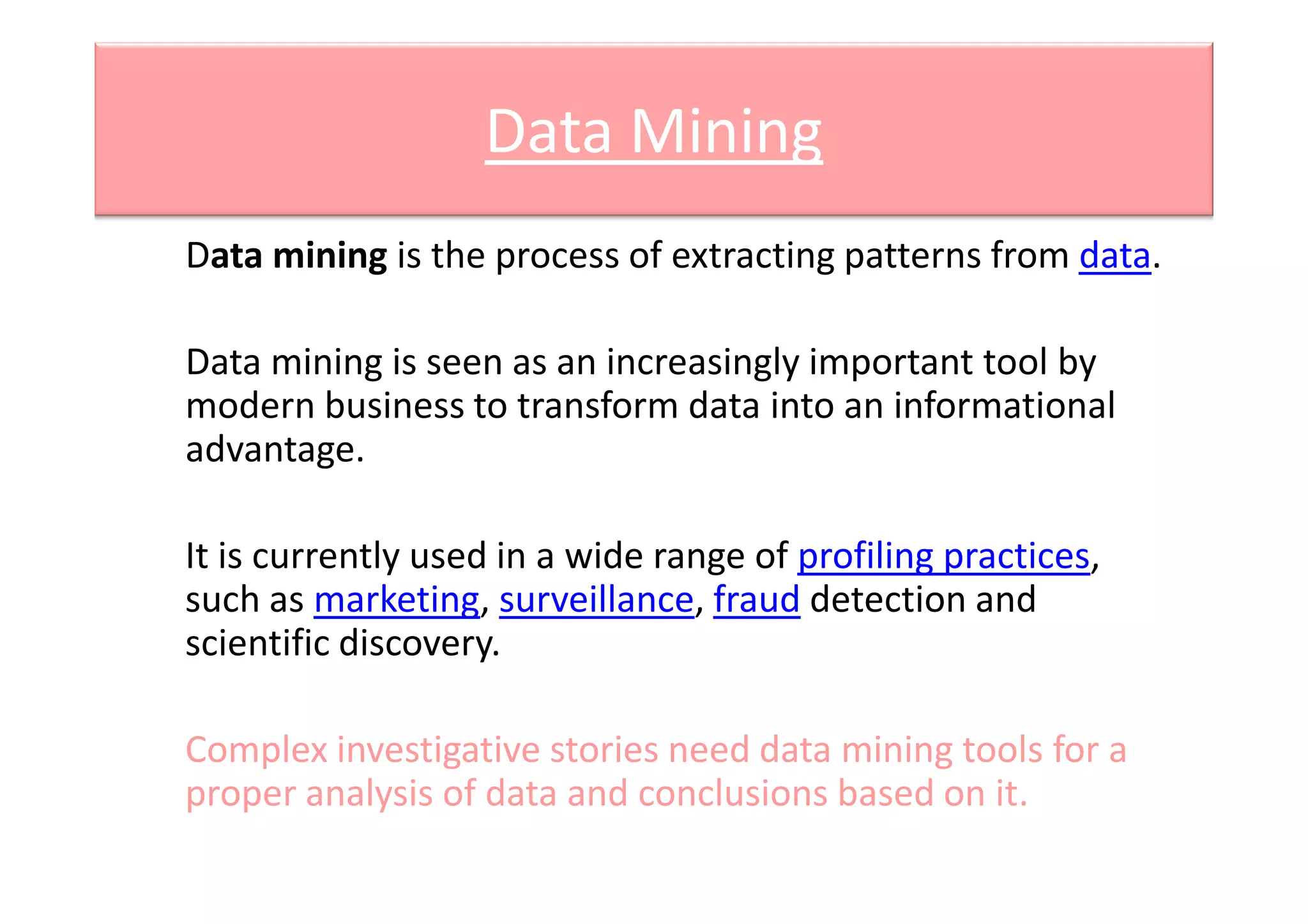
Computational journalism applies computational techniques like artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and data visualization to journalism activities. It helps analyze large amounts of structured and unstructured data from public and private databases to aid watchdog journalism. The field draws on computer science and aims to transform data into information to advance fact-based reporting through tools like digital dashboards for journalists.