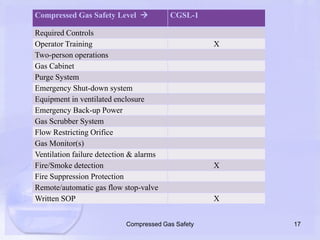
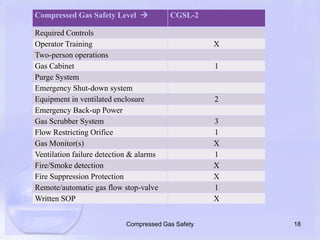
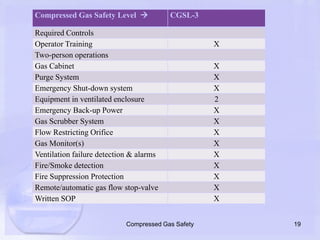
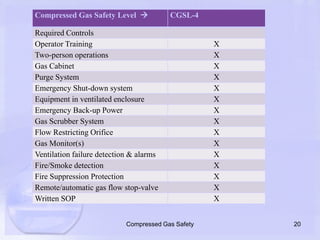
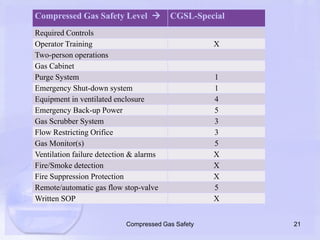
The document emphasizes the importance of proper handling and safety protocols for compressed gases, which are often underestimated by users. It outlines guidelines for secure storage, handling, and the necessity for engineering and administrative controls, highlighting various safety levels associated with different types of gases. Additionally, it stresses the need for end-user awareness to prevent safety hazards related to misuse of compressed gases.