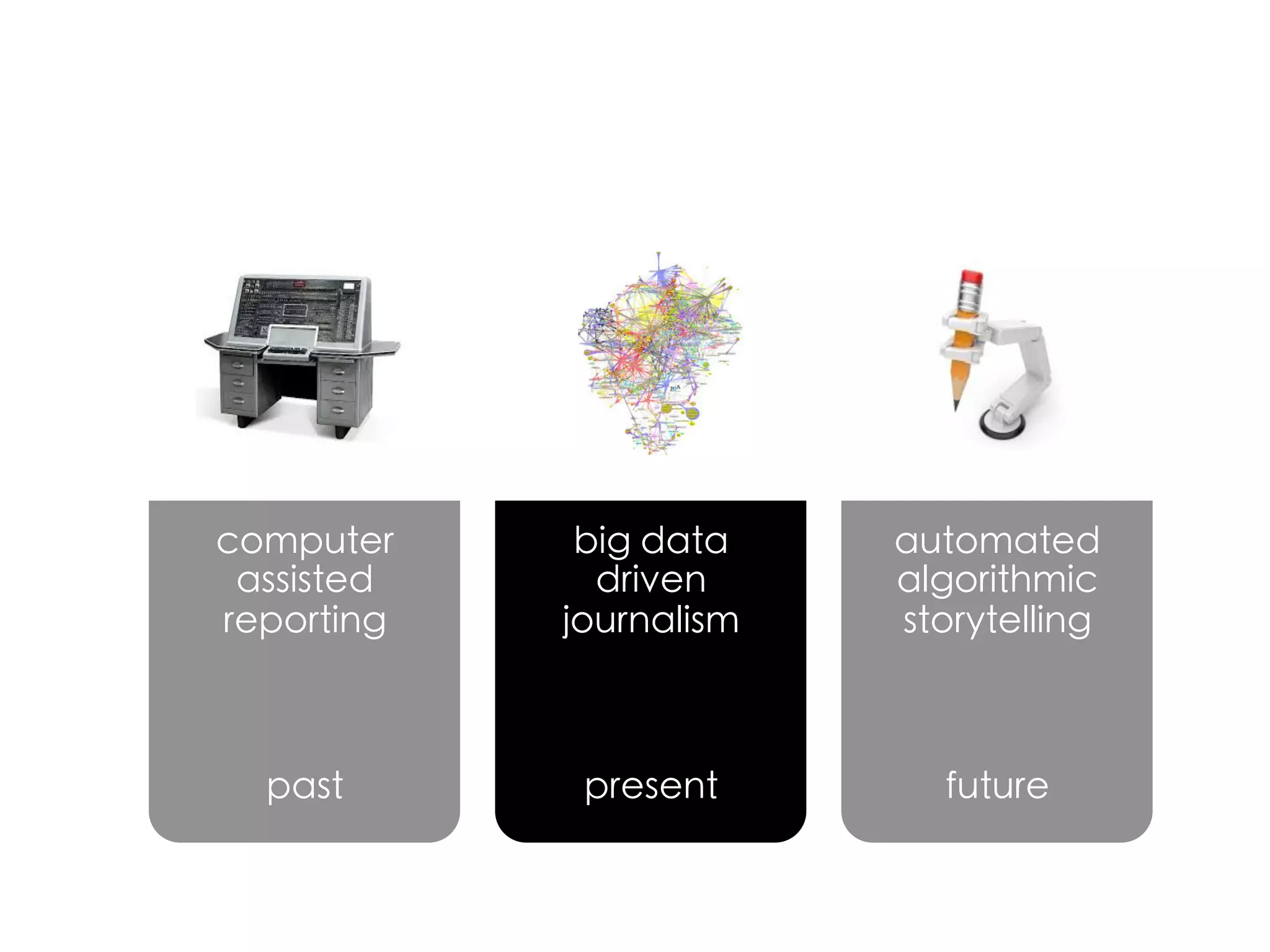
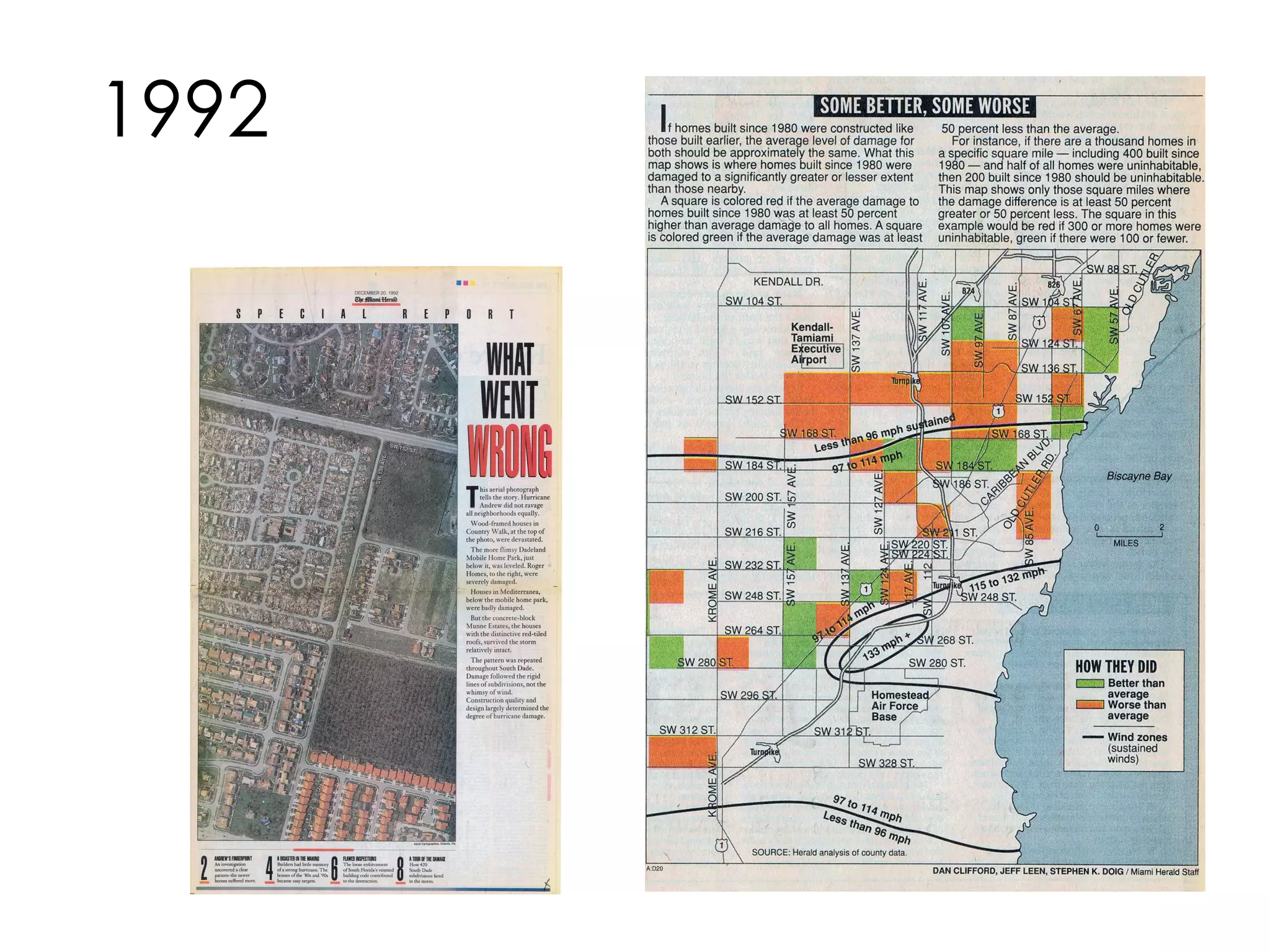
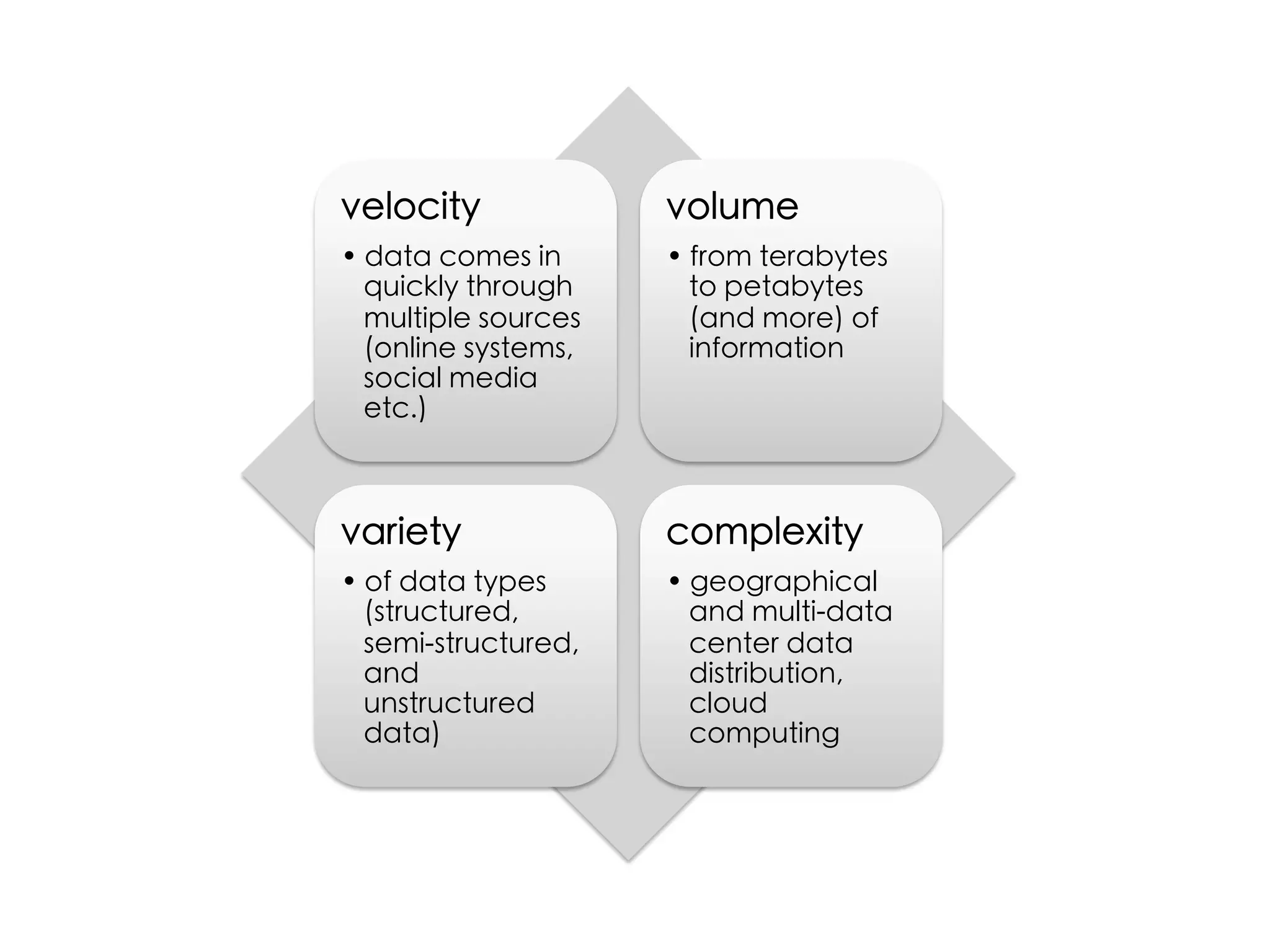
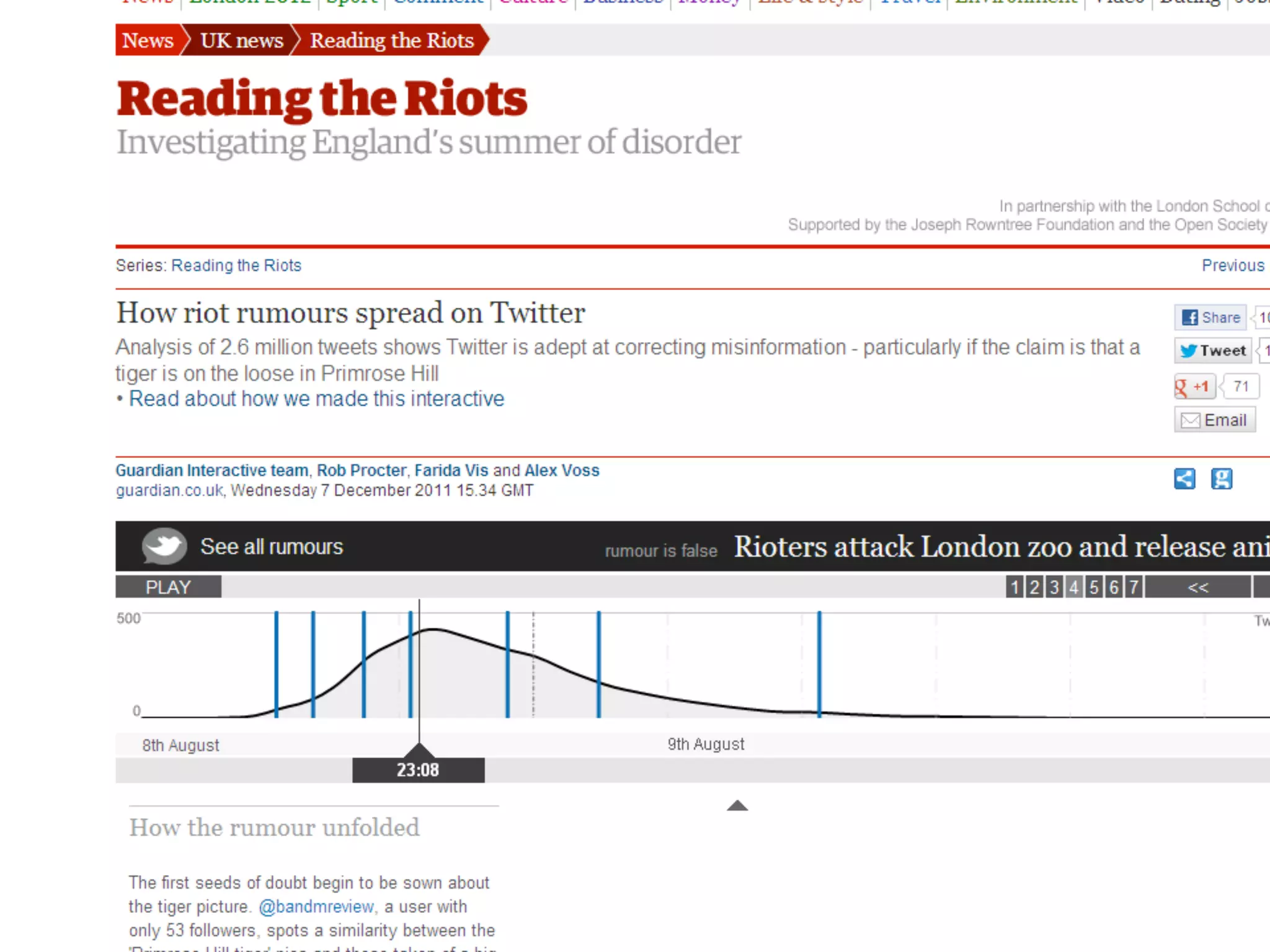
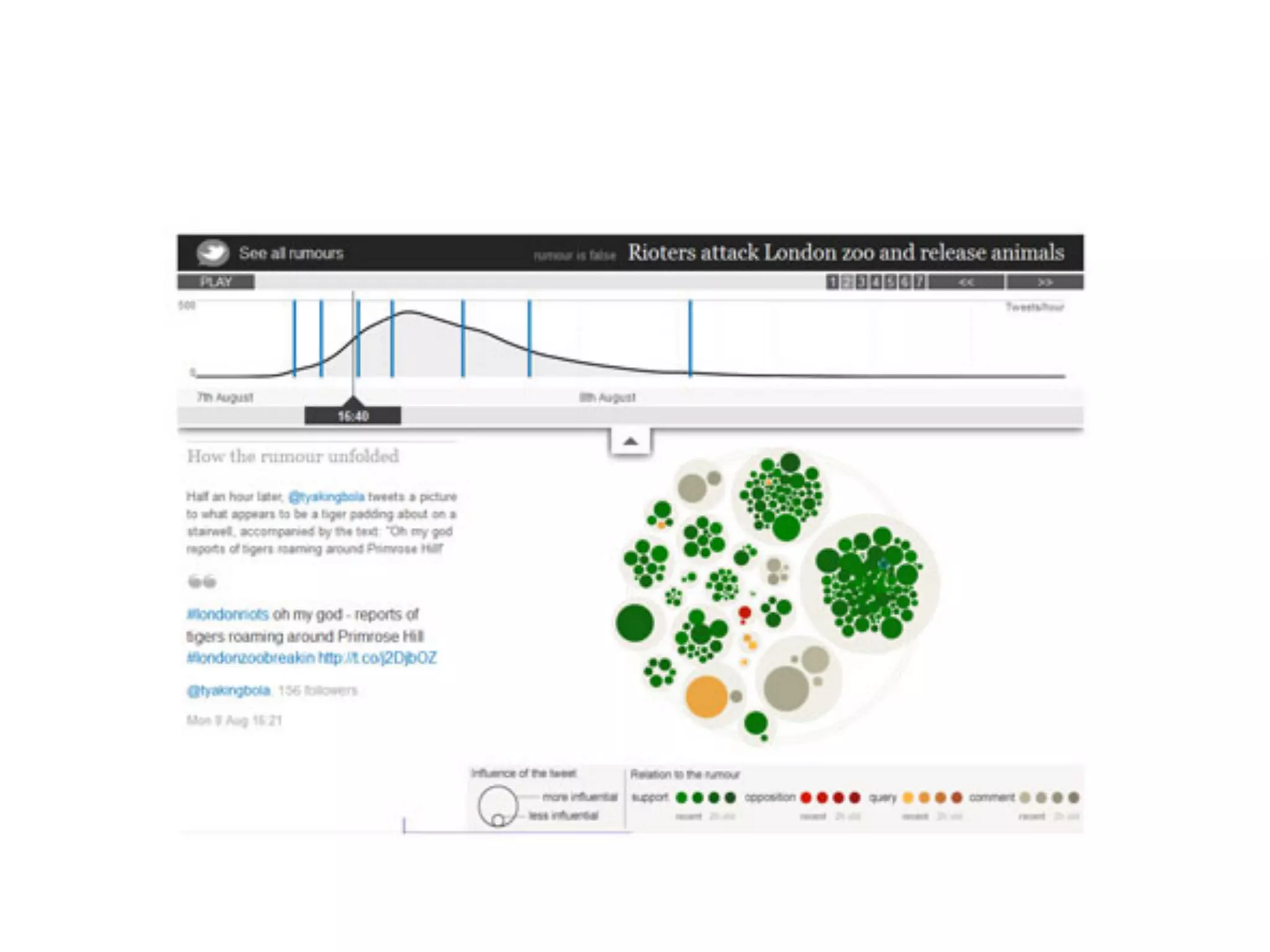
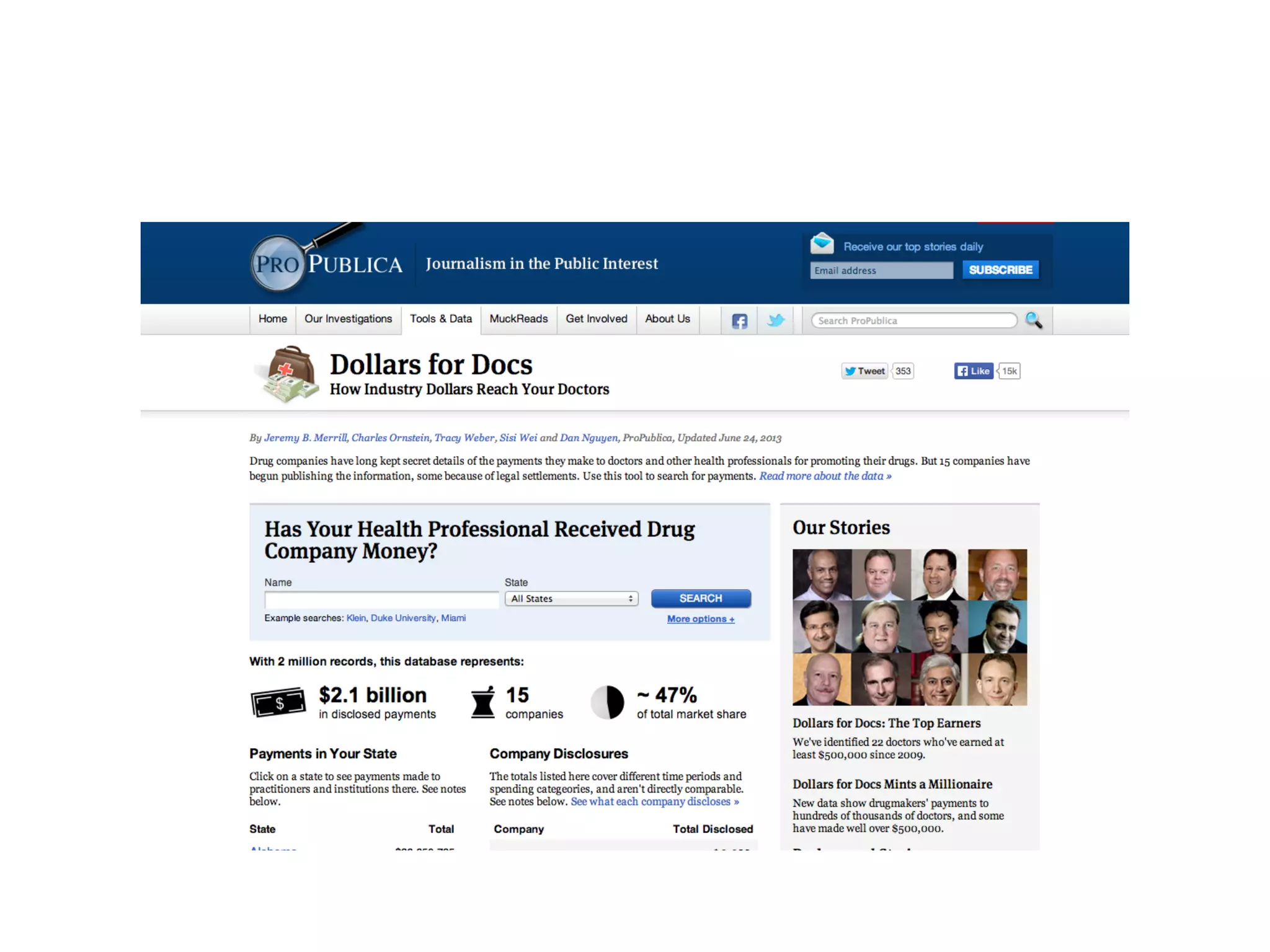
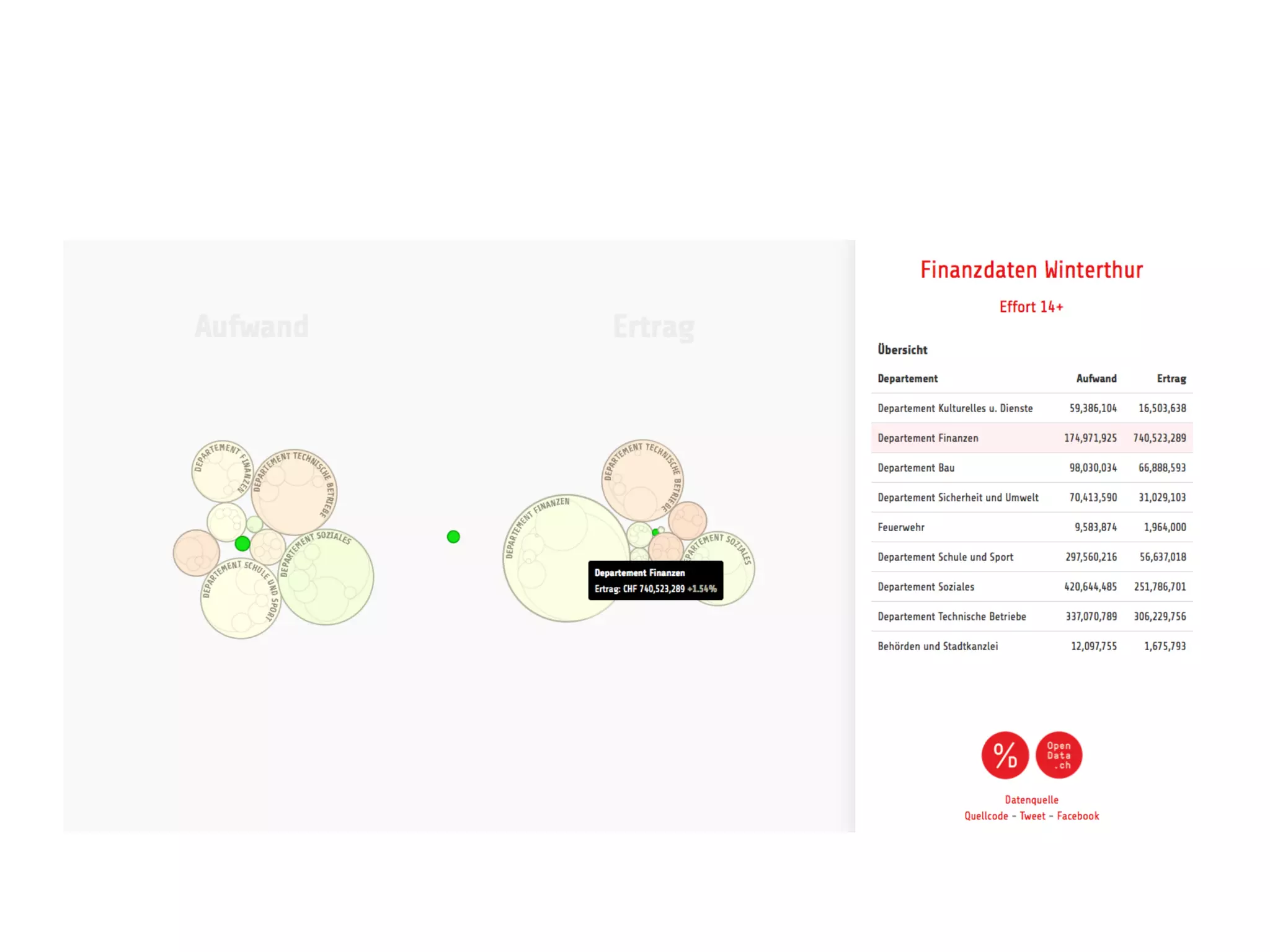
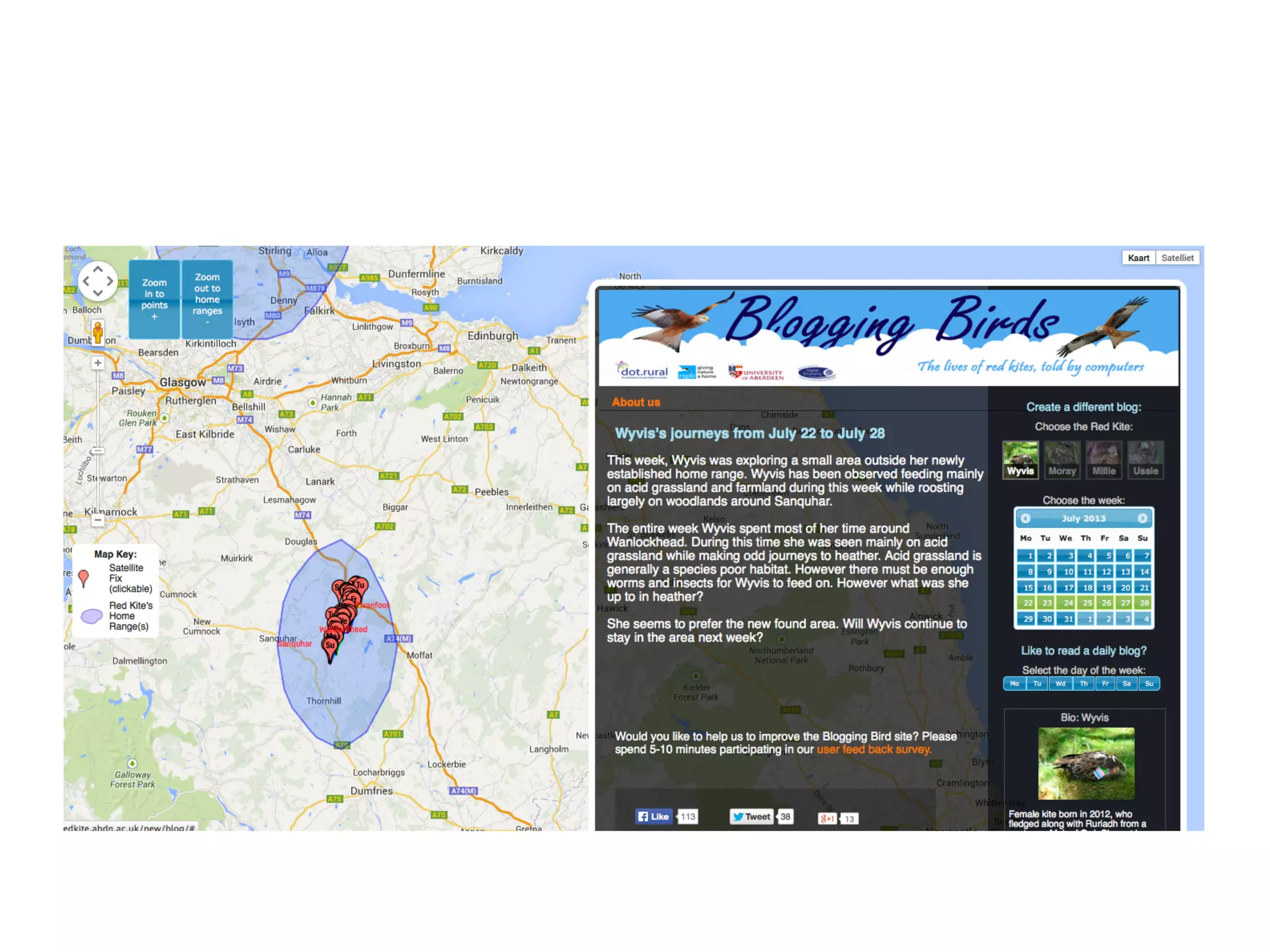
Data journalism faces challenges in evaluating and analyzing large datasets, maintaining objectivity, and developing needed skills. While not all journalists are data journalists, journalism must adapt to the "data revolution" by developing skills to find stories within complex datasets and understand data sources and algorithms. The line between activism and journalism has blurred, requiring careful evaluation of motivations and reliability of sources.